HarmonyOS 鸿蒙Next 如何创新玩转端云一体化开发 计算十二生肖-云数据库
HarmonyOS 鸿蒙Next 如何创新玩转端云一体化开发 计算十二生肖-云数据库
- 前言
上帖子使用云函数端云一体化开发计算十二生肖,此贴使用云数据库端云一体化开发计算十二生肖,在DevEco Studio可以完成端侧代码开发和云侧代码开发,一键部署云数据库,效果与之前使用云函数一样,计算获取方式不同。
- 真机效果
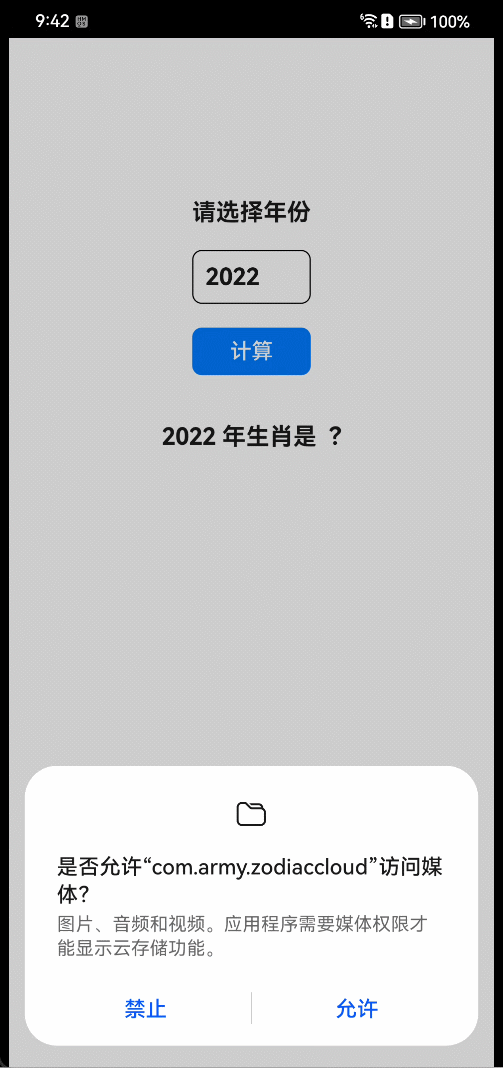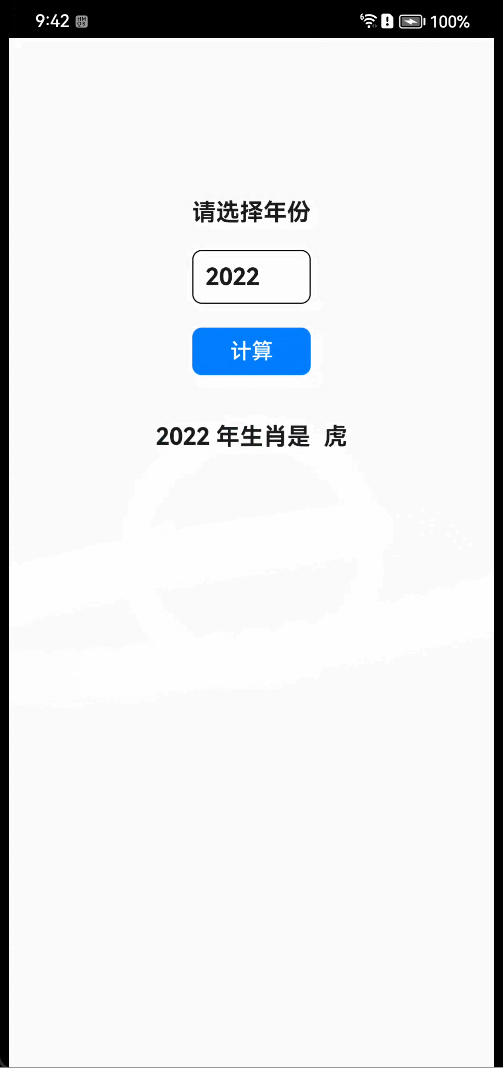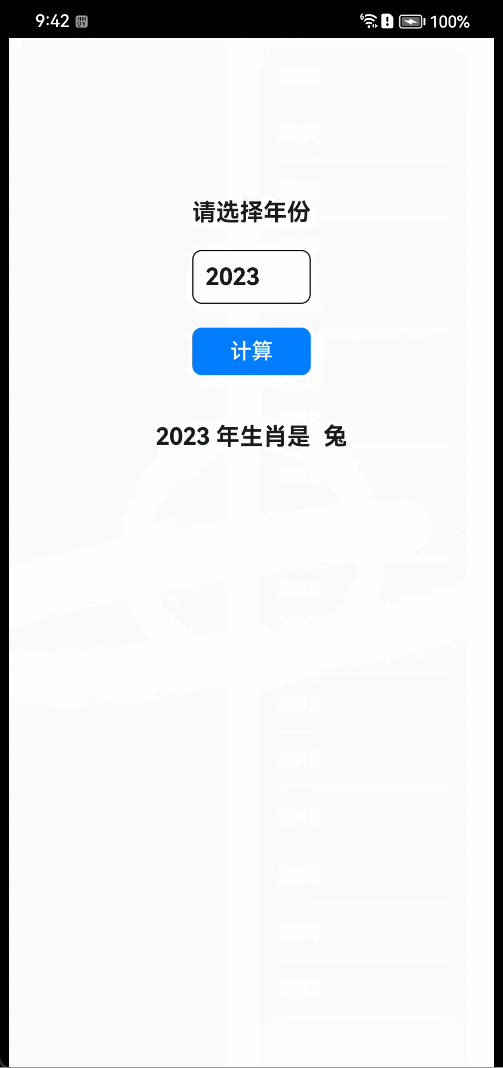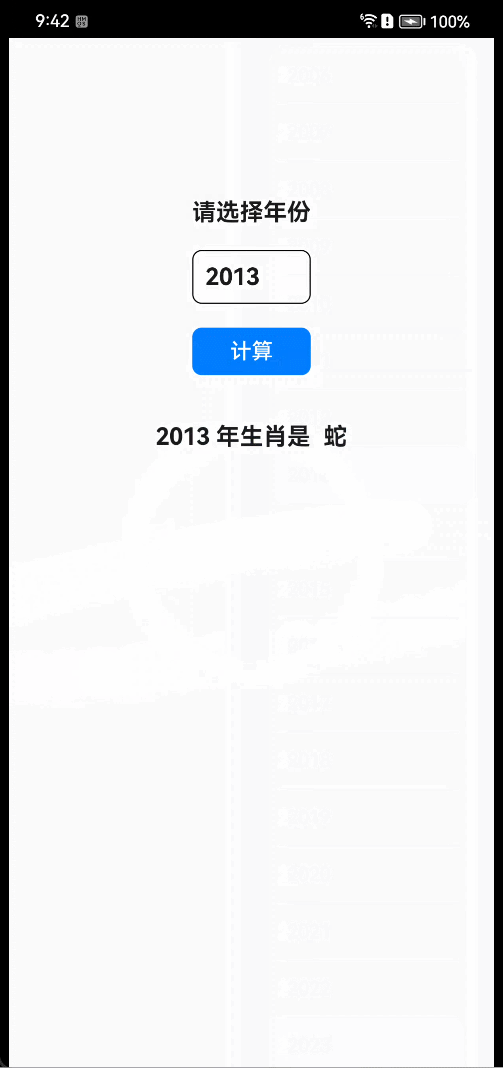
- 讲解
创建端云一体化项目,这里就不介绍的,创建、部署云数据库官方详细教程 开发云数据库-开发云工程-端云一体化开发-应用/服务开发-DevEco Studio使用指南(HarmonyOS)-工具-HarmonyOS应用开发 端云一体化项目结构和之前不一样,多了CloudProgram模块, 下面介绍项目开发,先从云侧开发开始,再到端侧开发。
