golang高性能并发FIFO队列插件库goconcurrentqueue的使用
golang高性能并发FIFO队列插件库goconcurrentqueue的使用
goconcurrentqueue是一个提供并发安全队列的Go语言库,它实现了多种并发安全的队列结构。
安装
执行以下命令安装:
go get github.com/enriquebris/goconcurrentqueue
队列类型
FIFO队列
FIFO是一个并发安全、自动扩容的队列。
优点:
- 可以无限添加元素
- 提供额外方法获取和移除元素
缺点:
- 性能略低于FixedFIFO
FixedFIFO队列
FixedFIFO是固定容量的并发安全队列。
优点:
- 在并发场景下性能至少是FIFO的2倍
缺点:
- 有固定容量限制
使用示例
FIFO队列基本使用
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/enriquebris/goconcurrentqueue"
)
type AnyStruct struct {
Field1 string
Field2 int
}
func main() {
queue := goconcurrentqueue.NewFIFO()
// 入队三种不同类型元素
queue.Enqueue("any string value")
queue.Enqueue(5)
queue.Enqueue(AnyStruct{Field1: "hello world", Field2: 15})
// 输出队列长度: 3
fmt.Printf("queue's length: %v\n", queue.GetLen())
// 出队
item, err := queue.Dequeue()
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
// 输出出队元素: "any string value"
fmt.Printf("dequeued item: %v\n", item)
// 输出队列长度: 2
fmt.Printf("queue's length: %v\n", queue.GetLen())
}
等待元素入队
package main
import (
"fmt"
"time"
"github.com/enriquebris/goconcurrentqueue"
)
func main() {
var (
fifo = goconcurrentqueue.NewFIFO()
done = make(chan struct{})
)
go func() {
fmt.Println("1 - Waiting for next enqueued element")
value, _ := fifo.DequeueOrWaitForNextElement()
fmt.Printf("2 - Dequeued element: %v\n", value)
done <- struct{}{}
}()
fmt.Println("3 - Go to sleep for 3 seconds")
time.Sleep(3 * time.Second)
fmt.Println("4 - Enqueue element")
fifo.Enqueue(100)
<-done
}
带超时的等待元素入队
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"time"
"github.com/enriquebris/goconcurrentqueue"
)
func main() {
var (
fifo = goconcurrentqueue.NewFIFO()
ctx, cancel = context.WithTimeout(context.Background(), 3*time.Second)
)
defer cancel()
fmt.Println("1 - Waiting for next enqueued element")
_, err := fifo.DequeueOrWaitForNextElementContext(ctx)
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("2 - Failed waiting for new element: %v\n", err)
return
