Golang中私有REST API的日志记录实现
Golang中私有REST API的日志记录实现 大家好,
我从未在生产环境中进行过日志记录,所以我的问题可能有些幼稚。
在我的微服务应用中,只有网关进行日志记录,其他服务仅使用以下结构将错误相互传递,直至网关:
type restErr struct {
// 发送给前端
ErrStatus int `json:"status"` // HTTP 状态码
ErrTitle string `json:"title"` // 状态码的字符串表示,如 "bad_request"
ErrMessage string `json:"message"` // 发送给前端的可选消息
// 不发送给前端,仅用于日志记录
ErrError error `json:"error"` // 由数据库、其他服务等返回的原始错误
ErrErrorMsg string `json:"error_msg"` // ErrError 的字符串表示
ErrCode string `json:"code"` // 来自数据库或其他服务的原始错误代码
}
错误由每个微服务的每一层包装,直至网关,网关会记录类似这样的错误:
2023-04-29T09:14:44+04:00 ERR | can't do what you want me to | error="gw.controllerX.MethodX: gw.httpclientY.MethodY: service1.controllerX.MethodX: service1.serviceY.MethodY: service2.controllerX.MethodX: service2.serviceY.MethodY: service2.repositoryY.MethodY: error 9009 in database" code=9009 correlationID=cgva1dg3lcjadv69n180 service=gw status=500
我确实有一个疑问,因为我相当确定我曾读到过一些应用仅从网关记录日志,但这会让我到处看到的 correlationID 变得完全无用。另一方面,我看到在 Go 中应该包装错误以便更好地跟踪执行路径,所以我有点困惑……任何建议对我来说都弥足珍贵。
以下是一个说明图:
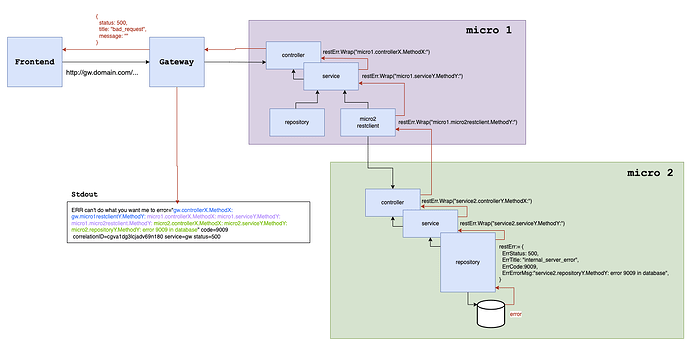
以及原始图表的链接,以便更清晰地查看:logging with microservices - Google Drive
非常感谢。
更多关于Golang中私有REST API的日志记录实现的实战教程也可以访问 https://www.itying.com/category-94-b0.html
更多关于Golang中私有REST API的日志记录实现的实战系列教程也可以访问 https://www.itying.com/category-94-b0.html
在微服务架构中,日志记录策略确实需要仔细设计。你的 restErr 结构体设计合理,但仅网关记录日志确实会丢失关键调试信息。以下是完整的实现方案:
1. 增强错误结构体
type RestErr struct {
// 客户端可见字段
Status int `json:"status"`
Title string `json:"title"`
Message string `json:"message"`
// 内部调试字段
Err error `json:"-"`
ErrMsg string `json:"-"`
Code string `json:"-"`
CorrelationID string `json:"-"`
Service string `json:"-"`
Timestamp time.Time `json:"-"`
StackTrace string `json:"-"`
}
func NewRestErr(status int, title, message string, err error) *RestErr {
return &RestErr{
Status: status,
Title: title,
Message: message,
Err: err,
ErrMsg: err.Error(),
Timestamp: time.Now(),
}
}
func (e *RestErr) Error() string {
return fmt.Sprintf("%s: %s", e.Title, e.Message)
}
func (e *RestErr) WithCorrelationID(id string) *RestErr {
e.CorrelationID = id
return e
}
func (e *RestErr) WithService(service string) *RestErr {
e.Service = service
return e
}
func (e *RestErr) WithStackTrace() *RestErr {
buf := make([]byte, 1024)
n := runtime.Stack(buf, false)
e.StackTrace = string(buf[:n])
return e
}
2. 中间件实现分布式日志记录
package middleware
import (
"context"
"net/http"
"time"
"github.com/google/uuid"
"go.uber.org/zap"
)
type contextKey string
const (
CorrelationIDKey contextKey = "correlation_id"
ServiceNameKey contextKey = "service_name"
)
func LoggingMiddleware(logger *zap.Logger, serviceName string) func(http.Handler) http.Handler {
return func(next http.Handler) http.Handler {
return http.HandlerFunc(func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
start := time.Now()
// 生成或获取 correlation ID
correlationID := r.Header.Get("X-Correlation-ID")
if correlationID == "" {
correlationID = uuid.New().String()
}
// 设置响应头
w.Header().Set("X-Correlation-ID", correlationID)
// 创建带日志字段的上下文
ctx := context.WithValue(r.Context(), CorrelationIDKey, correlationID)
ctx = context.WithValue(ctx, ServiceNameKey, serviceName)
// 包装 ResponseWriter 以捕获状态码
rw := &responseWriter{ResponseWriter: w, statusCode: http.StatusOK}
// 处理请求
next.ServeHTTP(rw, r)
// 记录访问日志
duration := time.Since(start)
logger.Info("request completed",
zap.String("correlation_id", correlationID),
zap.String("service", serviceName),
zap.String("method", r.Method),
zap.String("path", r.URL.Path),
zap.Int("status", rw.statusCode),
zap.Duration("duration", duration),