- 云侧开发
4.1 介绍云数据库目录结构
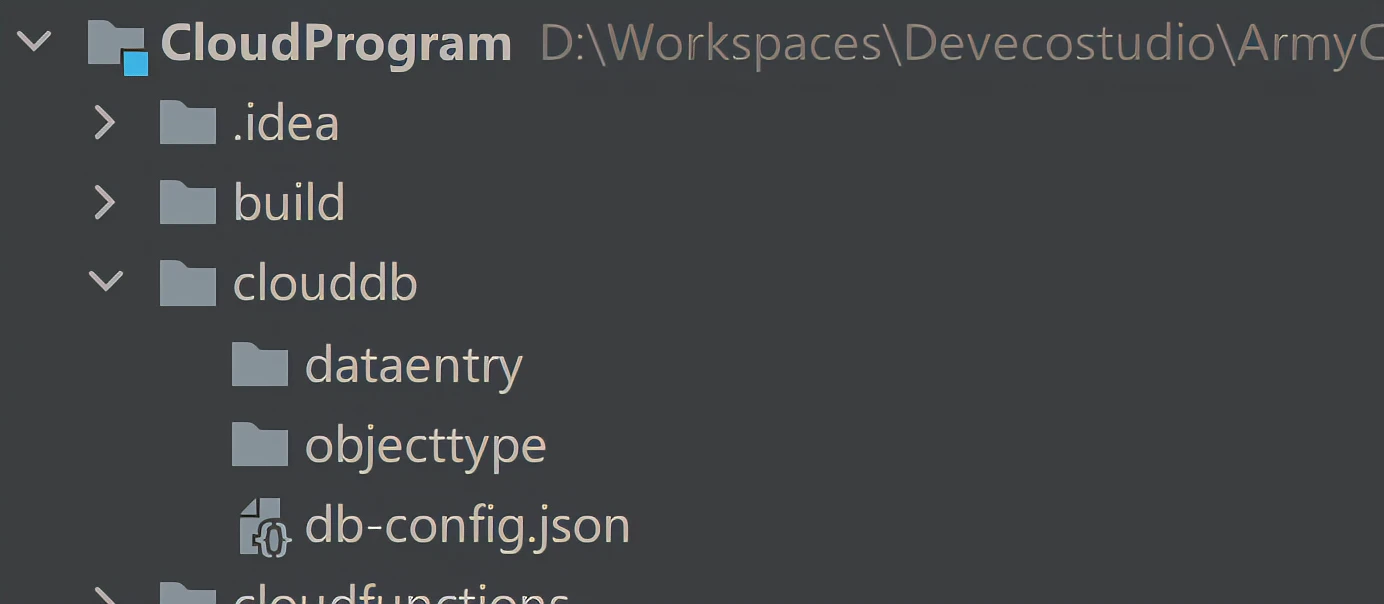
展开CloudProgram模块,展开clouddb目录,dataentry目录是存储数据条目文件,objecttype目录是存储对象类型文件,db-config.json自动生成,内容包含云数据库配置,目录结构如下图:
4.2 定义对象类型
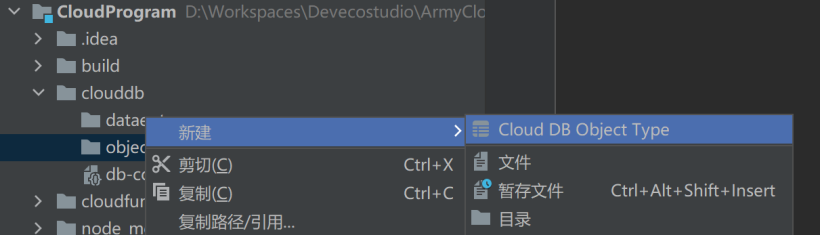
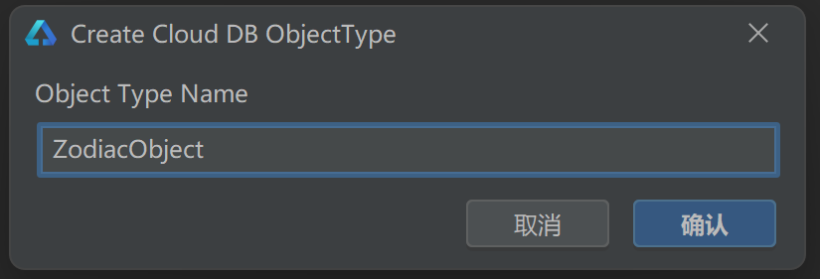
右击objecttype目录,创建对象类型
4.3 定义数据条目
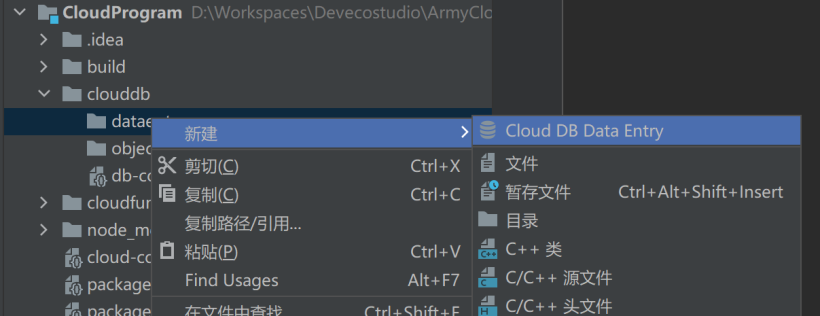
右击dataentry目录,创建数据条目
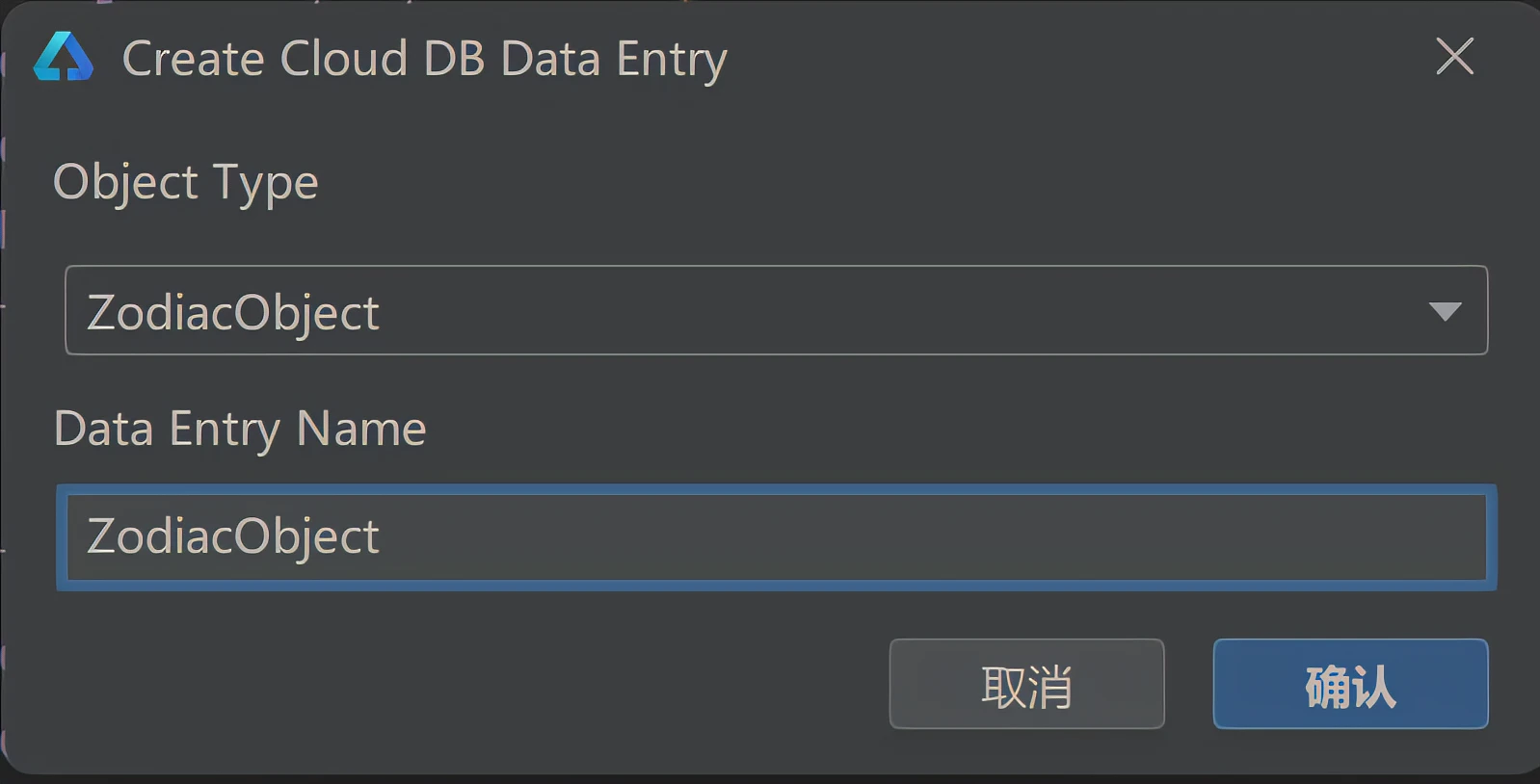
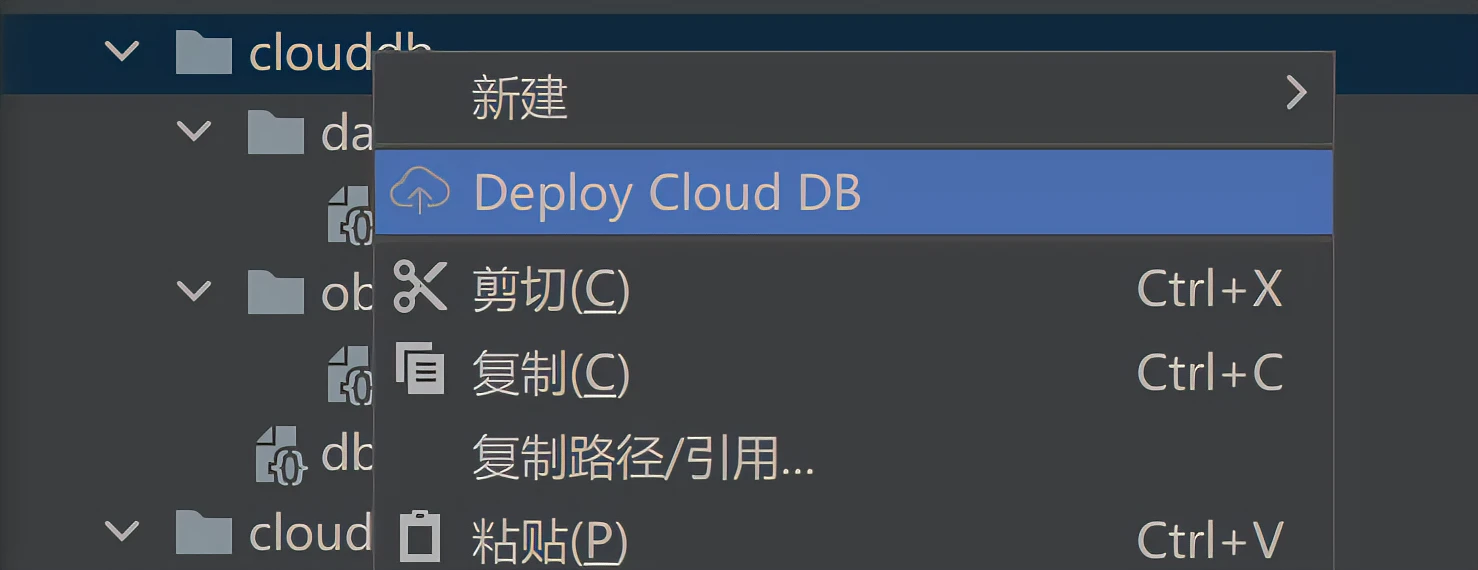
4.4 部署云数据库
部署云侧代码到AGC上,右击clouddb目录,选择Deploy Cloud DB, 自动部署到AGC上,如果提示没有登录,登录成功后,再操作一次部署。
