Golang中椭圆曲线实现的多重指数运算有哪些?
Golang中椭圆曲线实现的多重指数运算有哪些?
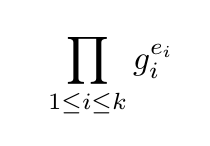
我试图寻找椭圆曲线 secp256k1 的多重幂运算实现:在 Golang 中(其中 gi 是椭圆曲线点,ei 是 bit.Int 类型),但一无所获。目前我只是分别计算 gi * ei 然后将它们全部相加,但这会耗费大量时间。
我找到的唯一多重幂运算实现是 OpenSSL 版本(https://github.com/openssl/openssl/blob/master/crypto/ec/ec_mult.c)。但我没有能力将其转换为 Golang 版本。此外,我还找到了许多关于如何实现该算法的论文。但作为密码学领域的新手,我只想要一个现成的 Golang 实现,这样可以节省大量时间。如果有人了解相关项目或信息,请告知我。提前感谢。
更多关于Golang中椭圆曲线实现的多重指数运算有哪些?的实战教程也可以访问 https://www.itying.com/category-94-b0.html
更多关于Golang中椭圆曲线实现的多重指数运算有哪些?的实战系列教程也可以访问 https://www.itying.com/category-94-b0.html
在 Go 中实现椭圆曲线 secp256k1 的多重指数运算(也称为多标量乘法)可以通过优化算法显著提升性能。虽然标准库 crypto/elliptic 未直接提供此功能,但你可以使用第三方库或自行实现。以下是一个基于 crypto/elliptic 和 math/big 的示例实现,它结合了滑动窗口方法和点加法优化,适用于 secp256k1 曲线。
首先,确保导入必要的包:
import (
"crypto/elliptic"
"math/big"
)
假设你有一个椭圆曲线点切片 points []*ECPoint(其中 ECPoint 是自定义类型,包含 X, Y *big.Int)和标量切片 scalars []*big.Int,以下代码实现了多重指数运算:
// 定义椭圆曲线点结构
type ECPoint struct {
X, Y *big.Int
}
// MultiExp 计算多重指数运算:sum(scalars[i] * points[i])
func MultiExp(curve elliptic.Curve, points []*ECPoint, scalars []*big.Int) (*ECPoint, error) {
if len(points) != len(scalars) {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("points and scalars slices must have same length")
}
// 使用滑动窗口方法,窗口大小设为 4
windowSize := 4
tables := make([]([]*ECPoint), len(points))
// 为每个点预计算表
for i, point := range points {
tables[i] = precomputeTable(curve, point, windowSize)
}
// 初始化结果为无穷远点
result := &ECPoint{new(big.Int), new(big.Int)}
result.X, result.Y = nil, nil // 表示无穷远点
// 从最高位开始遍历所有位
maxBits := curve.Params().BitSize
for j := maxBits - 1; j >= 0; j-- {
if result.X != nil {
// 当前结果加倍
result.X, result.Y = curve.Double(result.X, result.Y)
}
// 处理每个标量的当前窗口
for i := 0; i < len(scalars); i++ {
scalar := scalars[i]
// 获取当前窗口的索引
windowIndex := getWindowIndex(scalar, j, windowSize)
if windowIndex > 0 {
table := tables[i]
if result.X == nil {
// 如果结果是无穷远点,直接赋值
result.X, result.Y = new(big.Int).Set(table[windowIndex].X), new(big.Int).Set(table[windowIndex].Y)
} else {
// 否则进行点加法
result.X, result.Y = curve.Add(result.X, result.Y, table[windowIndex].X, table[windowIndex].Y)
}
}
}
}
return result, nil
}
// precomputeTable 预计算点的表,用于滑动窗口
func precomputeTable(curve elliptic.Curve, point *ECPoint, windowSize int) []*ECPoint {
tableSize := 1 << (windowSize - 1) // 2^(windowSize-1)
table := make([]*ECPoint, tableSize+1)
table[0] = &ECPoint{new(big.Int), new(big.Int)} // 无穷远点,用 nil 表示
table[1] = point // 原始点
// 计算 2P, 3P, ..., (2^(windowSize)-1)P
for i := 2; i <= tableSize; i++ {
if i%2 == 0 {
// 偶数索引:通过加倍得到
prev := table[i/2]
table[i] = &ECPoint{new(big.Int), new(big.Int)}
table[i].X, table[i].Y = curve.Double(prev.X, prev.Y)
} else {
// 奇数索引:通过加法得到
prev1 := table[i-1]
prev2 := point
table[i] = &ECPoint{new(big.Int), new(big.Int)}
table[i].X, table[i].Y = curve.Add(prev1.X, prev1.Y, prev2.X, prev2.Y)
}
}
return table
}
// getWindowIndex 获取标量在指定位置和窗口大小下的索引
func getWindowIndex(scalar *big.Int, bitPos int, windowSize int) int {
index := 0
for k := 0; k < windowSize && bitPos-k >= 0; k++ {
bit := scalar.Bit(bitPos - k)
index = (index << 1) | bit
}
return index
}
此代码通过预计算点表并使用滑动窗口方法减少点加法操作次数,从而优化性能。在实际应用中,你可能需要根据曲线参数调整窗口大小(例如,secp256k1 的位数为 256,窗口大小 4 是一个平衡选择)。此外,确保点坐标在曲线上,并处理无穷远点的情况。
对于生产环境,建议使用经过审计的库如 go-ethereum 的 crypto 模块(它包含 secp256k1 优化实现),但上述代码提供了一个基础的自定义实现。如果性能仍不满足,可以考虑更高级的算法如 Bos-Coster 或 Pippenger 方法。






