HarmonyOS鸿蒙Next中应用接续功能,如果涉及到大文件如何处理,才能保证接续的流畅?
HarmonyOS鸿蒙Next中应用接续功能,如果涉及到大文件如何处理,才能保证接续的流畅? 目前使用应用接续功能,需要从分布式目录/data/storage/el2/distributedfiles/中拷贝到/data/storage/el2/base/files/中。
但是现在遇到大文件拷贝迁移接续过程完成后并未迁移成功数据,不知具体原因。目前猜测可能是因为主线程阻塞导致的,为解决这一问题,尝试使用taskpool进行拷贝,但是使用taskpool形式会报错:13900012,错误信息如下图:
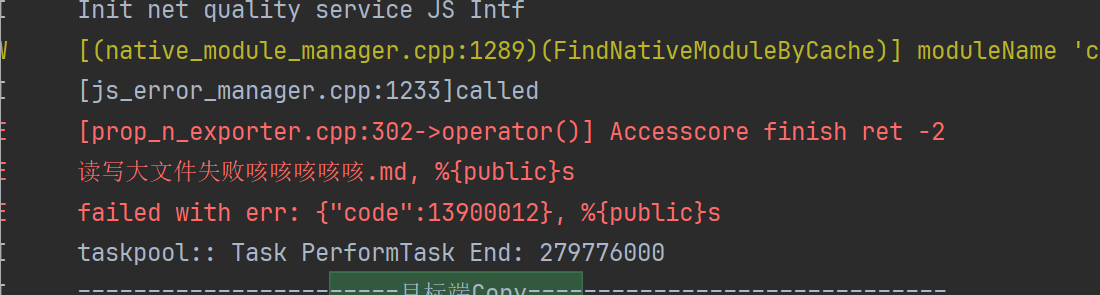
请问各位大佬,这类大文件进行分布式接续的业务场景应当如何处理比较好?希望给出具体处理的demo代码。
版本信息:【创新赛】HarmonyOS 6.0.0 Beta3
更多关于HarmonyOS鸿蒙Next中应用接续功能,如果涉及到大文件如何处理,才能保证接续的流畅?的实战教程也可以访问 https://www.itying.com/category-93-b0.html
【背景知识】 应用接续,指当用户在一个设备上操作某个应用时,可以在另一个设备的同一个应用中快速切换,并无缝衔接上一个设备的应用体验。
【解决方案】 为了接续体验,在onContinue回调中使用wantParam传输的数据需要控制在100KB以下,大数据量请使用分布式数据对象进行同步。可以参考以下链接:基于应用接续、分布式数据对象、分布式文件系统等功能,实现分布式邮件应用。
13900012表示拒绝许可。可能原因:1.文件操作被DAC或selinux拦截。2.文件沙箱路径地址错误。处理步骤可参考13900012 拒绝许可。
更多关于HarmonyOS鸿蒙Next中应用接续功能,如果涉及到大文件如何处理,才能保证接续的流畅?的实战系列教程也可以访问 https://www.itying.com/category-93-b0.html
目前我传输大文件使用的就是分布式数据对象进行的传输。目前遇到的问题是,较小的文件可以一次成功,但是较大的文件一次接续不成功,需要多试几次才会成功,不确定是不是文件较大导致的主线程阻塞,请帮忙分析一下这种情况具体可能是什么原因?
使用该demo测试时可以接续大文件,请问文件大小大概是多少呢,
开发者学堂的教程:大文件迁移(传输文件大小超过100kb)
@Entry
@Component
struct MailHomePage {
aboutToAppear() {
if ((this.isContinuation === CommonConstants.CAN_CONTINUATION) && (this.appendix.length >= 1)) {
this.readFile();
}
}
build() {
// ...
}
/**
* Reading file from distributed file systems.
*/
readFile(): void {
this.appendix.forEach((item: AppendixBean) => {
let filePath: string = this.distributedPath + item.fileName;
let savePath: string = getContext().filesDir + '/' + item.fileName;
try {
while (fileIo.accessSync(filePath)) {
let saveFile = fileIo.openSync(savePath, fileIo.OpenMode.READ_WRITE | fileIo.OpenMode.CREATE);
let file = fileIo.openSync(filePath, fileIo.OpenMode.READ_WRITE);
let buf: ArrayBuffer = new ArrayBuffer(CommonConstants.FILE_BUFFER_SIZE);
let readSize = 0;
let readLen = fileIo.readSync(file.fd, buf, { offset: readSize });
while (readLen > 0) {
readSize += readLen;
fileIo.writeSync(saveFile.fd, buf);
readLen = fileIo.readSync(file.fd, buf, { offset: readSize });
}
fileIo.closeSync(file);
fileIo.closeSync(saveFile);
}
} catch (error) {
let err: BusinessError = error as BusinessError;
Logger.error(`DocumentViewPicker failed with err: ${JSON.stringify(err)}`);
}
});
}
/**
* Add appendix from file manager.
