HarmonyOS鸿蒙Next中采用AVPlayer实现音乐动态光谱
HarmonyOS鸿蒙Next中采用AVPlayer实现音乐动态光谱 如何采用 AVPlayer 实现音乐动态光谱效果?
实现效果
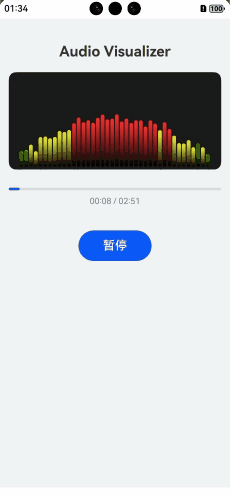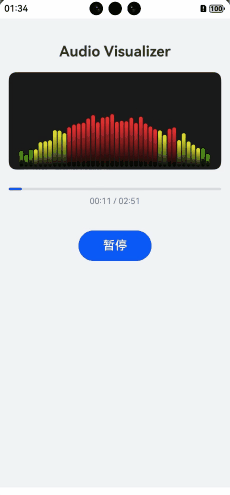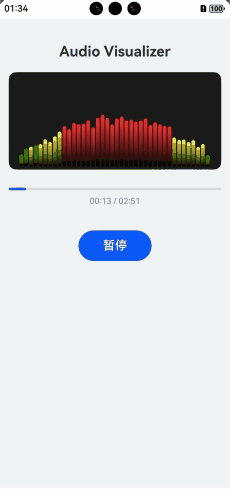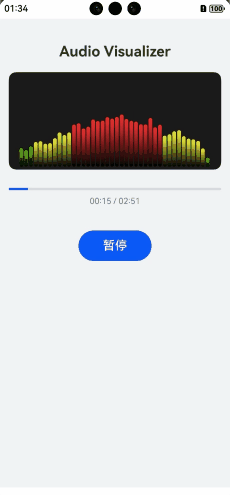
使用场景
主要使用在音乐播放,让效果看起来更加动感。
实现思路
第一步:创建频谱条数据模型,通过此数据模型存储频谱条动态数据。
第二步:创建 createAVPlayer,监听stateChange变更判断播放状态。
第三步:设置频谱条数据更新算法,播放时动态更新频谱条。
注意:需要在真机测试。
完整实现代码
import { media } from '@kit.MediaKit';
import { fileIo } from '@kit.CoreFileKit';
import { common } from '@kit.AbilityKit';
import { hilog } from '@kit.PerformanceAnalysisKit';
import json from '@ohos.util.json';
import { JSON } from '@kit.ArkTS';
const TAG = 'AudioVisualizerDemo';
// 频谱条数据模型
class BarData {
height: number = 5; // 默认高度
color: string = '#33ff00';
}
@Entry
@Component
struct AudioVisualizerPage {
@State message: string = 'Audio Visualizer';
@State isPlaying: boolean = false;
@State currentProgress: number = 0; // 当前进度 0-100
@State visualizerData: BarData[] = []; // 频谱数据源
@State duration: number = 0; // 总时长
@State timeStr: string = '00:00';
private avPlayer: media.AVPlayer | null = null;
private timerId: number = -1;
private readonly BAR_COUNT = 40; // 频谱条数量
private readonly SPEED = 1; // 刷新间隔 ms
aboutToAppear(): void {
// 初始化频谱数据
for (let i = 0; i < this.BAR_COUNT; i++) {
this.visualizerData.push(new BarData());
}
this.initAVPlayer();
}
aboutToDisappear(): void {
this.releasePlayer();
if (this.timerId !== -1) {
clearInterval(this.timerId);
}
}
// 初始化 AVPlayer
async initAVPlayer() {
try {
this.avPlayer = await media.createAVPlayer();
const avP = this.avPlayer;
this.avPlayer.on('stateChange', (state) => {
hilog.info(0x0000, TAG, `State changed to: ${state}`);
switch (state) {
case 'initialized':
this.avPlayer?.prepare();
break;
case 'prepared':
// 获取时长
this.duration = avP.duration;
this.updateTimeStr(0);
break;
case 'playing':
this.isPlaying = true;
this.startVisualizerLoop(); // 启动频谱刷新
this.startProgressLoop();
break;
case 'paused':
case 'completed':
this.isPlaying = false;
this.stopVisualizerLoop();
break;
case 'released':
this.isPlaying = false;
break;
}
});
// 设置播放源 : 这是一个测试的mp3,如果有需要自己换哈。
this.avPlayer.url = 'https://files.freemusicarchive.org/storage-freemusicarchive-org/music/no_curator/Tours/Enthusiast/Tours_-_01_-_Enthusiast.mp3';
this.avPlayer.setVolume(1.0);
} catch (error) {
hilog.error(0x0000, TAG, `Init AVPlayer failed: ${JSON.stringify(error)}`);
}
}
private updateVisualizerData() {
hilog.info(0x0000, TAG, JSON.stringify(this.visualizerData));
const newData:BarData[] = [];
for (let i = 0; i < this.BAR_COUNT; i++) {
// 模拟波形:中间高两边低,带有随机跳动
const baseHeight = Math.sin((i / this.BAR_COUNT) * Math.PI) * 60; // 0-60
const randomNoise = Math.random() * 40; // 0-40
// 如果正在播放,波动幅度大;暂停则缓慢归零
const targetHeight = this.isPlaying ? (baseHeight + randomNoise) : 2;
