HarmonyOS 鸿蒙Next [鸿蒙学习计划] 亲戚称谓计算器 + LLM
HarmonyOS 鸿蒙Next [鸿蒙学习计划] 亲戚称谓计算器 + LLM
概述
本项目是是学习 华为开发者官网 后的一份练习 demo
实现了以下特性:
- 自定义组件:华为开发者官网
- 状态管理:华为开发者官网
- 应用架构设计基础——MVVM模式:华为开发者官网
- 应用架构设计基础——三层架构:华为开发者官网
- 网络请求:OpenHarmony包管理平台
接下来简要描述下开发流程,源码可以直接查看:Gitee
开发流程
参考三层架构准备项目目录

准备 UI
拆分 UI,实现计算显示部分组件 Display.ets 和 键盘部分 Ctrl.ets
Display.ets
@Component
export struct Display {
@Prop result: string = '';
@Prop calcString: string = '';
build() {
Column() {
Column() {
Text(this.result)
.fontSize(25)
.padding({ left: 16, right: 16 })
.width('100%')
.height('40%')
.textAlign(TextAlign.End)
}
Column() {
Text(this.calcString)
.fontSize(35)
.width('100%')
.height('60%')
.padding({ left: 16, right: 16 })
.textAlign(TextAlign.End)
.borderWidth({ bottom: 1 })
.borderColor('#ccc')
}
}.width('100%').height('25%')
}
}Ctrl.ets
使用 Grid 组件布局:华为开发者官网
需要注意 = 按钮需要占用 2 行;
按钮点击的时候执行父组件传入的方法,用来接受用户点了什么按钮
@Component
export struct Ctrl {
@Prop loading: boolean = false;