zap.String("client_ip", r.RemoteAddr),
)
})
}
}
type responseWriter struct {
http.ResponseWriter
statusCode int
}
func (rw *responseWriter) WriteHeader(code int) {
rw.statusCode = code
rw.ResponseWriter.WriteHeader(code)
}
3. 服务层错误处理示例
package service
import (
"context"
"errors"
"go.uber.org/zap"
)
type UserService struct {
logger *zap.Logger
repo UserRepository
}
func (s *UserService) GetUser(ctx context.Context, userID string) (*User, *RestErr) {
correlationID, _ := ctx.Value(middleware.CorrelationIDKey).(string)
serviceName, _ := ctx.Value(middleware.ServiceNameKey).(string)
user, err := s.repo.FindByID(ctx, userID)
if err != nil {
// 记录服务层错误
s.logger.Error("failed to get user",
zap.String("correlation_id", correlationID),
zap.String("service", serviceName),
zap.String("method", "UserService.GetUser"),
zap.String("user_id", userID),
zap.Error(err),
)
// 包装错误并返回
restErr := NewRestErr(
http.StatusInternalServerError,
"internal_server_error",
"Failed to retrieve user",
err,
).WithCorrelationID(correlationID).
WithService(serviceName).
WithStackTrace()
return nil, restErr
}
// 业务逻辑错误示例
if user.Status == "suspended" {
s.logger.Warn("user is suspended",
zap.String("correlation_id", correlationID),
zap.String("service", serviceName),
zap.String("user_id", userID),
)
restErr := NewRestErr(
http.StatusForbidden,
"forbidden",
"User account is suspended",
errors.New("user_suspended"),
).WithCorrelationID(correlationID).
WithService(serviceName)
return nil, restErr
}
return user, nil
}
4. 网关统一错误处理
package gateway
import (
"encoding/json"
"net/http"
"go.uber.org/zap"
)
func ErrorHandler(logger *zap.Logger) func(http.ResponseWriter, *http.Request, *RestErr) {
return func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request, restErr *RestErr) {
// 记录网关层错误(包含完整调用链)
logger.Error("request failed",
zap.String("correlation_id", restErr.CorrelationID),
zap.String("service", "gateway"),
zap.String("method", r.Method),
zap.String("path", r.URL.Path),
zap.Int("status", restErr.Status),
zap.String("title", restErr.Title),
zap.String("message", restErr.Message),
zap.String("error_msg", restErr.ErrMsg),
zap.String("error_code", restErr.Code),
zap.String("stack_trace", restErr.StackTrace),
)
// 构建客户端响应
response := map[string]interface{}{
"status": restErr.Status,
"title": restErr.Title,
"message": restErr.Message,
}
w.Header().Set("Content-Type", "application/json")
w.WriteHeader(restErr.Status)
json.NewEncoder(w).Encode(response)
}
}
5. 日志配置示例
package main
import (
"os"
"go.uber.org/zap"
"go.uber.org/zap/zapcore"
)
func NewLogger(serviceName string) *zap.Logger {
encoderConfig := zapcore.EncoderConfig{
TimeKey: "timestamp",
LevelKey: "level",
NameKey: "logger",
CallerKey: "caller",
MessageKey: "msg",
StacktraceKey: "stacktrace",
LineEnding: zapcore.DefaultLineEnding,
EncodeLevel: zapcore.LowercaseLevelEncoder,
EncodeTime: zapcore.ISO8601TimeEncoder,
EncodeDuration: zapcore.SecondsDurationEncoder,
EncodeCaller: zapcore.ShortCallerEncoder,
}
core := zapcore.NewCore(
zapcore.NewJSONEncoder(encoderConfig),
zapcore.AddSync(os.Stdout),
zap.InfoLevel,
)
logger := zap.New(core, zap.AddCaller())
logger = logger.With(zap.String("service", serviceName))
return logger
}
6. 使用示例
func main() {
// 初始化日志
logger := NewLogger("user-service")
defer logger.Sync()
// 创建路由
mux := http.NewServeMux()
// 应用中间件
handler := middleware.LoggingMiddleware(logger, "user-service")(mux)
// 启动服务
http.ListenAndServe(":8080", handler)
}
这个实现方案中,每个服务都记录自己的错误,同时通过 correlationID 关联所有相关日志。网关记录汇总的错误信息,而每个服务记录详细的上下文信息。这样既保持了错误调用链的完整性,又实现了分布式追踪的能力。






