Python中如何使用seq2seq模型在200行代码内实现聊天机器人
大佬的项目,实测环境 Python3,CPU 跑不动,GPU 走起。
Chatbot in 200 lines of code
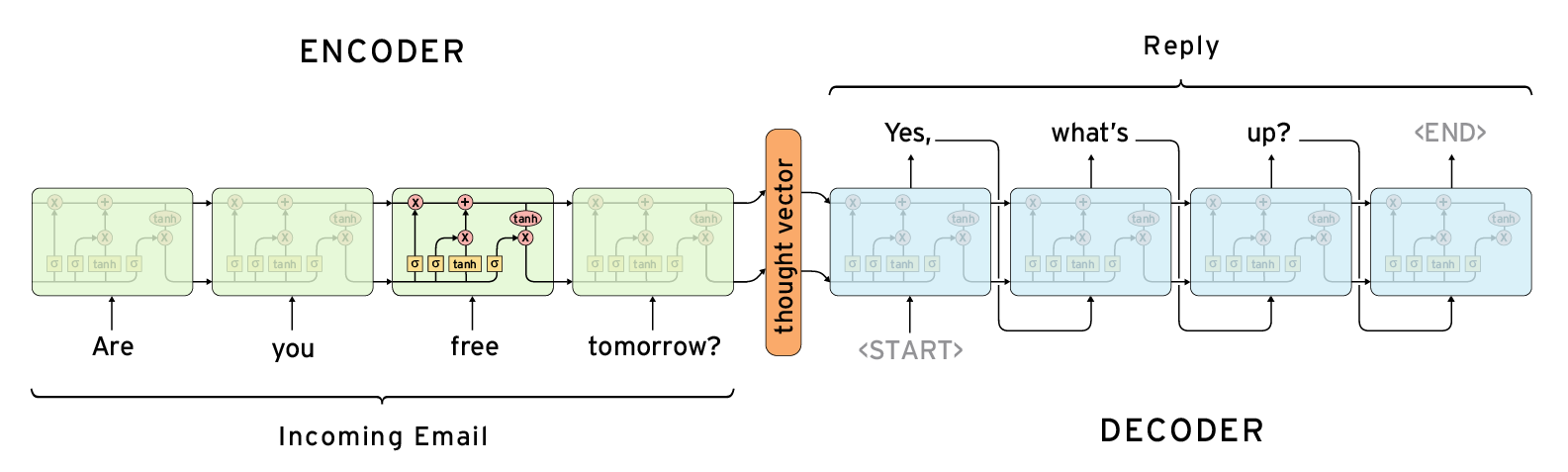
CPU 跑不动
github:https://github.com/zsdonghao/seq2seq-chatbot
更多英文,中文聊天机器人:
Python中如何使用seq2seq模型在200行代码内实现聊天机器人
5 回复
什么配置的机器跑得动
嘿,这个问题挺有意思的。用seq2seq在200行内实现聊天机器人确实有挑战,但核心逻辑可以做到。下面这个实现用了LSTM+attention,数据用简单的QA对。
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras.layers import LSTM, Dense, Embedding, Input, Attention, Concatenate
from tensorflow.keras.models import Model
import re
# 1. 数据准备
def create_dataset():
pairs = [
["hi", "hello"],
["how are you", "i'm fine"],
["what's your name", "i'm a bot"],
["bye", "goodbye"]
]
return pairs
# 2. 文本处理
def preprocess_text(text):
text = text.lower().strip()
text = re.sub(r"([.!?])", r" \1", text)
return text
# 3. 构建词汇表
def build_vocab(pairs):
words = set()
for pair in pairs:
for text in pair:
words.update(preprocess_text(text).split())
word2idx = {'<PAD>': 0, '<SOS>': 1, '<EOS>': 2}
idx2word = {0: '<PAD>', 1: '<SOS>', 2: '<EOS>'}
for i, word in enumerate(sorted(words), 3):
word2idx[word] = i
idx2word[i] = word
return word2idx, idx2word
# 4. 序列编码
def encode_sequence(sequence, word2idx, max_len):
encoded = [word2idx.get(word, 0) for word in sequence.split()]
encoded = [word2idx['<SOS>']] + encoded + [word2idx['<EOS>']]
padded = encoded[:max_len] + [0] * (max_len - len(encoded))
return padded
# 5. 构建模型
def build_seq2seq(vocab_size, embedding_dim=64, lstm_units=128, max_len=10):
# 编码器
encoder_inputs = Input(shape=(max_len,))
encoder_embedding = Embedding(vocab_size, embedding_dim)(encoder_inputs)
encoder_lstm = LSTM(lstm_units, return_sequences=True, return_state=True)
encoder_outputs, state_h, state_c = encoder_lstm(encoder_embedding)
encoder_states = [state_h, state_c]
# 解码器
decoder_inputs = Input(shape=(max_len,))
decoder_embedding = Embedding(vocab_size, embedding_dim)(decoder_inputs)
decoder_lstm = LSTM(lstm_units, return_sequences=True, return_state=True)
decoder_outputs, _, _ = decoder_lstm(decoder_embedding, initial_state=encoder_states)
# Attention机制
attention = Attention()([decoder_outputs, encoder_outputs])
decoder_concat = Concatenate(axis=-1)([decoder_outputs, attention])
# 输出层
decoder_dense = Dense(vocab_size, activation='softmax')