}
}
依赖倒置原则使用队列
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/enriquebris/goconcurrentqueue"
)
func main() {
var (
queue goconcurrentqueue.Queue
dummyCondition = true
)
// 根据条件选择队列实现
if dummyCondition {
queue = goconcurrentqueue.NewFIFO()
} else {
queue = goconcurrentqueue.NewFixedFIFO(10)
}
fmt.Printf("queue's length: %v\n", queue.GetLen())
workWithQueue(queue)
fmt.Printf("queue's length: %v\n", queue.GetLen())
}
// 使用Queue接口进行工作
func workWithQueue(queue goconcurrentqueue.Queue) error {
// 入队一个元素
if err := queue.Enqueue("test value"); err != nil {
return err
}
return nil
}
性能对比
在2012款MacBook Pro(i7 2.3GHz, 16GB内存)上使用Go 1.12测试:
入队操作性能
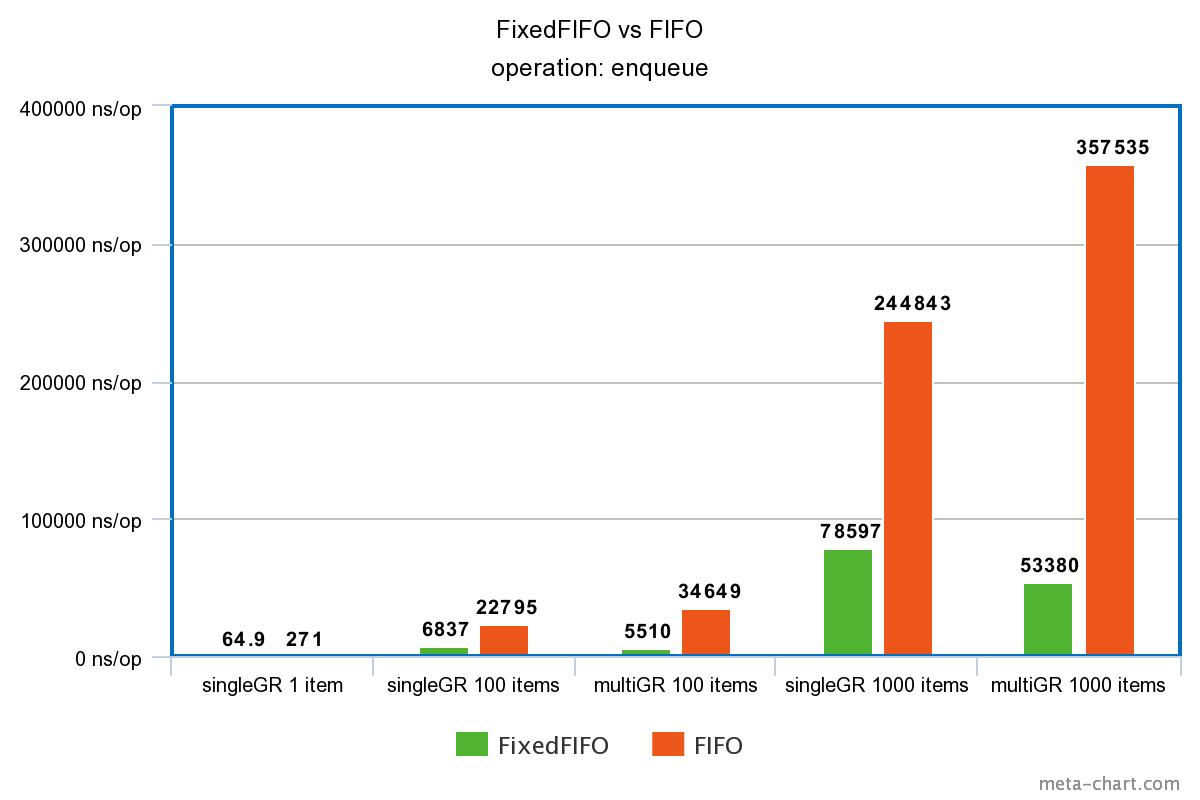
出队操作性能
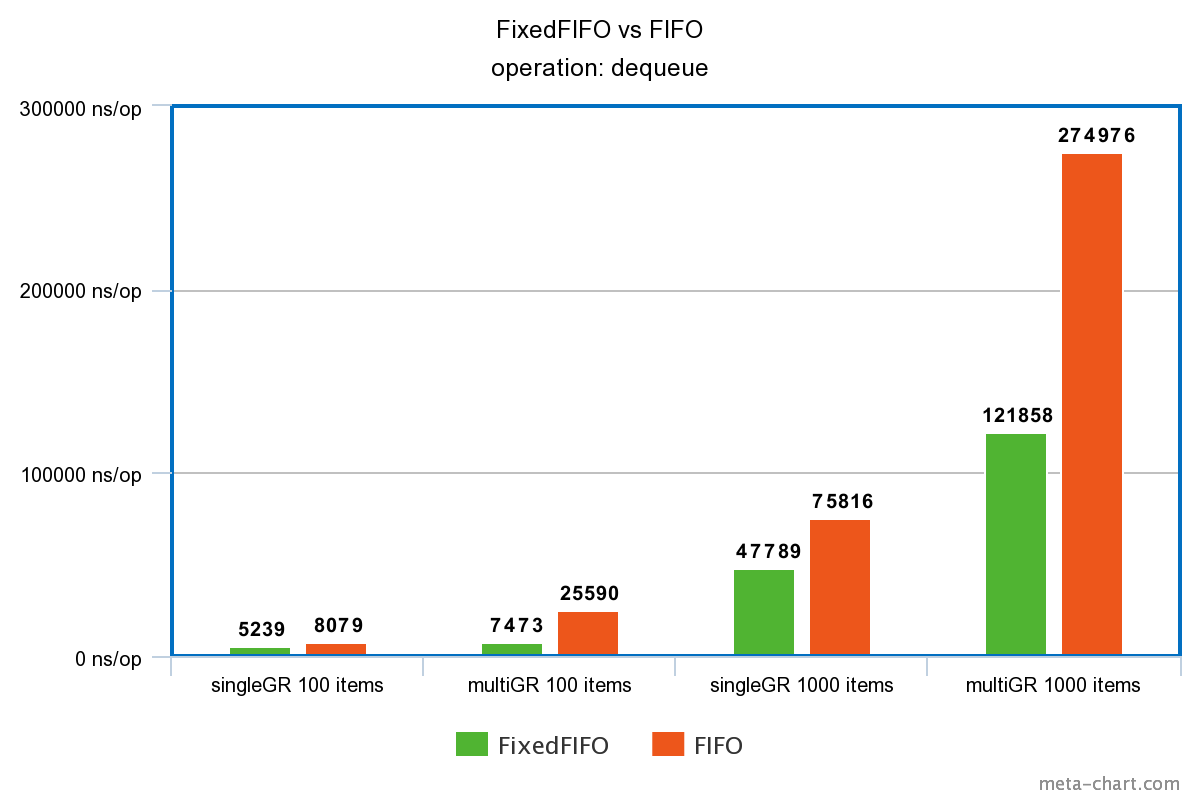
从图中可以看出FixedFIFO在并发场景下性能优势明显。
更多关于golang高性能并发FIFO队列插件库goconcurrentqueue的使用的实战教程也可以访问 https://www.itying.com/category-94-b0.html
1 回复
更多关于golang高性能并发FIFO队列插件库goconcurrentqueue的使用的实战系列教程也可以访问 https://www.itying.com/category-94-b0.html
GoConcurrentQueue - 高性能并发FIFO队列插件库使用指南
GoConcurrentQueue 是一个专门为 Go 语言设计的高性能并发安全 FIFO 队列库,它提供了简单易用的 API 和出色的并发性能。
安装
go get github.com/enriquebris/goconcurrentqueue
基本使用
创建队列
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/enriquebris/goconcurrentqueue"
)
func main() {
// 创建一个新的FIFO队列
queue := goconcurrentqueue.NewFIFO()
// 添加元素到队列
queue.Enqueue("item1")
queue.Enqueue(2)
queue.Enqueue(3.14)
// 获取队列长度
fmt.Println("Queue length:", queue.GetLen()) // 输出: Queue length: 3
// 从队列中取出元素
item, err := queue.Dequeue()
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Dequeue error:", err)
return
}
fmt.Println("Dequeued item:", item) // 输出: Dequeued item: item1
}
高级特性
并发安全操作
package main
import (
"fmt"
"sync"
"time"
"github.com/enriquebris/goconcurrentqueue"
)
func producer(queue *goconcurrentqueue.FIFO, id int, wg *sync.WaitGroup) {
defer wg.Done()
for i := 0; i < 5; i++ {
item := fmt.Sprintf("producer-%d-item-%d", id, i)
queue.Enqueue(item)