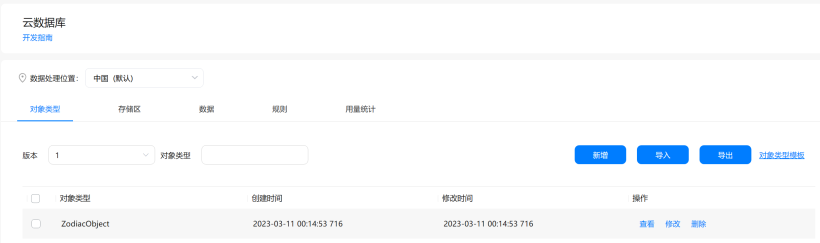
4.5 导出文件格式
4.5.1 登录到AGC->云数据库,进入当前项目的云数据库服务菜单,可分别在“对象类型”、“存储区”与“数据”页签查看到您刚刚部署的云数据库资源。
4.5.2 导出json格式文件
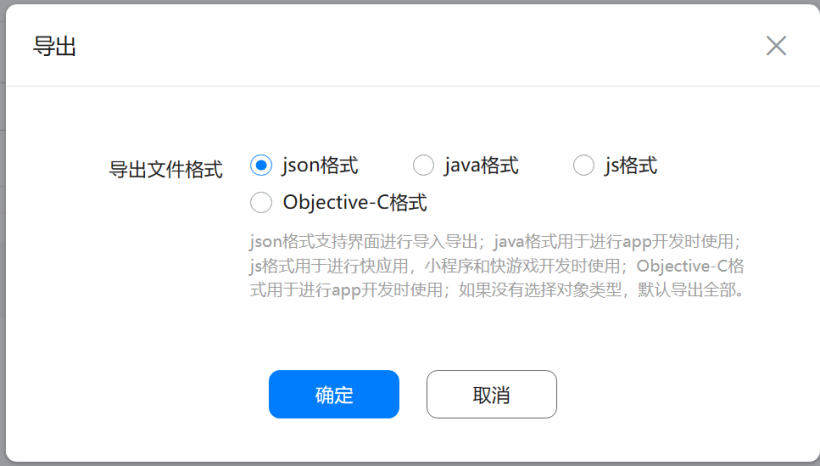
4.5.3 导出js格式文件
4.5.3 导出json文件和js文件,端侧使用到。
- 端侧开发
5.1 端侧模块结构
先看一下端侧模块结构:

5.2 common目录
目录放一些公共的封装类,比如Log类; components目录放自定义组件;entryability是自动生成的,里面有一个EntryAbility类,包含生命周期;pages目录放UI布局页面;services目录放业务逻辑类,比如调用云侧接口。
5.3 services目录
这里只介绍services目录的工作,先介绍如何和AGC连接上的,这里使用一个单独的文件来处理:
5.3.1 services目录下AgcConfig.ts
import agconnect from '@hw-agconnect/api-ohos';