outputs = decoder_dense(decoder_concat)
model = Model([encoder_inputs, decoder_inputs], outputs)
model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy')
return model
# 6. 训练数据生成
def prepare_training_data(pairs, word2idx, max_len=10):
encoder_input_data = []
decoder_input_data = []
decoder_target_data = []
for input_text, target_text in pairs:
encoder_input = encode_sequence(preprocess_text(input_text), word2idx, max_len)
decoder_input = encode_sequence(preprocess_text(target_text), word2idx, max_len)
decoder_target = decoder_input[1:] + [0] # 偏移一位
encoder_input_data.append(encoder_input)
decoder_input_data.append(decoder_input)
decoder_target_data.append(decoder_target)
return (np.array(encoder_input_data),
np.array(decoder_input_data),
np.array(decoder_target_data))
# 7. 推理函数
def predict_response(input_text, model, word2idx, idx2word, max_len=10):
processed = preprocess_text(input_text)
encoder_input = encode_sequence(processed, word2idx, max_len)
encoder_input = np.array([encoder_input])
decoder_input = np.array([[word2idx['<SOS>']] + [0]*(max_len-1)])
response = []
for i in range(max_len):
predictions = model.predict([encoder_input, decoder_input], verbose=0)
predicted_id = np.argmax(predictions[0, i, :])
if predicted_id == word2idx['<EOS>']:
break
response.append(idx2word.get(predicted_id, ''))
if i < max_len-1:
decoder_input[0, i+1] = predicted_id
return ' '.join(response)
# 8. 主程序
def main():
# 准备数据
pairs = create_dataset()
word2idx, idx2word = build_vocab(pairs)
vocab_size = len(word2idx)
# 准备训练数据
encoder_input, decoder_input, decoder_target = prepare_training_data(pairs, word2idx)
# 构建模型
model = build_seq2seq(vocab_size)
# 训练
model.fit([encoder_input, decoder_input], decoder_target,
batch_size=2, epochs=100, verbose=0)
# 测试
test_input = "hi"
response = predict_response(test_input, model, word2idx, idx2word)
print(f"Input: {test_input}")
print(f"Response: {response}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
这个实现包含了seq2seq的核心组件:编码器-解码器结构、LSTM、attention机制。数据用简单的QA对,实际使用时需要更大的对话数据集。模型用teacher forcing训练,推理时用贪心解码。
要扩展功能的话,可以加beam search、更好的预处理、更大的数据集。不过200行内能跑起来的基础版本就是这样了。
总结:用LSTM+attention实现基础seq2seq聊天机器人。
CPU 不行,我 i7 32g 没鸟用。搞显卡你跑一跑试下吧。
RNN 嘛~
是的。