fmt.Printf("Producer %d enqueued: %s\n", id, item)
time.Sleep(time.Millisecond * 100)
}
}
func consumer(queue *goconcurrentqueue.FIFO, id int, wg *sync.WaitGroup) {
defer wg.Done()
for i := 0; i < 5; i++ {
item, err := queue.Dequeue()
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Consumer %d error: %v\n", id, err)
continue
}
fmt.Printf("Consumer %d dequeued: %v\n", id, item)
time.Sleep(time.Millisecond * 150)
}
}
func main() {
queue := goconcurrentqueue.NewFIFO()
var wg sync.WaitGroup
// 启动3个生产者协程
for i := 0; i < 3; i++ {
wg.Add(1)
go producer(queue, i, &wg)
}
// 启动2个消费者协程
for i := 0; i < 2; i++ {
wg.Add(1)
go consumer(queue, i, &wg)
}
wg.Wait()
fmt.Println("Final queue length:", queue.GetLen())
}
阻塞式获取元素
package main
import (
"fmt"
"time"
"github.com/enriquebris/goconcurrentqueue"
)
func main() {
queue := goconcurrentqueue.NewFIFO()
// 启动一个消费者协程
go func() {
// 阻塞等待直到有元素可用
item, err := queue.DequeueOrWaitForNextElement()
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error waiting for element:", err)
return
}
fmt.Println("Received item after waiting:", item)
}()
// 主协程稍后添加元素
time.Sleep(2 * time.Second)
queue.Enqueue("delayed item")
// 给消费者时间处理
time.Sleep(time.Second)
}
带超时的阻塞获取
package main
import (
"fmt"
"time"
"github.com/enriquebris/goconcurrentqueue"
)
func main() {
queue := goconcurrentqueue.NewFIFO()
// 尝试获取元素,最多等待1秒
item, err := queue.DequeueOrWaitForNextElementWithTimeout(time.Second)
if err != nil {
if err == goconcurrentqueue.ErrEmptyQueue {
fmt.Println("Queue is empty after waiting")
} else {
fmt.Println("Error:", err)
}
return
}
fmt.Println("Received item:", item)
}
性能优化建议
- 批量操作:对于大量小项,考虑批量入队/出队以减少锁竞争
- 适当队列大小:根据场景选择合适队列容量
- 避免长时间持有锁:在队列操作中尽量减少耗时操作
与其他队列实现的比较
GoConcurrentQueue 相比标准库的 channel 和 sync.Mutex 保护的 slice 有以下优势:
- 更丰富的 API(阻塞获取、超时等)
- 动态容量(不像 channel 需要预先指定大小)
- 专门优化的并发性能
总结
GoConcurrentQueue 是一个功能强大且易于使用的并发安全队列实现,特别适合需要高性能 FIFO 队列的 Go 并发程序。它提供了丰富的特性集,包括阻塞获取、超时控制等,同时保持了优异的性能表现。