import "@hw-agconnect/core-ohos";
import "@hw-agconnect/auth-ohos";
import '@hw-agconnect/auth-types-ohos';
import { Log } from '../common/Log';
const TAG = "[AGCConfig]";
export function getAGConnect(context) {
try {
agconnect.instance().init(context);
Log.info(TAG, "xx init AGC SDK success");
return agconnect;
}
catch (err) {
Log.error(TAG, "xx initAgcSDK failed" + err);
}
}
5.3.2 在services目录下创建app-schema.json文件,复制上面在AGC下载的json格式文件内容到app-schema.json里
{
"schemaVersion": 1,
"permissions": [
{
"permissions": [
{
"role": "World",
"rights": ["Read"]
},
{
"role": "Authenticated",
"rights": ["Read", "Upsert"]
},
{
"role": "Creator",
"rights": ["Read", "Upsert", "Delete"]
},
{
"role": "Administrator",
"rights": ["Read", "Upsert", "Delete"]
}
],
"objectTypeName": "ZodiacObject"
}
],
"objectTypes": [
{
"indexes": [
{
"indexName": "zodiacIndex",
"indexList": [
{
"fieldName": "zodiacName",
"sortType": "DESC"
}
]
},
{
"indexName": "idxIndex",
"indexList": [
{
"fieldName": "idx",
"sortType": "ASC"
}
]
}
],
"objectTypeName": "ZodiacObject",
"fields": [
{
"isNeedEncrypt": false,
"fieldName": "idx",
"notNull": true,
"isSensitive": false,
"belongPrimaryKey": true,
"fieldType": "Integer"
},
{
"isNeedEncrypt": false,
"fieldName": "zodiacName",
"notNull": false,
"isSensitive": false,
"belongPrimaryKey": false,
"fieldType": "String"
}
]
}
]
}
5.3.3 在services目录下创建ZodiacObject.js文件,复制上面在AGC下载的js格式文件内容到ZodiacObject.js里
/*
* Copyright (c) Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 2020-2020. All rights reserved.
* Generated by the CloudDB ObjectType compiler. DO NOT EDIT!