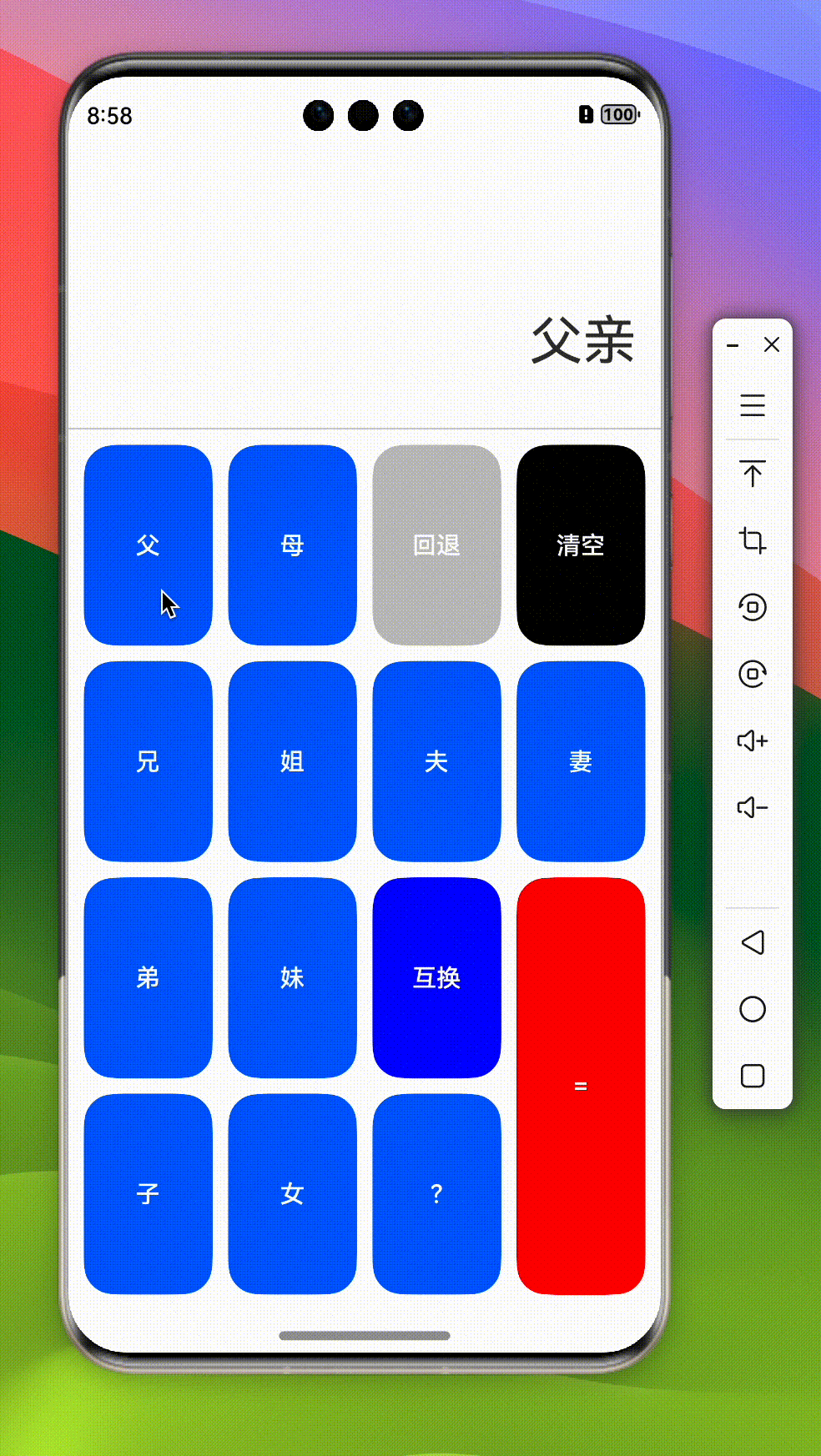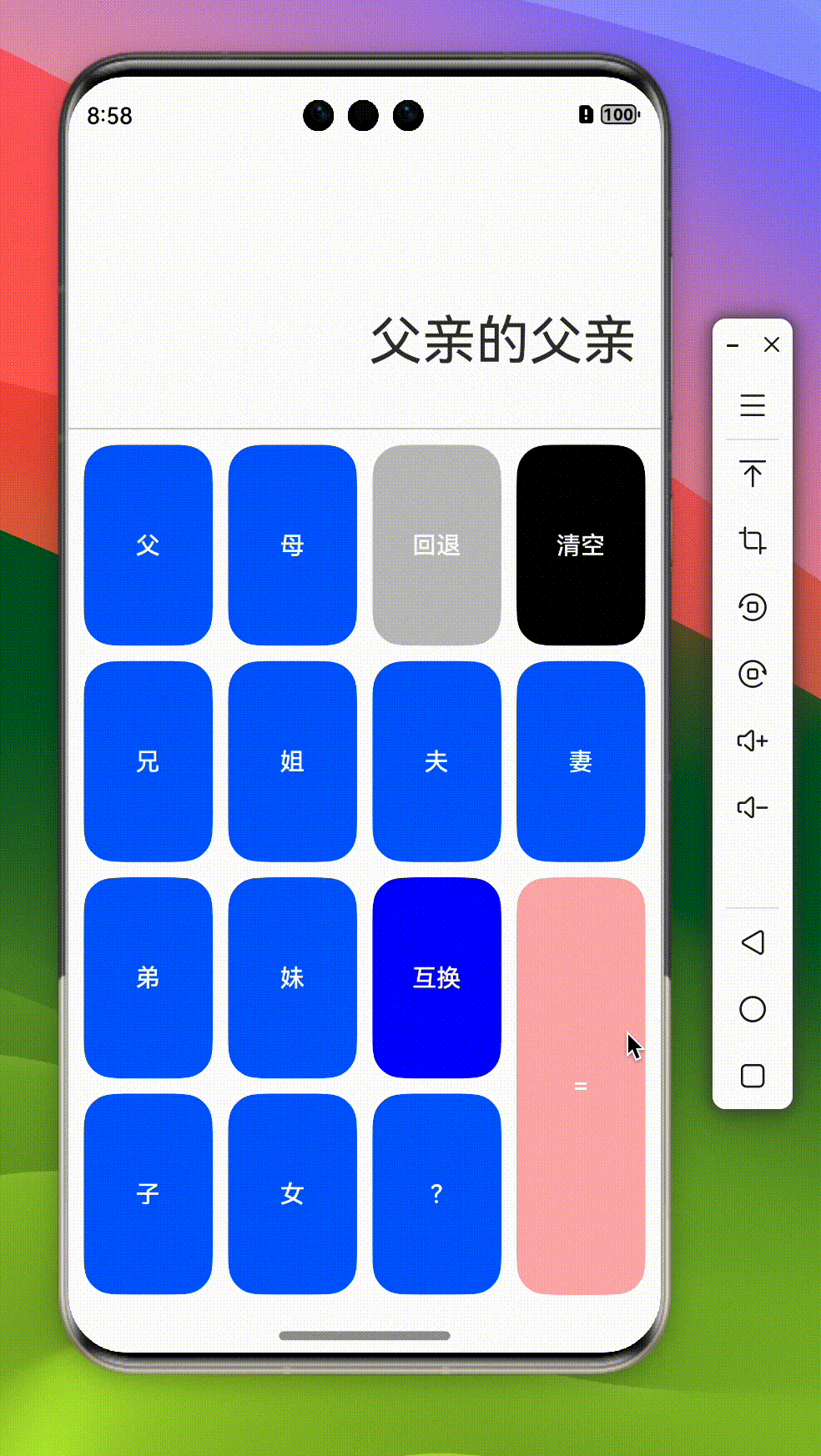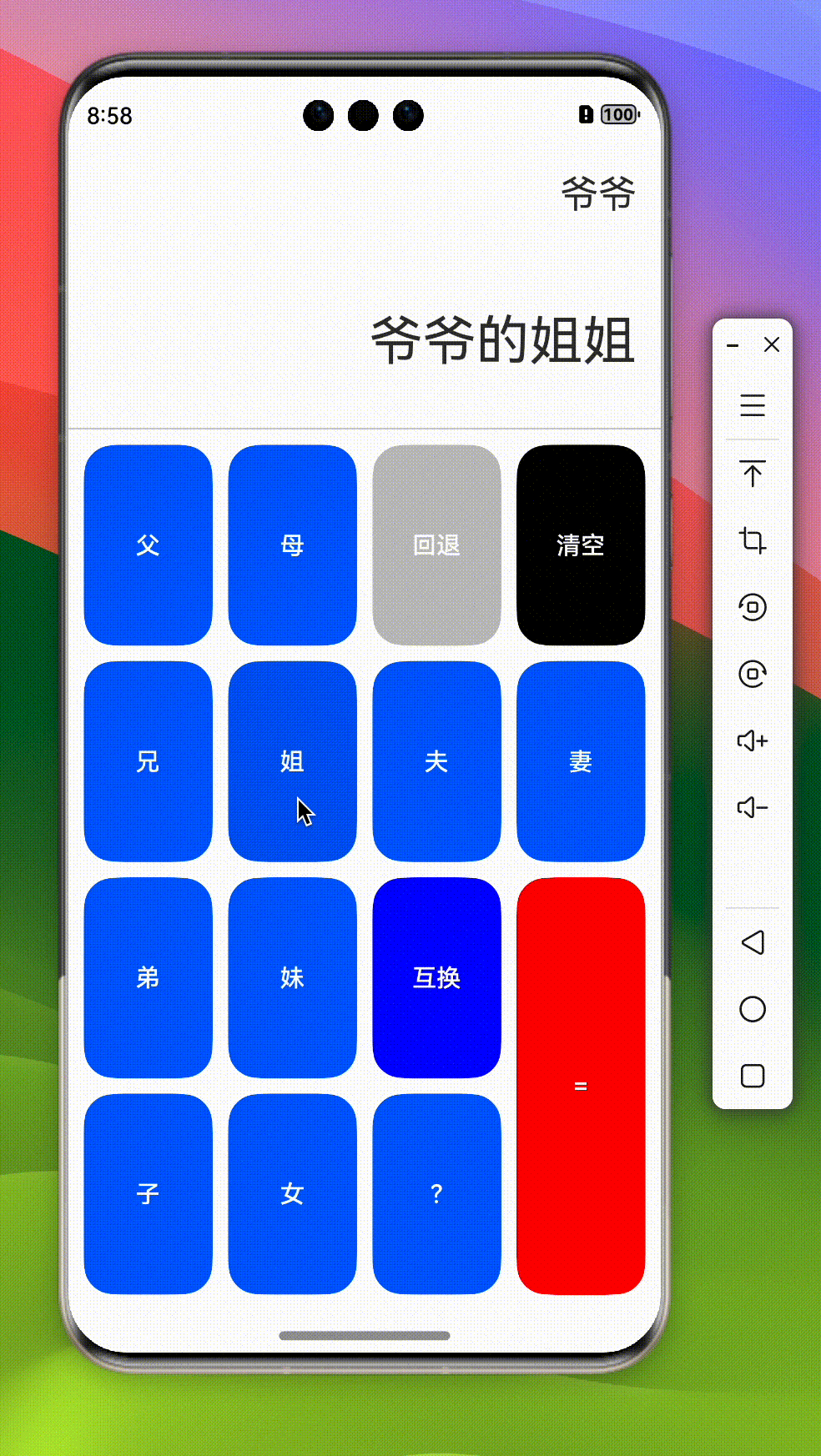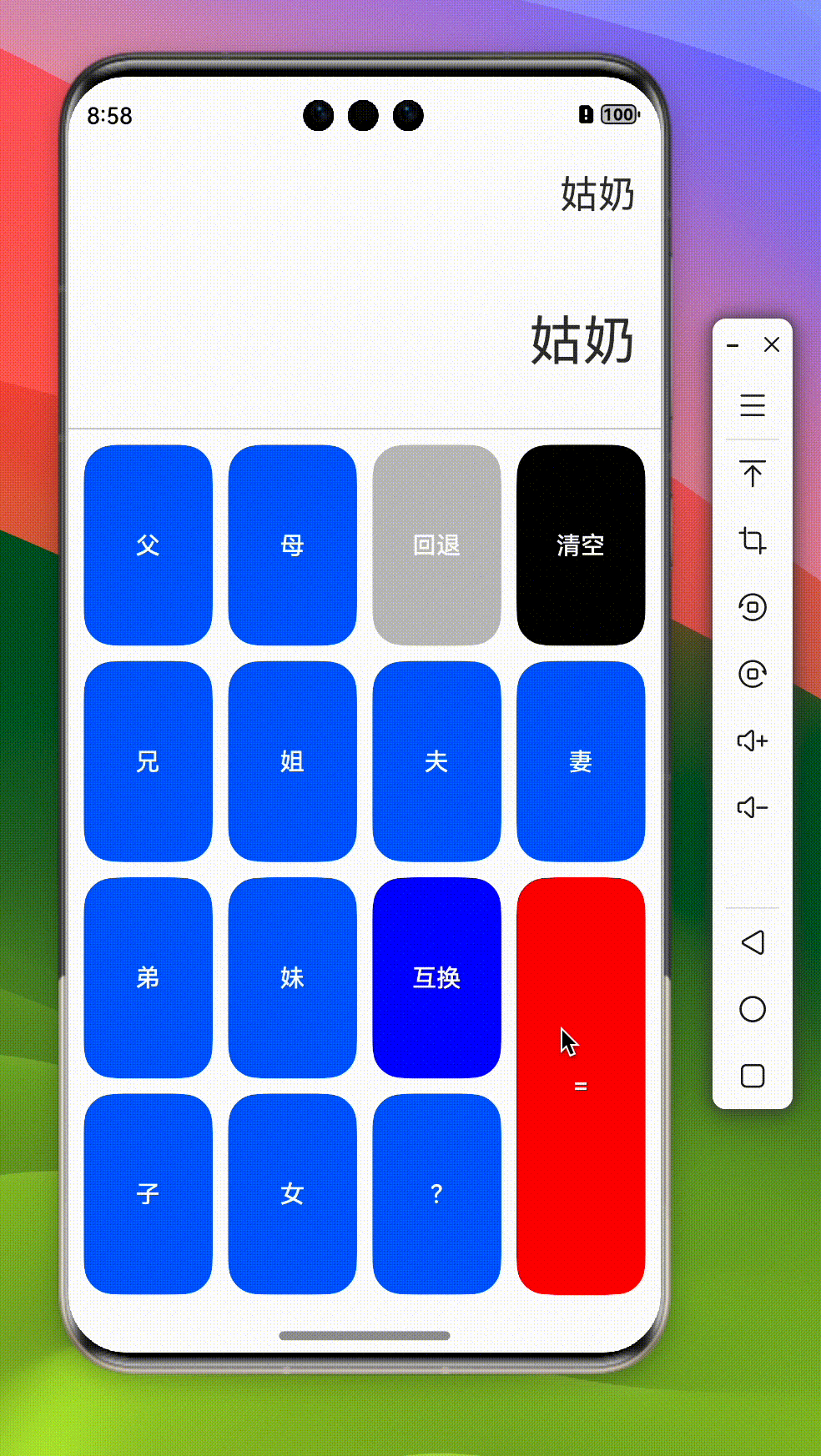
btns: string[][] = [
['Item', '父', '父亲'],
['Item', '母', '母亲'],
['Function', '回退', 'back', 'gray'],
['Function', '清空', 'clear', 'black'],
['Item', '兄', '哥哥'],
['Item', '姐', '姐姐'],
['Item', '夫', '老公'],
['Item', '妻', '老婆'],
['Item', '弟', '弟弟'],
['Item', '妹', '妹妹'],
['Function', '互换', 'change', 'blue'],
['Function', '=', '=', 'red'],
['Item', '子', '儿子'],
['Item', '女', '女儿'],
['Function', '?', '?']
];
onBtnClick?: (data: string[]) => void
layoutOptions: GridLayoutOptions = {
regularSize: [1, 1],
onGetRectByIndex: (index: number) => {
if (index === 11) {
// 控制 = 按钮占有 2 行
return [2, 3, 2, 1]
}
return [index / 4 - 1, index / 4 - 1, 1, 1];
}
}
build() {
Grid(undefined, this.layoutOptions) {
ForEach(this.btns, (data: string[]) => {
GridItem() {
if (data[1] === '=') {
Button(data[1])
.type(ButtonType.Normal)
.onClick(() => {
if (this.loading) return;
