Golang如何将二维数组转换为RGB图像?
Golang如何将二维数组转换为RGB图像? 这是使用Python的代码:
# Channel01,02,03都是2748*2748大小的二维uint16数组。
# 这里的技巧是先转换为灰度图像,然后将灰度图像合并为RGB图像...
# 我不知道背后的原因,但它确实有效...
r = Image.fromarray(Channel03*0.1).convert('L')
g = Image.fromarray(Channel02*0.1).convert('L')
b = Image.fromarray(Channel01*0.1).convert('L')
image_output = Image.merge("RGB", (r, g, b))
image_output.save("map_picture.bmp)
我尝试在Go中实现相同的行为:
rect := image.Rect(0, 0, 2748, 2748)
imgSet := image.NewRGBA64(rect)
for i := 0; i < length; i++ {
x := i % 2748
y := i / 2748
pixel := color.RGBA64{
// channel1,2,3与py代码中的相同
R: channel3[i]/10,
G: channel2[i]/10,
B: channel1[i]/10,
A: 65535,
}
imgSet.Set(x, y, pixel)
}
outFile, err := os.Create("hybrid.bmp")
if err != nil {
t.Error(err)
return
}
defer outFile.Close()
err = bmp.Encode(outFile, imgSet)
if err != nil {
t.Error(err)
return
}
}
比较结果如下,Go生成的图像看起来质量损失很严重…
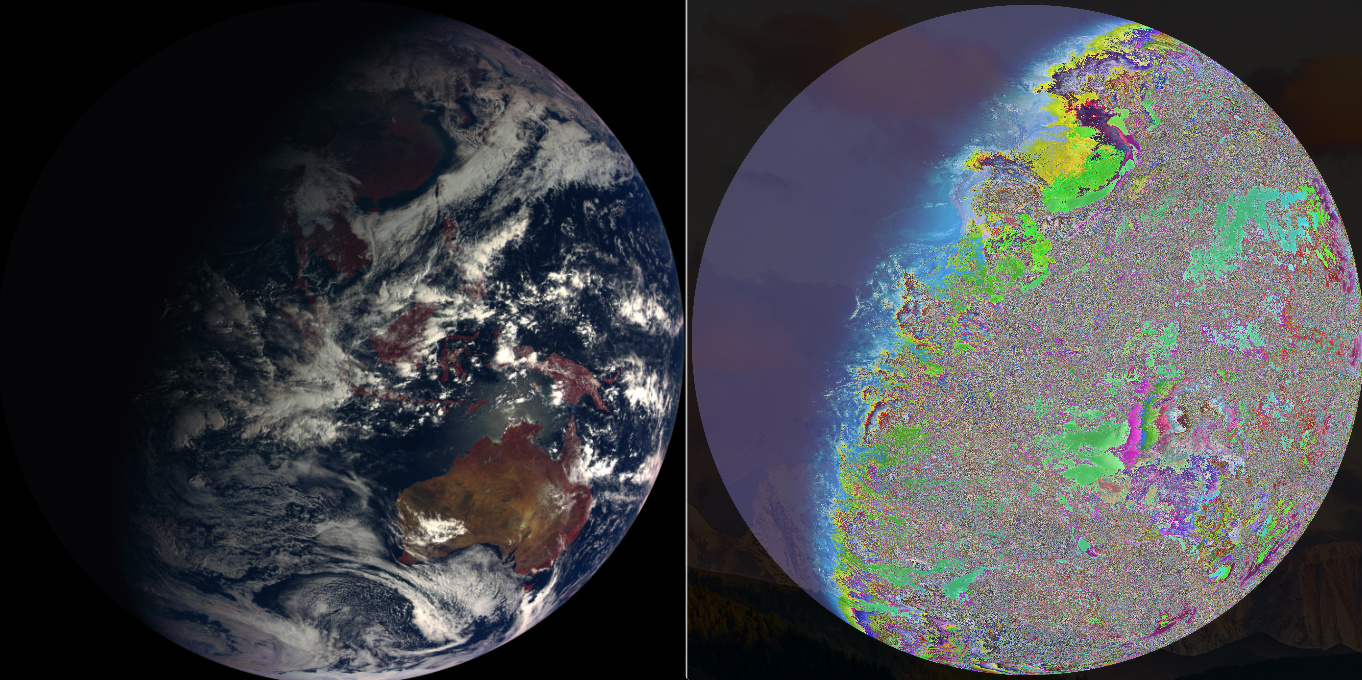
那么,如何使用Go获得相同的结果?
