Golang实现本地代理并注入Proxy-Authorization头转发至远程代理
Golang实现本地代理并注入Proxy-Authorization头转发至远程代理 我正在开发一个基于Go和Selenium的自动化工具,名为IGopher,并且收到了一些用户请求,希望实现原生代理支持。
然而,我在处理需要身份验证的代理时遇到了问题…… 我无法将代理凭据发送给Chrome,如果没有这些凭据,Chrome会通过一个弹窗要求进行身份验证,而我很难通过Selenium与之交互(我甚至不确定在无头模式下是否可能)。
因此,我想到一个方案:在我的程序中本地托管一个中间代理系统,该系统将添加“Proxy-Authorization”请求头,并将请求转发到远程代理。
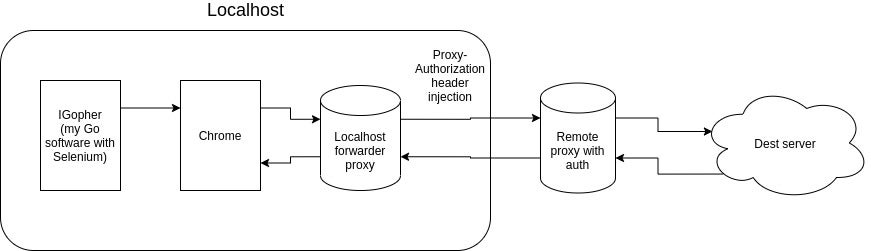
类似于这样的项目:proxy-login-automator
说实话,我对代理不是很熟悉,但我尝试了两种方法: 第一种是使用HandlerFunc:
var (
localServerHost string
remoteServerHost string
remoteServerAuth string
)
// ProxyConfig 存储所有远程代理配置
type ProxyConfig struct {
IP string `yaml:"ip"`
Port int `yaml:"port"`
Username string `yaml:"username"`
Password string `yaml:"password"`
Enabled bool `yaml:"activated"`
}
// LaunchForwardingProxy 启动转发服务器,用于将代理身份验证头注入到传出请求中
func LaunchForwardingProxy(localPort uint16, remoteProxy ProxyConfig) error {
localServerHost = fmt.Sprintf("localhost:%d", localPort)
remoteServerHost = fmt.Sprintf(
"%s:%d",
remoteProxy.IP,
remoteProxy.Port,
)
remoteServerAuth = fmt.Sprintf(
"%s:%s",
remoteProxy.Username,
remoteProxy.Password,
)
handler := http.HandlerFunc(handleFunc)
server := &http.Server{
Addr: ":8880",
Handler: handler,
ReadTimeout: 10 * time.Second,
WriteTimeout: 10 * time.Second,
MaxHeaderBytes: 1 << 20,
}
go func() {
if err := server.ListenAndServe(); err != nil {
logrus.Fatal(err)
}
}()
logrus.Infof("端口转发服务器已启动并在 %s 上监听", localServerHost)
// 设置信号捕获
stop := make(chan os.Signal, 1)
signal.Notify(stop, os.Interrupt)
// 等待SIGINT信号 (pkill -2)
<-stop
ctx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(context.Background(), 5*time.Second)
defer cancel()
if err := server.Shutdown(ctx); err != nil {
logrus.Errorf("转发代理关闭失败: %v", err)
}
logrus.Info("转发代理已停止")
return nil
}
func handleFunc(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
// 将代理身份验证头注入到传出请求的新Header中
basicAuth := "Basic " + base64.StdEncoding.EncodeToString([]byte(remoteServerAuth))
r.Header.Add("Proxy-Authorization", basicAuth)
// 为远程代理准备新请求
bodyRemote, err := ioutil.ReadAll(r.Body)
if err != nil {
http.Error(w, err.Error(), http.StatusInternalServerError)
return
}
/*准备新请求
这部分我不太确定 */
// 创建新请求
hostURL := fmt.Sprintf("%s://%s", "http", remoteServerHost)
proxyReq, err := http.NewRequest(r.Method, hostURL, bytes.NewReader(bodyRemote))
if err != nil {
http.Error(w, "无法创建新请求", 500)
return
}
// 复制请求头
proxyReq.Header = r.Header
logrus.Info(proxyReq)
/* 请求准备结束 */
// 将请求转发到远程代理服务器
httpClient := http.Client{}
resp, err := httpClient.Do(proxyReq)
if err != nil {
logrus.Info(err)
http.Error(w, "无法连接到源服务器", 500)
return
}
defer resp.Body.Close()
logrus.Infof("响应: %v", resp)
// 将响应头从源服务器传输到客户端
for name, values := range resp.Header {
w.Header()[name] = values
}
w.WriteHeader(resp.StatusCode)
// 将响应体从源服务器传输到客户端
if resp.ContentLength > 0 {
io.CopyN(w, resp.Body, resp.ContentLength)
} else if resp.Close {
// 复制直到EOF或发生其他错误
for {
if _, err := io.Copy(w, resp.Body); err != nil {
break
}
}
}
}
使用这段代码,我能够拦截请求并更新请求头。然而,目前的情况是,我只向我的代理发送了一个CONNECT请求,所以它完全没用:
