Nodejs 未读消息成渣渣了
Nodejs 未读消息成渣渣了
<img src=http://img.itc.cn/photo/ol0KlVLlsSV>
好的,我会根据你的需求编写一篇关于“Nodejs 未读消息成渣渣了”的文章。我们将讨论如何处理未读消息的存储、更新和查询,以确保高效且可靠的数据管理。
Nodejs 未读消息成渣渣了
在现代Web应用中,未读消息功能是一个非常常见的特性。然而,在实现这一功能时,我们可能会遇到一些挑战,比如数据冗余、性能瓶颈以及复杂性增加。本文将介绍如何使用Node.js来有效地管理未读消息,并提供一个简单的示例代码来说明这些概念。
数据模型设计
首先,我们需要定义一个合理的数据模型来存储未读消息。我们可以使用MongoDB这样的NoSQL数据库来简化数据操作。假设我们有一个User模型和一个Message模型,每个用户可以有多个未读消息。
const mongoose = require('mongoose');
const userSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
username: String,
unreadMessages: [{ type: mongoose.Schema.Types.ObjectId, ref: 'Message' }]
});
const messageSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
content: String,
sender: { type: mongoose.Schema.Types.ObjectId, ref: 'User' },
recipients: [{ type: mongoose.Schema.Types.ObjectId, ref: 'User' }],
isRead: { type: Boolean, default: false }
});
const User = mongoose.model('User', userSchema);
const Message = mongoose.model('Message', messageSchema);
存储未读消息
当新消息被创建时,我们需要将其添加到相关用户的未读消息列表中。以下是一个示例函数,用于创建一条新消息并将其添加到指定用户的未读消息列表:
async function createMessage(senderId, recipientIds, content) {
const sender = await User.findById(senderId);
if (!sender) throw new Error('Sender not found');
const message = new Message({
content,
sender: sender._id,
recipients: recipientIds,
isRead: false
});
await message.save();
// Update the unread messages list for each recipient
for (const recipientId of recipientIds) {
const recipient = await User.findById(recipientId);
if (recipient) {
recipient.unreadMessages.push(message._id);
await recipient.save();
}
}
return message;
}
查询未读消息
为了查询用户的未读消息,我们可以从用户的未读消息列表中查找相应的消息,并返回这些消息的内容。以下是一个示例函数,用于获取用户的未读消息:
async function getUnreadMessages(userId) {
const user = await User.findById(userId).populate('unreadMessages');
if (!user) throw new Error('User not found');
return user.unreadMessages;
}
更新消息状态
当用户阅读了一条消息后,我们需要将该消息的状态更改为已读。以下是一个示例函数,用于将消息标记为已读:
async function markMessageAsRead(messageId, userId) {
const message = await Message.findById(messageId);
if (!message) throw new Error('Message not found');
message.isRead = true;
await message.save();
const user = await User.findById(userId);
if (user) {
user.unreadMessages = user.unreadMessages.filter(id => !id.equals(messageId));
await user.save();
}
}
通过上述方法,我们可以有效地管理和维护未读消息的功能,避免数据冗余和性能问题。希望这些示例代码对你有所帮助!
请注意,以上示例代码是为了说明概念而编写的,实际应用中可能需要更多的错误处理和优化措施。
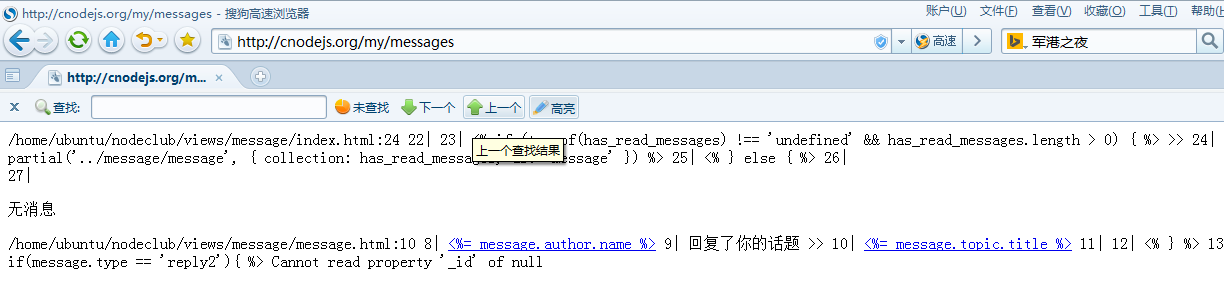
出问题了
又挂了。。。
又挂鸟:(
我也碰到过,不知道是什么问题。
从问题标题和内容来看,提问者可能遇到了关于未读消息处理上的困难。为了更好地帮助提问者,我们可以假设他们是在使用某种聊天应用或系统时遇到了未读消息显示不正确或丢失的问题。
解决方案:
假设这是一个基于Node.js的聊天应用,我们可以通过维护一个用户和其未读消息的记录来解决这个问题。下面提供一个简单的示例,展示如何通过Express.js和MongoDB来实现这个功能。
示例代码
-
安装依赖
npm install express mongoose -
创建用户模型
// models/User.js const mongoose = require('mongoose'); const userSchema = new mongoose.Schema({ username: { type: String, required: true }, unreadMessages: [{ type: mongoose.Schema.Types.ObjectId, ref: 'Message' }] }); module.exports = mongoose.model('User', userSchema); -
创建消息模型
// models/Message.js const mongoose = require('mongoose'); const messageSchema = new mongoose.Schema({ content: { type: String, required: true }, isRead: { type: Boolean, default: false } }); module.exports = mongoose.model('Message', messageSchema); -
API 接口
// app.js const express = require('express'); const mongoose = require('mongoose'); const User = require('./models/User'); const Message = require('./models/Message'); mongoose.connect('mongodb://localhost/chatApp', { useNewUrlParser: true, useUnifiedTopology: true }); const app = express(); app.post('/messages/:userId', async (req, res) => { try { const { userId } = req.params; const { content } = req.body; const message = await Message.create({ content }); await User.findByIdAndUpdate(userId, { $push: { unreadMessages: message._id } }); res.status(201).json(message); } catch (error) { res.status(500).send(error.message); } }); app.listen(3000, () => console.log('Server running on port 3000'));
上述代码展示了一个基本的解决方案,通过维护用户的未读消息列表来确保消息的准确跟踪。这只是一个基础示例,实际生产环境中可能需要考虑更多的因素,如并发控制、错误处理等。
如果问题具体到图片中提到的情况,请提供更多细节以便于更精确的帮助。