*
* @param fileType
*/
documentSelect(fileType: number): void {
try {
let DocumentSelectOptions = new picker.DocumentSelectOptions();
let documentPicker = new picker.DocumentViewPicker();
documentPicker.select(DocumentSelectOptions).then((DocumentSelectResult: Array<string>) => {
for (let documentSelectResultElement of DocumentSelectResult) {
let buf = new ArrayBuffer(CommonConstants.FILE_BUFFER_SIZE);
let readSize = 0;
let file = fileIo.openSync(documentSelectResultElement, fileIo.OpenMode.READ_ONLY);
let readLen = fileIo.readSync(file.fd, buf, { offset: readSize });
// File name is not supported chinese name.
let fileName = file.name;
if (!fileName.endsWith(imageIndex[fileType].fileType) ||
new RegExp("[\\u4E00-\\u9FA5]|[\\uFE30-\\uFFA0]", "gi").test(fileName)) {
promptAction.showToast({
message: $r('app.string.alert_message_chinese')
})
return;
}
let destination = fileIo.openSync(getContext()
.filesDir + '/' + fileName, fileIo.OpenMode.READ_WRITE | fileIo.OpenMode.CREATE);
let destinationDistribute = fileIo.openSync(getContext()
.distributedFilesDir + '/' + fileName, fileIo.OpenMode.READ_WRITE | fileIo.OpenMode.CREATE);
while (readLen > 0) {
readSize += readLen;
fileIo.writeSync(destination.fd, buf);
fileIo.writeSync(destinationDistribute.fd, buf);
console.info(destinationDistribute.path);
readLen = fileIo.readSync(file.fd, buf, { offset: readSize });
}
fileIo.closeSync(file);
fileIo.closeSync(destination);
fileIo.closeSync(destinationDistribute);
this.appendix.push({ iconIndex: fileType, fileName: fileName });
}
Logger.info(`DocumentViewPicker.select successfully, DocumentSelectResult uri: ${JSON.stringify(DocumentSelectResult)}`);
}).catch((err: BusinessError) => {
Logger.error(`DocumentViewPicker.select failed with err: ${JSON.stringify(err)}`);
});
} catch (error) {
let err: BusinessError = error as BusinessError;
Logger.error(`DocumentViewPicker failed with err: ${JSON.stringify(err)}`);
}
}
}
将大文件拆分为多个小块,通过循环分批传输,结合 taskpool 异步处理:
import taskpool from '@kit.TaskPoolKit';
import fs from '@kit.FileKit';
import { BusinessError } from '@ohos.base';
async function copyLargeFileAsync(sourcePath: string, targetPath: string): Promise<void> {
const CHUNK_SIZE = 1024 * 1024; // 1MB分片
const stat = fs.statSync(sourcePath);
const fileSize = stat.size;
let offset = 0;
while (offset < fileSize) {
const readSize = Math.min(CHUNK_SIZE, fileSize - offset);
const buffer = new ArrayBuffer(readSize);
const readOptions: fs.ReadOptions = {
offset: offset,
length: readSize
};
// 分片读取
fs.readSync(sourcePath, buffer, readOptions);
// 分片写入(异步任务)
await taskpool.execute(async () => {
const writeOptions: fs.WriteOptions = {
offset: offset,
encoding: fs.Encoding.UTF8
};
try {
fs.writeSync(targetPath, buffer, writeOptions);
} catch (error) {
const err = error as BusinessError;
console.error(`分片写入失败: ${err.code}, ${err.message}`);
}
}, taskpool.Priority.LOW);
offset += readSize;
}
}
使用 context 获取分布式文件路径,避免硬编码路径导致的权限错误:
import UIAbility from '@ohos.app.ability.UIAbility';
import { BusinessError } from '@ohos.base';
export default class EntryAbility extends UIAbility {
onContinue(wantParam: Record<string, Object>) {
const context = this.context;
const distributedDir = context.filesDir + '/distributed/'; // 合法分布式目录
const baseDir = context.filesDir + '/base/'; // 目标目录
// 启动异步拷贝
taskpool.execute(() => {
try {
copyLargeFileSync(distributedDir + 'largefile.dat', baseDir + 'largefile.dat');
wantParam['file_transfer_status'] = 'success';
} catch (error) {
wantParam['file_transfer_status'] = 'failed';
}
}, taskpool.Priority.HIGH);
return AbilityConstant.OnContinueResult.AGREE;
}
}
为保证接续流畅体验,在onContinue回调中使用wantParam传输的数据需要控制在100KB以下,大数据量请使用分布式数据对象进行同步 applications_large_data_continuance
鸿蒙Next的应用接续功能通过分布式文件系统和智能预加载机制处理大文件。系统会识别文件使用场景,按需分段传输和缓存关键数据块,减少等待时间。同时利用设备间高速互联协议优化传输效率,确保接续过程流畅。
针对大文件在应用接续中的处理,建议采用分块传输机制避免主线程阻塞。taskpool报错13900012通常是由于文件路径或权限问题导致,分布式文件操作需确保路径正确且具有相应访问权限。
以下是处理大文件接续的示例代码,使用分块读取和写入:
import fs from '@ohos.file.fs';
import common from '@ohos.app.ability.common';
async function copyLargeFile(srcPath: string, destPath: string, context: common.Context) {
const stat = await fs.stat(srcPath);
const fileSize = stat.size;
const chunkSize = 1024 * 1024; // 1MB per chunk
let offset = 0;
while (offset < fileSize) {
const buffer = new ArrayBuffer(chunkSize);
const readOptions = {
offset: offset,
length: chunkSize
};
const readLen = await fs.read(srcPath, buffer, readOptions);
const writeOptions = {
offset: offset,
length: readLen
};
await fs.write(destPath, buffer, writeOptions);
offset += readLen;
}
}
// 调用示例
let src = '/data/storage/el2/distributedfiles/largefile.dat';
let dest = '/data/storage/el2/base/files/largefile.dat';
copyLargeFile(src, dest, this.context).then(() => {
console.log('File copy completed');
}).catch((err) => {
console.error('Copy failed: ' + JSON.stringify(err));
});
注意事项:
- 确保源文件和目标路径存在且可访问
- 分块大小可根据实际调整,平衡性能与内存占用
- 添加进度回调可提升用户体验
- 考虑接续过程中的异常处理和断点续传机制
这种方案能有效避免主线程阻塞,确保大文件接续的稳定性。