&{CONNECT http://<PROXY_IP>:3128 HTTP/1.1 1 1 map[Connection:[keep-alive] Proxy-Authorization:[Basic <auth>] Proxy-Connection:[keep-alive] User-Agent:[Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Ubuntu; Linux x86_64; rv:86.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/86.0]] {} 0x71fe20 0 [] false <PROXY_IP>:3128 map[] map[] <nil> map[] <nil> <nil> <nil> 0xc0000260e0}
我认为我需要更改NewRequest的URL,但我不知道该放什么……
我也尝试了使用NewSingleHostReverseProxy:
func PrintResponse(r *http.Response) error {
logrus.Infof("Response: %+v\n", r)
return nil
}
// LaunchForwardingProxy launch forward server used to inject proxy authentication header
// into outgoing requests
func LaunchForwardingProxy(localPort uint16, remoteProxy ProxyConfig) error {
localServerHost = fmt.Sprintf("localhost:%d", localPort)
remoteServerHost = fmt.Sprintf(
"http://%s:%d",
remoteProxy.IP,
remoteProxy.Port,
)
remoteServerAuth = fmt.Sprintf(
"%s:%s",
remoteProxy.Username,
remoteProxy.Password,
)
remote, err := url.Parse(remoteServerHost)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
proxy := httputil.NewSingleHostReverseProxy(remote)
d := func(req *http.Request) {
logrus.Infof("Pre-Edited request: %+v\n", req)
// Inject proxy authentication headers to outgoing request into new Header
basicAuth := "Basic " + base64.StdEncoding.EncodeToString([]byte(remoteServerAuth))
req.Header.Set("Proxy-Authorization", basicAuth)
// Change host to the remote proxy
req.URL = remote
logrus.Infof("Edited Request: %+v\n", req)
logrus.Infof("Scheme: %s, Host: %s, Port: %s\n", req.URL.Scheme, req.URL.Host, req.URL.Port())
}
proxy.Director = d
proxy.ModifyResponse = PrintResponse
http.ListenAndServe(localServerHost, proxy)
return nil
}
同样,我成功拦截了请求并编辑了请求头,但这次CONNECT请求转发失败,并出现以下错误信息:
INFO[0007] Pre-Edited request: &{Method:CONNECT URL://google.com:443 Proto:HTTP/1.1 ProtoMajor:1 ProtoMinor:1 Header:map[Proxy-Connection:[Keep-Alive] User-Agent:[curl/7.68.0]] Body:<nil> GetBody:<nil> ContentLength:0 TransferEncoding:[] Close:false Host:google.com:443 Form:map[] PostForm:map[] MultipartForm:<nil> Trailer:map[] RemoteAddr:127.0.0.1:46672 RequestURI:google.com:443 TLS:<nil> Cancel:<nil> Response:<nil> ctx:0xc0002986c0} function=func1 line=58
INFO[0007] Edited Request: &{Method:CONNECT URL://google.com:443 Proto:HTTP/1.1 ProtoMajor:1 ProtoMinor:1 Header:map[Proxy-Authorization:[Basic aWdvcGhlcjpwYXNzd29yZA==] Proxy-Connection:[Keep-Alive] User-Agent:[curl/7.68.0]] Body:<nil> GetBody:<nil> ContentLength:0 TransferEncoding:[] Close:false Host:http://51.178.42.90:3128 Form:map[] PostForm:map[] MultipartForm:<nil> Trailer:map[] RemoteAddr:127.0.0.1:46672 RequestURI:google.com:443 TLS:<nil> Cancel:<nil> Response:<nil> ctx:0xc0002986c0} function=func1 line=64
2021/03/14 12:10:07 http: proxy error: unsupported protocol scheme ""
如果你有办法完善我的做法,或者有其他方法,那就太好了! 我想我误解了请求结构以及URL/Host字段的作用。
你可以在这里找到IGopher的所有源代码:GitHub仓库(代理相关代码除外)
更多关于Golang实现本地代理并注入Proxy-Authorization头转发至远程代理的实战教程也可以访问 https://www.itying.com/category-94-b0.html







