Golang中关于http.Get的用法解析
Golang中关于http.Get的用法解析
我编写了 net.go 文件如下:
package main
import (
"io"
"net/http"
)
func indexHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, req *http.Request) {
io.WriteString(w, "Hello, world!\n")
}
func main() {
http.HandleFunc("/", indexHandler)
http.ListenAndServe(":8482", nil)
}
它在浏览器中可以正常工作:

我想从另一个 Go 文件中调用它,所以在第一个文件 net.go 的同一文件夹下编写了 get.go 文件,内容如下:
package main
import "net/http"
func main() {
resp, err := http.Get("http://localhost:8482/")
if err != nil {
println("err: ", err)
} else {
println("resp: ", resp)
}
}
但在运行它时,我遇到了以下错误:
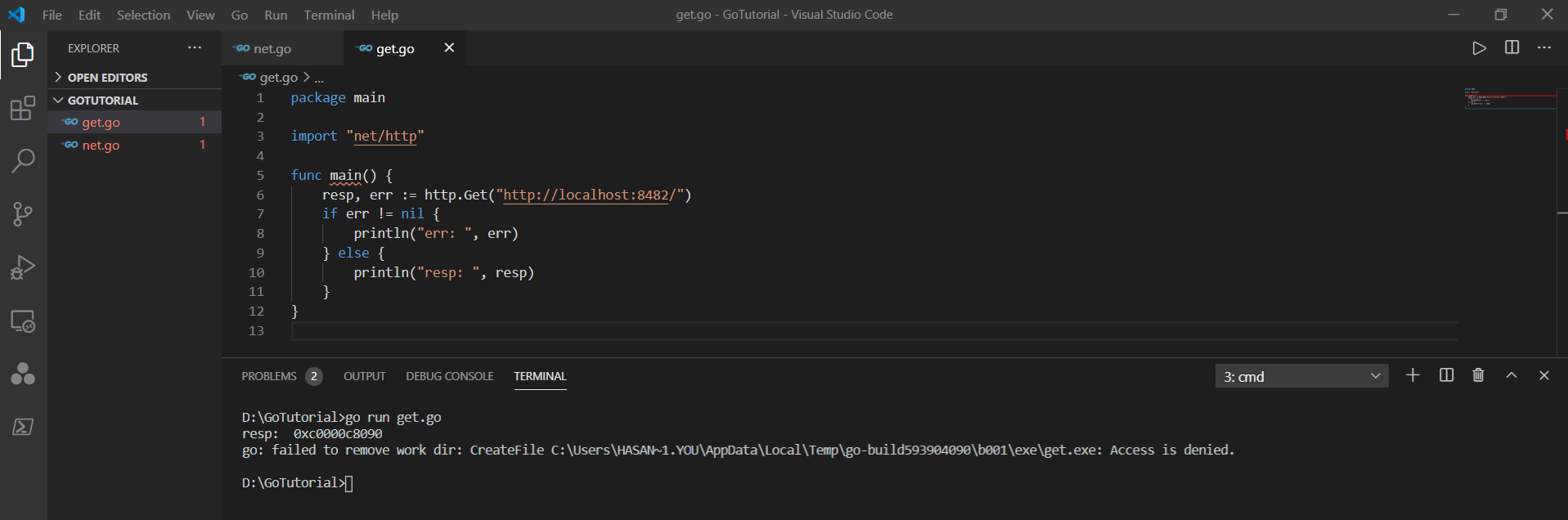
更多关于Golang中关于http.Get的用法解析的实战教程也可以访问 https://www.itying.com/category-94-b0.html
看起来程序执行正确。它显示了 resp 变量中指针的地址。这看起来像是Windows系统的问题?我在这方面不是专家。
响应是一个 http.Response 结构体。你可以通过检查 resp.StatusCode 来查看状态码。
func main() {
fmt.Println("hello world")
}
更多关于Golang中关于http.Get的用法解析的实战系列教程也可以访问 https://www.itying.com/category-94-b0.html
这个错误看起来要么是 Windows 权限问题,要么是 Go 语言本身的问题 —— 你的代码本身没有问题!
如果你使用 go build 命令构建可执行文件,然后再运行它,我确信它会正常工作。
以下代码对我有效:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"io/ioutil"
"log"
"net/http"
)
func main() {
res, err := http.Get("http://localhost:8483")
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
robots, err := ioutil.ReadAll(res.Body)
res.Body.Close()
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
fmt.Printf("%s", robots)
}
在运行 get.go 前,需要先启动 net.go 中的 HTTP 服务器。由于两个文件都是 package main,无法同时运行。以下是解决方案:
方案一:分终端运行
- 终端1启动服务器:
go run net.go
- 终端2执行客户端请求:
go run get.go
方案二:修改 get.go 为独立程序
package main
import (
"fmt"
"io"
"net/http"
)
func main() {
// 先启动服务器(协程方式)
go func() {
http.HandleFunc("/", func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
io.WriteString(w, "Hello, world!\n")
})
http.ListenAndServe(":8482", nil)
}()
// 等待服务器启动
resp, err := http.Get("http://localhost:8482/")
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("请求错误: %v\n", err)
return
}
defer resp.Body.Close()
// 读取响应
body, _ := io.ReadAll(resp.Body)
fmt.Printf("响应状态: %s\n响应内容: %s", resp.Status, body)
}
方案三:使用 http.Client 控制超时
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"io"
"net/http"
"time"
)
func main() {
// 启动服务器
go func() {
http.HandleFunc("/", func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
io.WriteString(w, "Hello from server!\n")
})
http.ListenAndServe(":8482", nil)
}()
// 给服务器启动时间
time.Sleep(100 * time.Millisecond)
// 创建带超时的客户端
client := &http.Client{
Timeout: 5 * time.Second,
}
// 发送请求
resp, err := client.Get("http://localhost:8482/")
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("客户端错误: %v\n", err)
return
}
defer resp.Body.Close()
// 处理响应
if resp.StatusCode == http.StatusOK {
bodyBytes, _ := io.ReadAll(resp.Body)
fmt.Printf("成功响应: %s", string(bodyBytes))
}
}
错误分析:原错误是因为 localhost:8482 端口没有服务在监听。必须确保 HTTP 服务器先运行,客户端才能成功连接。






