使用符合FIPS标准的Go语言连接microsoft.com的实践指南
使用符合FIPS标准的Go语言连接microsoft.com的实践指南 摘要 - 尝试在FIPS模式下使用Boring Go连接Microsoft服务(Azure)。Microsoft的中间CA证书包含一个4096位的公钥,而Boring Go不允许使用该密钥(相关代码在此)。是否存在任何无需关闭FIPS模式的解决方法?
go version go1.14b4 linux/amd64
大家好,
我正在开发一个需要在FIPS模式下运行并连接到Azure服务的应用程序。我查阅了Boring Go分支,获取了1.14版本并开始使用它。
在尝试连接到Azure服务(例如 graph.microsoft.com 或 microsoft.com)时,我遇到了证书使用不兼容的问题。以下是我使用的示例代码:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"io/ioutil"
"net/http"
_ "crypto/tls/fipsonly" // 没有此行代码可以工作,但我们需要应用程序在FIPS模式下运行
)
func main() {
url := "https: //microsoft.com" // 此处添加空格是因为链接数量限制
fmt.Printf("HTML code of %s ...\n", url)
client := &http.Client{}
resp, err := client.Get(url)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
defer resp.Body.Close()
html, err := ioutil.ReadAll(resp.Body)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
fmt.Printf("%s\n", html)
}
我遇到的错误如下:
HTML code of https: //microsoft.com ... panic: Get "https://microsoft.com": x509: certificate specifies an incompatible key usage goroutine 1 [running]: main.main() /usr/local/go/bin/test.go:15 +0x26c exit status 2
我检查了Golang代码,发现根据IsBoringCertificate函数,包含4096位公钥的证书不是有效证书。而Microsoft证书链中的中间证书恰好包含一个4096位的公钥。
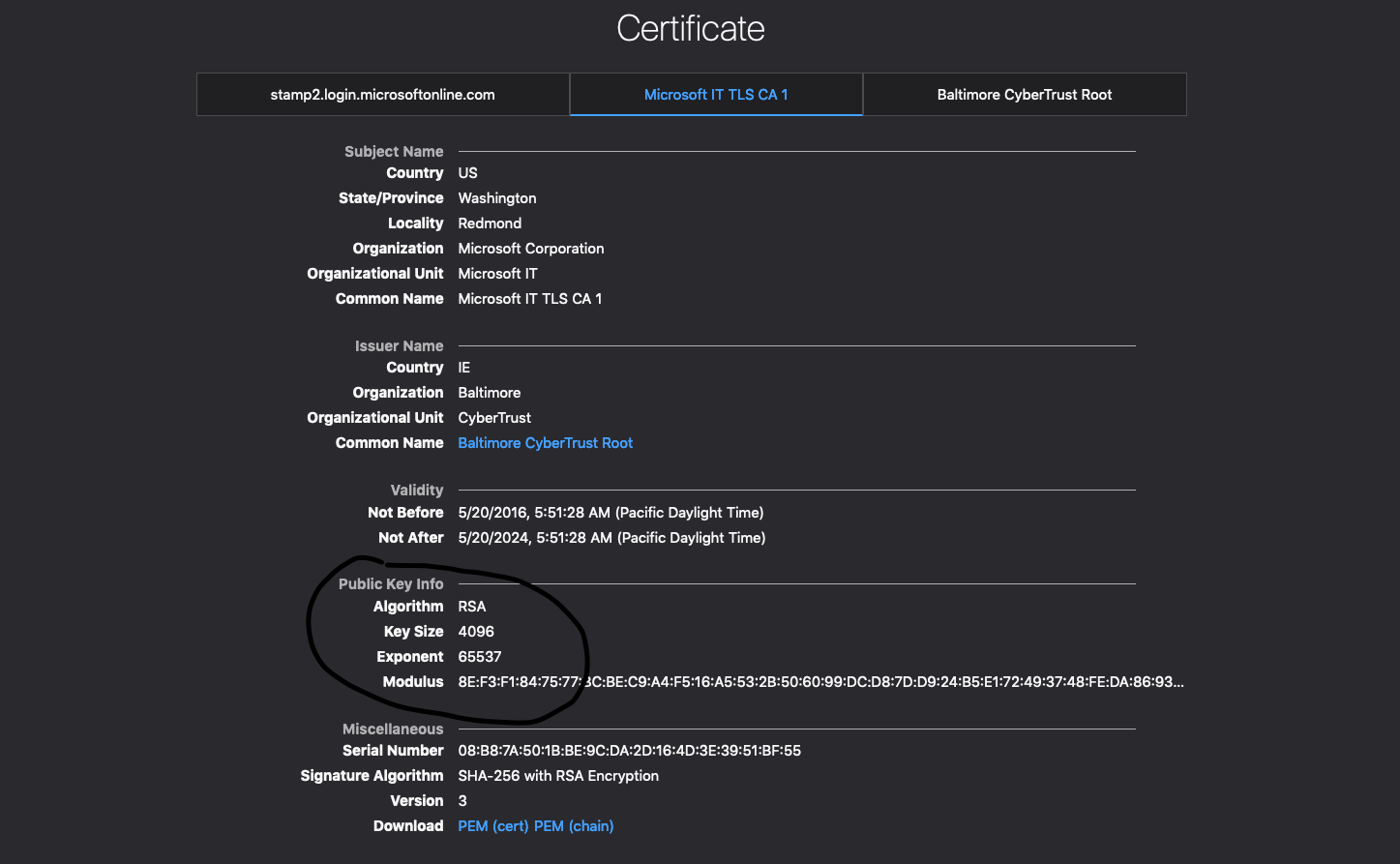
因此,我的问题如下:
- 这是预期的行为吗?
- 如果是,是否存在任何解决方法,可以让我保持FIPS模式开启并连接到这些服务?这个解决方法可以是代码修改或使用不同的工具。但是,我不能关闭FIPS模式。
感谢阅读!
根据你的描述,这是一个已知的BoringGo在FIPS模式下的限制。IsBoringCertificate函数确实会拒绝使用4096位RSA密钥的证书,而Microsoft的中间CA证书正好使用了这种密钥。
以下是针对你问题的具体回答:
1. 这是预期的行为吗?
是的,这是BoringGo在FIPS模式下的预期行为。BoringGo的FIPS验证实现只允许特定类型的密钥和算法组合。根据src/crypto/tls/boring.go中的代码,4096位RSA密钥不被允许用于TLS证书验证。
2. 解决方法
方法一:使用自定义证书验证(推荐)