// 简单的平滑过渡算法
const current = this.visualizerData[i].height;
const diff = targetHeight - current;
const newHeight = current + diff * 0.4; // 0.4 是平滑系数
let newColor = "#33ff00";
// 动态颜色:高度越高越红,越低越绿
if (newHeight > 60) {
newColor = '#ff3333'; // Red
} else if (this.visualizerData[i].height > 30) {
newColor = '#ffff33'; // Yellow
} else {
newColor = '#33ff00'; // Green
}
newData.push({
height:newHeight,
color:newColor
})
}
this.visualizerData = [...newData];
}
startVisualizerLoop() {
if (this.timerId !== -1) return;
this.timerId = setInterval(() => {
this.updateVisualizerData();
}, this.SPEED);
}
stopVisualizerLoop() {
if (this.timerId !== -1) {
clearInterval(this.timerId);
this.timerId = -1;
}
// 停止时缓慢归零
const resetInterval = setInterval(() => {
let allZero = true;
for (let i = 0; i < this.BAR_COUNT; i++) {
if (this.visualizerData[i].height > 0.5) {
this.visualizerData[i].height *= 0.8;
allZero = false;
} else {
this.visualizerData[i].height = 0;
}
}
if (allZero) clearInterval(resetInterval);
}, 30);
}
startProgressLoop() {
const progressTimer = setInterval(() => {
if (!this.isPlaying || !this.avPlayer) {
clearInterval(progressTimer);
return;
}
const currentTime = this.avPlayer.currentTime;
this.currentProgress = (currentTime / this.duration) * 100;
this.updateTimeStr(currentTime);
}, 1000);
}
updateTimeStr(ms: number) {
const totalSeconds = Math.floor(ms / 1000);
const minutes = Math.floor(totalSeconds / 60).toString().padStart(2, '0');
const seconds = (totalSeconds % 60).toString().padStart(2, '0');
this.timeStr = `${minutes}:${seconds}`;
}
async playOrPause() {
if (!this.avPlayer) return;
try {
if (this.isPlaying) {
this.avPlayer.pause();
} else {
this.avPlayer.play();
}
} catch (error) {
hilog.error(0x0000, TAG, `Play/Pause error: ${JSON.stringify(error)}`);
}
}
releasePlayer() {
if (this.avPlayer) {
this.avPlayer.release();
this.avPlayer = null;
}
}
build() {
Column() {
Text(this.message)
.fontSize(24)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.margin({ top: 40, bottom: 20 })
Row() {
ForEach(this.visualizerData, (item: BarData, index: number) => {
Column() {
// 频谱柱
Column()
.width(6)
.height(item.height)
.borderRadius(3)
.linearGradient({
angle: 180,
colors: [[item.color, 0.0], ['#000000', 1.0]]
})
}
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.End)
.height(150)
.margin({ right: 2 })
}, (item: BarData, index: number) => `${index}_${item.height}`)
}
.width('90%')
.height(160)
.backgroundColor('#1a1a1a')
.borderRadius(12)
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.margin({ bottom: 30 })
// 进度条
Progress({ value: this.currentProgress, total: 100, type: ProgressType.Linear })
.width('90%')
.color(Color.Blue)
.margin({ bottom: 10 })
Text(`${this.timeStr} / ${Math.floor(this.duration / 1000) / 60 > 0 ?