*/
class ZodiacObject {
constructor() {
this.idx = undefined;
this.zodiacName = undefined;
}
setIdx(idx) {
this.idx = idx;
}
getIdx() {
return this.idx;
}
setZodiacName(zodiacName) {
this.zodiacName = zodiacName;
}
getZodiacName() {
return this.zodiacName;
}
}
ZodiacObject.className = 'ZodiacObject';
export {ZodiacObject}
5.3.4 services目录下创建CloudDB.ts
import * as schema from './app-schema.json'
import { ZodiacObject } from './ZodiacObject'
import { AGConnectCloudDB, CloudDBZone, CloudDBZoneQuery } from '@hw-agconnect/database-ohos'
import { AGCRoutePolicy } from '@hw-agconnect/core-ohos'
import { getAGConnect } from './AgcConfig'
export class CloudDBService {
private static ZONE_NAME: string = "cloudDBZoneZodiac"
private static async init(context: any): Promise<CloudDBZone> {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// 获取AGC连接
getAGConnect(context);
AGConnectCloudDB.initialize(context);
AGConnectCloudDB.getInstance({
context: context,
agcRoutePolicy: AGCRoutePolicy.CHINA,
objectTypeInfo: schema
}).then((ret) => {
return resolve(ret.openCloudDBZone(this.ZONE_NAME));
}).catch((err) => {
return reject(err);
});
})
}
public static async query(context: any, year: number): Promise<ZodiacObject> {
let idx = year % 12;
return new Promise(async (resolve, reject) => {
const query = CloudDBZoneQuery.where(ZodiacObject).equalTo("idx", idx);
await this.init(context).then(async (ret) => {
await ret.executeQuery(query).then((ret) => {
resolve(ret.getSnapshotObjects()[0]);
})
}).catch((err) => {
reject(err);
});
})
}
}
5.4 pages目录
目录 Index.ts 这里是页面布局,上面看到的效果,就是这里实现的。
import { CloudDBService } from '../services/CloudDB';
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
// 存储选择年份
@State year: number = 2022
// 计算出来生肖
@State born: string = "?"
// 是否在计算中
@State flag: boolean = false
// 计算生肖
getBorn() {
// 标识为计算中
this.flag = true;
console.info('xx Page year: ' + this.year)
// 封装参数
let params = {
"year": this.year
}
// 调用云数据库
CloudDBService.query(getContext(this), this.year).then((res) => {
console.info('xx cloud db result: ' + JSON.stringify(res));
// 计算完成
this.flag = false;
// 结果赋值给生肖变量
this.born = res.zodiacName;
}).catch((err) => {
// 计算完成
this.flag = false;
console.error('xx error: ', err && err.message);
});
}
build() {
Stack() {
if (!this.flag) {
Column({space: 20}) {
Text('请选择年份')
.fontSize(20)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
// 选择年份
Column() {
Text(this.year + '')
.fontSize(20)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.padding(10)
.width(100)
.border({ width: 1, radius: 8 })
}
.bindMenu([
{ value: '2006', action: () => {this.year = 2006; this.born = '?'} },
{ value: '2007', action: () => {this.year = 2007; this.born = '?'} },
{ value: '2008', action: () => {this.year = 2008; this.born = '?'} },
{ value: '2009', action: () => {this.year = 2009; this.born = '?'} },
{ value: '2010', action: () => {this.year = 2010; this.born = '?'} },
{ value: '2011', action: () => {this.year = 2011; this.born = '?'} },
{ value: '2012', action: () => {this.year = 2012; this.born = '?'} },
{ value: '2013', action: () => {this.year = 2013; this.born = '?'} },
{ value: '2014', action: () => {this.year = 2014; this.born = '?'} },
{ value: '2015', action: () => {this.year = 2015; this.born = '?'} },
{ value: '2016', action: () => {this.year = 2016; this.born = '?'} },