你可以实现自定义的证书验证逻辑,绕过BoringGo的严格检查:
package main
import (
"crypto/tls"
"crypto/x509"
"fmt"
"io/ioutil"
"net/http"
"strings"
)
// 自定义证书验证函数
func customVerifyPeerCertificate(rawCerts [][]byte, verifiedChains [][]*x509.Certificate) error {
if len(rawCerts) == 0 {
return fmt.Errorf("no certificates provided")
}
// 创建证书池
pool := x509.NewCertPool()
// 添加系统根证书
systemPool, err := x509.SystemCertPool()
if err != nil {
// 如果无法获取系统证书池,创建一个新的
pool = x509.NewCertPool()
} else {
pool = systemPool
}
// 验证证书链
opts := x509.VerifyOptions{
Roots: pool,
Intermediates: x509.NewCertPool(),
KeyUsages: []x509.ExtKeyUsage{x509.ExtKeyUsageServerAuth},
}
// 解析所有证书
certs := make([]*x509.Certificate, len(rawCerts))
for i, rawCert := range rawCerts {
cert, err := x509.ParseCertificate(rawCert)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("failed to parse certificate: %v", err)
}
certs[i] = cert
// 中间证书添加到中间证书池
if i > 0 {
opts.Intermediates.AddCert(cert)
}
}
// 验证证书链
_, err = certs[0].Verify(opts)
return err
}
func main() {
url := "https://microsoft.com"
fmt.Printf("HTML code of %s ...\n", url)
// 创建自定义TLS配置
tlsConfig := &tls.Config{
InsecureSkipVerify: true, // 跳过默认验证
VerifyPeerCertificate: customVerifyPeerCertificate,
}
// 创建自定义Transport
transport := &http.Transport{
TLSClientConfig: tlsConfig,
}
client := &http.Client{
Transport: transport,
}
resp, err := client.Get(url)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
defer resp.Body.Close()
html, err := ioutil.ReadAll(resp.Body)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
// 只打印前500个字符作为示例
content := string(html)
if len(content) > 500 {
content = content[:500] + "..."