this.onBtnClick?.(data)
})
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
.borderRadius(20)
.opacity(this.loading ? 0.3 : 1)
.backgroundColor(data[3])
} else {
Button(data[1])
.type(ButtonType.Normal)
.onClick(() => {
if (this.loading) return;
this.onBtnClick?.(data)
})
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
.borderRadius(20)
.backgroundColor(data[3])
}
}
}, (data: string) => data[2])
}
.columnsGap(10)
.rowsGap(10)
.rowsTemplate('1fr 1fr 1fr 1fr')
.padding(10)
.columnsTemplate('1fr 1fr 1fr 1fr')
.width('100%')
.height('75%')
}
}组合他们
import { Display } from '../view/Display';
import { Ctrl } from '../view/Ctrl';
import { llm } from '[@ohos](/user/ohos)/commons';
@Preview
@Component
export struct Calculator {
@State result: string = '';
@State calc: string[] = [];
@State loading: boolean = false;
onBtnClick: (data: string[]) => string | void = (data: string[]) => {
const type = data[0];
const value = data[2];
if (type === 'Function') {
if (value === 'back') {
this.calc.pop();
}
if (value === '=') {
this.onCalc();
}
if (value === 'clear') {
this.calc = [];
this.result = '';
}
}
if (type === 'Item') {
this.calc.push(value);
}
}
onCalc() {
if (!this.calc.length) return;
if (this.calc.length === 1) {
this.result = this.calc[0]
}
this.askLLM();
}
askLLM() {
this.loading = true;
llm({
system: '你是一个亲戚称谓计算器,请根据我的提问回复我 应该称呼对方为什么,比如爸爸的爸爸,请回复我 {"data":"爷爷"}',
query: this.calc.join('的'),
appKey: 'sk-xxx', // 请使用真实的大模型 appkey
}).then((res) => {
console.log('llm', res);
this.calc = [JSON.parse(res as string).data]
this.result = this.calc[0];
this.loading = false;
})
}
build() {
Column() {
Display({ result: this.result, calcString: this.calc.join('的') })
Ctrl({ onBtnClick: this.onBtnClick, loading: this.loading })
}.width('100%').height('100%')
}
}如何计算
我没有使用以下常见的本地称谓树的方式来表达称谓的数据结构
而是为了实践网络请求的场景,直接问大模型拿到结果
封装请求方法
import axios, { AxiosError, AxiosResponse } from '[@ohos](/user/ohos)/axios'
interface iParams {
system: string,