Math.floor(Math.floor(this.duration / 1000) / 60).toString().padStart(2,'0') : '00'}:${(Math.floor(this.duration / 1000) % 60).toString().padStart(2,'0')}`)
.fontSize(14)
.fontColor(Color.Gray)
.margin({ bottom: 40 })
// 控制按钮
Row() {
Button(this.isPlaying ? '暂停' : '播放')
.fontSize(20)
.width(120)
.height(50)
.onClick(() => this.playOrPause())
}
}
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
.backgroundColor('#F1F3F5')
}
}
更多关于HarmonyOS鸿蒙Next中采用AVPlayer实现音乐动态光谱的实战系列教程也可以访问 https://www.itying.com/category-93-b0.html
HarmonyOS Next中AVPlayer结合AudioRenderer可实现音频频谱可视化。通过AVPlayer获取音频数据流,使用AudioRenderer的getAudioTime方法获取时间戳,配合FFT算法将时域信号转换为频域数据。开发者需调用OH_AVCapability获取音频参数,通过OH_AudioRenderer_GetFrameSize计算帧大小,利用OH_AudioRenderer_Write渲染音频流并提取振幅数据。频谱绘制需使用Canvas组件进行动态渲染,通过监听AVPlayer的on(‘timeUpdate’)事件实时更新频谱数据。
在HarmonyOS Next中,使用AVPlayer结合Canvas等图形绘制能力可以实现音乐动态光谱效果。核心思路是利用AVPlayer的音频播放能力获取实时音频数据,再通过图形接口进行可视化渲染。
主要步骤如下:
- 初始化AVPlayer:配置AVPlayer用于音频播放,并准备音频源。
- 获取音频数据(关键):通过AVPlayer的
audioRenderer或相关音频模块(如AudioRenderer)获取播放时的PCM音频数据。这通常需要设置音频回调,在回调中接收原始的、时域的音频样本数据。 - 数据处理:对获取的时域音频样本进行快速傅里叶变换(FFT),将其转换为频域数据。频域数据反映了各个频率成分的强度,这正是光谱可视化所需的基础数据。
- 图形绘制:
- 使用
CanvasRenderingContext2D或Canvas组件进行绘制。 - 将处理后的频域数据(通常是幅度谱)映射为可视化的柱状条、波形或粒子等图形元素。例如,每个频率区间对应一个垂直柱状条,其高度与该频率区间的幅度成正比。
- 在
onFrame回调或使用动画引擎(如Animator)中持续更新绘制,实现动态效果。
- 使用
简要代码思路示意:
// 1. 初始化AVPlayer
const avPlayer = new media.AVPlayer();
// ... 配置avPlayer
// 2. 获取音频数据(此处为概念示意,具体API可能涉及AudioRenderer或AVPlayer的回调)
// 假设通过某种回调获取到音频样本数组 audioSamples (时域数据)
// 3. 数据处理:对audioSamples进行FFT,得到频域数据frequencyData
let frequencyData = performFFT(audioSamples); // 需自行实现或使用第三方FFT库
// 4. 图形绘制
const ctx = canvas.getContext('2d');
function drawSpectrum() {
ctx.clearRect(0, 0, canvas.width, canvas.height);
const barWidth = canvas.width / frequencyData.length;
for (let i = 0; i < frequencyData.length; i++) {
const barHeight = frequencyData[i] * scaleFactor; // 缩放因子
ctx.fillRect(i * barWidth, canvas.height - barHeight, barWidth - 1, barHeight);
}
requestAnimationFrame(drawSpectrum); // 持续更新
}
drawSpectrum();
注意事项:
- 实时性:确保音频数据获取和图形绘制的帧率足够高,以实现流畅的动态效果。
- 性能:FFT计算和图形绘制可能消耗较多资源,需注意优化,例如降低FFT点数、使用Worker线程处理计算等。
- API差异:HarmonyOS Next的AVPlayer及相关音频API可能与旧版本有差异,请以最新官方文档为准。
此方案实现了从音频播放、数据采集、频域转换到动态绘制的完整流程,是HarmonyOS Next上实现音乐动态光谱的典型方法。