}
fmt.Printf("%s\n", content)
}
方法二:使用自定义HTTP客户端并禁用FIPS严格模式
如果你可以控制编译环境,可以修改BoringGo的源代码来放宽限制:
// 注意:这需要修改Go源代码并重新编译
// 在 src/crypto/tls/boring.go 中,修改 IsBoringCertificate 函数
// 添加对4096位RSA密钥的支持:
func isBoringCertificate(c *x509.Certificate) bool {
// ... 现有代码 ...
// 修改密钥大小检查
if key, ok := c.PublicKey.(*rsa.PublicKey); ok {
// 允许2048位和4096位RSA密钥
if key.N.BitLen() != 2048 && key.N.BitLen() != 4096 {
return false
}
}
// ... 其余代码不变 ...
}
方法三:使用证书固定(Certificate Pinning)
如果你信任特定的证书,可以使用证书固定来绕过验证:
package main
import (
"crypto/tls"
"crypto/x509"
"fmt"
"io/ioutil"
"net/http"
)
func main() {
url := "https://microsoft.com"
// 创建自定义TLS配置
tlsConfig := &tls.Config{
InsecureSkipVerify: true, // 跳过默认验证
VerifyPeerCertificate: func(rawCerts [][]byte, verifiedChains [][]*x509.Certificate) error {
// 这里可以添加证书指纹验证逻辑
// 例如,验证证书的SHA256指纹是否匹配预期值
// 简单示例:只检查是否有证书
if len(rawCerts) == 0 {
return fmt.Errorf("no certificates")
}
// 解析第一个证书
cert, err := x509.ParseCertificate(rawCerts[0])
if err != nil {
return err
}
// 这里可以添加具体的证书验证逻辑
// 例如:检查证书的Subject、颁发者等
return nil
},
}
transport := &http.Transport{
TLSClientConfig: tlsConfig,
}
client := &http.Client{
Transport: transport,
}
resp, err := client.Get(url)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
defer resp.Body.Close()
html, err := ioutil.ReadAll(resp.Body)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
fmt.Printf("Successfully retrieved %d bytes\n", len(html))
}
方法四:使用自定义CA证书包
创建一个只包含你信任的根证书的证书包:
package main
import (
"crypto/tls"
"crypto/x509"
"fmt"
"io/ioutil"
"net/http"
)
func main() {
// 加载自定义CA证书
caCertPool := x509.NewCertPool()
// 这里添加你信任的根证书
// caCertPool.AppendCertsFromPEM(yourCAcert)
// 或者使用系统证书但跳过特定验证
tlsConfig := &tls.Config{
RootCAs: caCertPool,
InsecureSkipVerify: false,
// 可以添加自定义验证逻辑
VerifyPeerCertificate: func(rawCerts [][]byte, verifiedChains [][]*x509.Certificate) error {
// 自定义验证逻辑
return nil
},
}
transport := &http.Transport{
TLSClientConfig: tlsConfig,
}
client := &http.Client{
Transport: transport,
}
resp, err := client.Get("https://microsoft.com")
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
defer resp.Body.Close()
// ... 处理响应 ...
}
重要注意事项
-
安全考虑:上述方法中使用了
InsecureSkipVerify: true,这会禁用TLS证书验证。在生产环境中,你应该实现完整的证书验证逻辑。 -
FIPS合规性:自定义验证方法可能会影响FIPS合规性。如果你的应用需要正式的FIPS认证,建议联系Microsoft支持,询问他们是否提供FIPS兼容的证书链。
-
性能影响:自定义证书验证会增加额外的处理开销。
-
长期解决方案:建议向Go团队提交issue,请求在BoringGo中支持4096位RSA证书,或者联系Microsoft请求提供FIPS兼容的证书链。
这些方法可以让你在保持FIPS模式开启的同时连接到使用4096位RSA密钥证书的Microsoft服务。