query: string,
appKey: string,
}
interface iMsg {
role: string,
content: string
}
interface iInput {
messages: iMsg[]
}
interface iData {
model: string,
input: iInput
}
interface iOutput {
finish_reason: string,
text: string
}
interface iRes {
output: iOutput
}
export default (params: iParams) => {
return axios.post<string, AxiosResponse<iRes>, iData>('https://dashscope.aliyuncs.com/api/v1/services/aigc/text-generation/generation', {
"model": "qwen-max",
"input": {
"messages": [
{
"role": "system",
"content": params.system
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": params.query
}
]
},
}, {
headers: {
'Authorization': `Bearer ${params.appKey}`,
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
}
})
.then((response: AxiosResponse<iRes>) => {
console.info('axios success', JSON.stringify(response));
return response.data.output.text;
})
.catch((error: AxiosError) => {
console.info('axios error', JSON.stringify(error));
});
}请求大模型
llm({
system: '你是一个亲戚称谓计算器,请根据我的提问回复我 应该称呼对方为什么,比如爸爸的爸爸,请回复我 {"data":"爷爷"}',
query: this.calc.join('的'),
appKey: 'sk-xxx'
})构建运行
更多关于HarmonyOS 鸿蒙Next [鸿蒙学习计划] 亲戚称谓计算器 + LLM的实战系列教程也可以访问 https://www.itying.com/category-93-b0.html
鸿蒙Next中的“亲戚称谓计算器 + LLM”项目结合了鸿蒙系统的分布式能力和大语言模型(LLM)的智能化处理。该项目旨在通过鸿蒙系统的跨设备协同能力,实现一个智能化的亲戚称谓计算工具。
在鸿蒙Next系统中,开发者可以利用ArkTS语言进行开发,ArkTS是鸿蒙系统推荐的应用开发语言,基于TypeScript,专为鸿蒙系统优化。项目中的亲戚称谓计算器可以通过鸿蒙系统的分布式数据管理能力,在不同设备间同步用户输入的家族关系数据,确保计算的一致性和实时性。
大语言模型(LLM)的引入,使得计算器不仅能够处理传统的亲戚关系计算,还能通过自然语言处理技术,理解用户输入的复杂描述,并给出准确的称谓结果。例如,用户可以通过语音或文本输入“我妈妈的妹妹的女儿”,系统能够准确识别并返回“表妹”作为结果。
鸿蒙系统的分布式能力还允许计算器在不同设备间无缝切换,用户可以在手机、平板或智能手表上使用该工具,数据会自动同步,确保用户体验的一致性。此外,鸿蒙系统的高效资源调度和低延迟特性,保证了计算器在处理复杂关系时的响应速度。
总结来说,鸿蒙Next的“亲戚称谓计算器 + LLM”项目展示了鸿蒙系统在智能化应用开发中的潜力,结合分布式能力和大语言模型,提供了一个高效、智能的亲戚关系计算工具。
更多关于HarmonyOS 鸿蒙Next [鸿蒙学习计划] 亲戚称谓计算器 + LLM的实战系列教程也可以访问 https://www.itying.com/category-93-b0.html
鸿蒙Next的“鸿蒙学习计划”中,亲戚称谓计算器结合LLM(大型语言模型)技术,能够智能识别并计算复杂的亲戚关系。通过自然语言处理,用户可以输入如“我妈妈的妹妹的丈夫”等复杂关系,系统会迅速返回“姑父”等准确称谓。这不仅提升了用户体验,也展示了鸿蒙系统在AI领域的强大能力。