{ value: '2017', action: () => {this.year = 2017; this.born = '?'} },
{ value: '2018', action: () => {this.year = 2018; this.born = '?'} },
{ value: '2019', action: () => {this.year = 2019; this.born = '?'} },
{ value: '2020', action: () => {this.year = 2020; this.born = '?'} },
{ value: '2021', action: () => {this.year = 2021; this.born = '?'} },
{ value: '2022', action: () => {this.year = 2022; this.born = '?'} },
{ value: '2023', action: () => {this.year = 2023; this.born = '?'} },
{ value: '2024', action: () => {this.year = 2024; this.born = '?'} },
{ value: '2025', action: () => {this.year = 2025; this.born = '?'} }
])
// 计算按钮操作
Button('计算', {type: ButtonType.Normal, stateEffect: true})
.fontSize(18)
.borderRadius(8)
.width(100)
.margin({bottom: 20})
.onClick(() => {
// 根据年份计算生肖
this.getBorn()
})
// 显示计算结果
Text(`${this.year} 年生肖是 ${this.born}`)
.fontSize(20)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
}
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
.padding({top: '33%'})
} else {
// 计算中
LoadingProgress().color(Color.Blue)
.backgroundColor(Color.Transparent)
}
}
}
}
- 总结
由于调用云侧云数据库是异步的,不能马上返回结果,这里添加LoadingProgress组件,让用户知道在运行中,效果看得不是很明显,可能录制时,网速很快,LoadingProgress组件闪一下就不见了,如果遇到网络慢时,LoadingProgress就会一直转,直到云数据库返回响应时,再消失LoadingProgress。
更多关于HarmonyOS 鸿蒙Next 如何创新玩转端云一体化开发 计算十二生肖-云数据库的实战教程也可以访问 https://www.itying.com/category-93-b0.html
云数据库插入或更新都是调用executeUpsert接口,批量也是调用这个接口,特别要注意的是:
如果项目里没有用到认证服务,那么云数据库权限里,要把更新权限添加给所有人,不然添加或更新不了数据 ,也就是说,CloudDB对操作权限有做限制,需要认证用户才能进行增删改操作。
//插入单条数目
public static insert(context: any, object: ZodiacObject): Promise<number> {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
this.init(context).then((ret) => {
ret.executeUpsert(object).then((res) => {
resolve(res)
})
}).catch((err) => {
console.warn('xx 3 ' + JSON.stringify(err))
reject(err);
});
})
}
// 批量插入数目
public static batchInsert(context: any, objectList: Array<ZodiacObject>): Promise<number> {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
this.init(context).then((ret) => {
ret.executeUpsert(objectList).then((ret) => {
resolve(ret)
})
}).catch((err) => {
reject(err);
});
})
}
更多关于HarmonyOS 鸿蒙Next 如何创新玩转端云一体化开发 计算十二生肖-云数据库的实战系列教程也可以访问 https://www.itying.com/category-93-b0.html
你可以在catch里面,把错误信息打印出来看看,比如这样打印:
console.error('xx ’ + JSON.stringify(err))
前面加多xx 方便在控制台过滤。 你也在services里把参数打印一下,看看参数传过去是什么
console.info('xx ' + Village )
找到原因了,感谢大佬指点迷津!
姓名: 张三 职位: 软件工程师 简介: 拥有超过10年的软件开发经验,擅长Java和Python。
你好,请教一下大佬,在services目录下创建CloudDB.ts下可以封装多个查询静态方法吗?但是我在页面调用这些查询静态方法时,每次都会初始化init数据库连接,而且页面只会显示空白。
下面是我的问题帖子
https://developer.huawei.com/consumer/cn/forum/topic/0201116420841632463?fid=0102822233052010012
你可以在init时,判断一下,如果为null才创建,或者把init初始放在entryAbility里的onCreate函数初始化,然后用保存到全局变量,在其它地方使用。
大佬,请问插入数据的方法应该怎么封装?
姓名: 张三
职位: 软件工程师
简介: 拥有超过10年的软件开发经验,擅长Java和Python编程。曾在多家知名公司担任要职,具有丰富的项目管理经验。
互相学习,共同进步,
功能简单,知识丰富
学习
HarmonyOS 鸿蒙Next在端云一体化开发方面提供了强大的支持,使得开发者能够轻松实现设备端与云端的无缝连接与数据交互。在计算十二生肖这一应用场景中,可以通过以下方式创新玩转端云一体化开发:
首先,利用鸿蒙系统提供的分布式数据库能力,将十二生肖的相关数据存储到云数据库中。这样,无论是设备端还是云端,都可以随时访问和更新这些数据,实现数据的实时同步和共享。
其次,通过鸿蒙系统的分布式能力,可以实现设备端与云端的协同计算。例如,设备端可以负责用户交互和数据的初步处理,而云端则可以进行更复杂的数据分析和计算。这种协同计算的方式,不仅可以提高应用的性能,还可以降低设备端的资源消耗。
最后,在开发过程中,可以利用鸿蒙系统提供的丰富API和工具,快速构建出功能完善、性能稳定的应用。同时,鸿蒙系统还支持多种编程语言和开发框架,使得开发者可以根据自己的喜好和需求选择最适合的开发方式。
如果问题依旧没法解决请联系官网客服,官网地址是:https://www.itying.com/category-93-b0.html。