更多关于Golang如何将二维数组转换为RGB图像?的实战教程也可以访问 https://www.itying.com/category-94-b0.html
1 回复
更多关于Golang如何将二维数组转换为RGB图像?的实战系列教程也可以访问 https://www.itying.com/category-94-b0.html
在Go中实现与Python代码相同的效果,需要正确理解Python PIL库的转换逻辑。主要问题在于Python代码中的.convert('L')操作和Image.merge()方法。
以下是修正后的Go实现:
package main
import (
"image"
"image/color"
"os"
"golang.org/x/image/bmp"
)
func main() {
width, height := 2748, 2748
rect := image.Rect(0, 0, width, height)
// 创建三个独立的灰度图像,模拟Python中的convert('L')
grayR := image.NewGray16(rect)
grayG := image.NewGray16(rect)
grayB := image.NewGray16(rect)
// 填充灰度图像
for y := 0; y < height; y++ {
for x := 0; x < width; x++ {
idx := y*width + x
// 应用0.1缩放因子(相当于除以10)
grayR.Set(x, y, color.Gray16{Y: channel3[idx] / 10})
grayG.Set(x, y, color.Gray16{Y: channel2[idx] / 10})
grayB.Set(x, y, color.Gray16{Y: channel1[idx] / 10})
}
}
// 创建最终的RGB图像
rgbImg := image.NewRGBA64(rect)
// 合并三个灰度通道到RGB图像
for y := 0; y < height; y++ {
for x := 0; x < width; x++ {
// 获取每个通道的灰度值
r := grayR.Gray16At(x, x).Y
g := grayG.Gray16At(x, x).Y
b := grayB.Gray16At(x, x).Y
// 设置RGB像素,Alpha通道设为最大值
rgbImg.SetRGBA64(x, y, color.RGBA64{
R: r,
G: g,
B: b,
A: 65535,
})
}
}
// 保存为BMP文件
outFile, err := os.Create("map_picture.bmp")
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
defer outFile.Close()
if err := bmp.Encode(outFile, rgbImg); err != nil {
panic(err)
}
}
或者使用更直接的方法,直接创建RGB图像:
package main
import (
"image"
"image/color"
"os"
"golang.org/x/image/bmp"
)
func main() {
width, height := 2748, 2748
rect := image.Rect(0, 0, width, height)
img := image.NewRGBA64(rect)
for y := 0; y < height; y++ {
for x := 0; x < width; x++ {
idx := y*width + x
// 直接应用缩放并设置RGB值
// 注意:Python代码中channel03对应R,channel02对应G,channel01对应B
r := uint16(float64(channel3[idx]) * 0.1)
g := uint16(float64(channel2[idx]) * 0.1)
b := uint16(float64(channel1[idx]) * 0.1)
// 确保值在0-65535范围内
if r > 65535 {
r = 65535
}
if g > 65535 {
g = 65535
}
if b > 65535 {
b = 65535
}
img.SetRGBA64(x, y, color.RGBA64{
R: r,
G: g,
B: b,
A: 65535,
})
}
}
outFile, err := os.Create("map_picture.bmp")
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
defer outFile.Close()
if err := bmp.Encode(outFile, img); err != nil {
panic(err)
}
}
如果图像质量仍然有问题,可以尝试使用NRGBA64格式:
package main
import (
"image"
"image/color"
"os"
"golang.org/x/image/bmp"
)
func main() {
width, height := 2748, 2748
rect := image.Rect(0, 0, width, height)
img := image.NewNRGBA64(rect)
for y := 0; y < height; y++ {
for x := 0; x < width; x++ {
idx := y*width + x
// 使用浮点数计算确保精度
r := uint16(float64(channel3[idx]) * 0.1)
g := uint16(float64(channel2[idx]) * 0.1)
b := uint16(float64(channel1[idx]) * 0.1)
img.SetNRGBA64(x, y, color.NRGBA64{
R: r,
G: g,
B: b,
A: 65535,
})
}
}
outFile, err := os.Create("map_picture.bmp")
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
defer outFile.Close()
if err := bmp.Encode(outFile, img); err != nil {
panic(err)
}
}
关键点:
- Python的
convert('L')创建的是灰度图像,在Go中对应image.Gray16 - 确保使用正确的通道顺序:channel03→R,channel02→G,channel01→B
- 使用浮点数计算缩放因子0.1,而不是整数除法
- 考虑使用
NRGBA64格式,它支持预乘alpha通道






