HarmonyOS 鸿蒙Next中使用 Date 实现高精度毫秒级秒表
HarmonyOS 鸿蒙Next中使用 Date 实现高精度毫秒级秒表 如何使用 Date 实现高精度毫秒级秒表应用?以此来实现跑步计时?
3 回复
实现效果
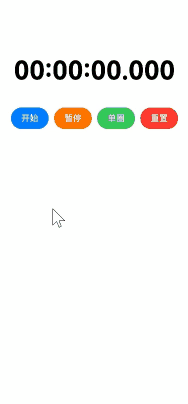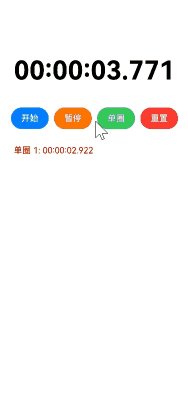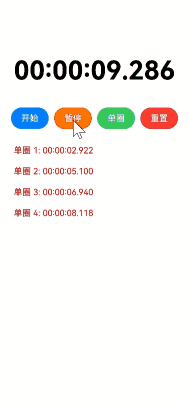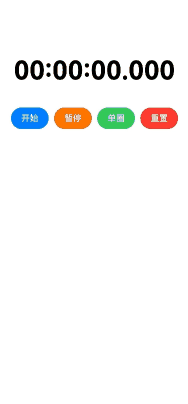
使用场景
跑步、游泳计圈、定时闹钟等
实现思路
第一步:创建一个HighPrecisionStopwatch管理方法类,维护一个 elapsedTime,定时器每次触发时,elapsedTime += 10。
第二步:通过lapTimes一个数组来 管理日期记录以此来实现圈数数据的记录。
完整实现代码
import { hilog } from '@kit.PerformanceAnalysisKit';
export class HighPrecisionStopwatch {
private startTime: number = 0;
private elapsedTime: number = 0;
private isRunning: boolean = false;
private lapTimes: number[] = [];
// 开始计时
start(): void {
if (!this.isRunning) {
this.startTime = Date.now() - this.elapsedTime;
this.isRunning = true;
hilog.info(0x0000, 'Stopwatch', '秒表开始计时');
}
}
// 暂停计时
pause(): void {
if (this.isRunning) {
this.elapsedTime = Date.now() - this.startTime;
this.isRunning = false;
hilog.info(0x0000, 'Stopwatch', `秒表暂停,当前时间: ${this.getFormattedTime()}`);
}
}
// 记录单圈时间
lap(): string {
if (this.isRunning) {
const currentTime = Date.now();
const lapTime = currentTime - this.startTime;
this.lapTimes.push(lapTime);
const formattedLap = this.formatMilliseconds(lapTime);
hilog.info(0x0000, 'Stopwatch', `单圈时间: ${formattedLap}`);
return formattedLap;
}
return '00:00:00.000';
}
// 重置秒表
reset(): void {
this.startTime = 0;
this.elapsedTime = 0;
this.isRunning = false;
this.lapTimes = [];
hilog.info(0x0000, 'Stopwatch', '秒表已重置');
}
// 获取当前时间(毫秒)
getCurrentTime(): number {
if (this.isRunning) {
return Date.now() - this.startTime;
}
return this.elapsedTime;
}
// 格式化时间显示
getFormattedTime(): string {
const time = this.getCurrentTime();
return this.formatMilliseconds(time);
}
// 毫秒格式化
private formatMilliseconds(ms: number): string {
const hours = Math.floor(ms / 3600000);
const minutes = Math.floor((ms % 3600000) / 60000);
const seconds = Math.floor((ms % 60000) / 1000);
const milliseconds = Math.floor(ms % 1000);
return `${hours.toString().padStart(2, '0')}:${
minutes.toString().padStart(2, '0')}:${
seconds.toString().padStart(2, '0')}.${
milliseconds.toString().padStart(3, '0')}`;
}
// 获取所有单圈时间
getAllLaps(): string[] {
return this.lapTimes.map((lap, index) =>
`单圈 ${index + 1}: ${this.formatMilliseconds(lap)}`
);
}
}
import { HighPrecisionStopwatch } from './HighPrecisionStopwatch';
@Entry
@Component
struct StopwatchPage {
private stopwatch: HighPrecisionStopwatch = new HighPrecisionStopwatch();
@State currentTime: string = '00:00:00.000';
@State laps: string[] = [];
private timerId: number = 0;
aboutToAppear(): void {
this.startTimer();
}
aboutToDisappear(): void {
this.stopTimer();
}
// 定时更新UI
startTimer(): void {
this.timerId = setInterval(() => {
if (this.stopwatch) {
this.currentTime = this.stopwatch.getFormattedTime();
}
}, 10);
}
stopTimer(): void {
if (this.timerId) {
clearInterval(this.timerId);
}
}
build() {
Column({ space: 0 }) {
// 时间显示
Text(this.currentTime)
.fontSize(48)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.fontColor(Color.Black)
.margin({ top: 50 })
// 控制按钮
Row({ space: 10 }) {
Button('开始')
.backgroundColor('#007DFF')
.onClick(() => {
this.stopwatch.start();
})
.width(70)
.height(40)
Button('暂停')
.backgroundColor('#FF7500')
.onClick(() => {
this.stopwatch.pause();
})
.width(70)
.height(40)
Button('单圈')
.backgroundColor('#34C759')
.onClick(() => {
this.stopwatch.lap()
this.laps = this.stopwatch.getAllLaps();
})
.width(70)
.height(40)
Button('重置')
.backgroundColor('#FF3B30')
.onClick(() => {
this.stopwatch.reset();
this.laps = [];
this.currentTime = '00:00:00.000';
})
.width(70)
.height(40)
}
.margin({ top: 40 })
// 单圈时间列表
List() {
ForEach(this.laps, (item: string) => {
ListItem() {
Text(item)
.fontColor(Color.Red)
.fontSize(16)
.padding(10)
}
})
}
.layoutWeight(1)
.width('100%')
.margin({ top: 20 })
}
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
.padding(20)
}
}
更多关于HarmonyOS 鸿蒙Next中使用 Date 实现高精度毫秒级秒表的实战系列教程也可以访问 https://www.itying.com/category-93-b0.html
在HarmonyOS Next中,使用Date实现高精度毫秒级秒表,可通过Date.now()获取当前时间戳。记录开始时间戳,结束时再次获取并计算差值,得到精确到毫秒的耗时。示例代码:
let startTime = Date.now();
// 执行操作...
let endTime = Date.now();
let elapsed = endTime - startTime; // 毫秒级耗时
注意:Date.now()基于系统时间,精度受系统限制。
在HarmonyOS Next中,使用Date类实现毫秒级秒表的核心是精确获取并计算时间差。虽然Date本身精度可达毫秒,但直接连续调用可能受系统调度影响。以下是关键实现方案:
- 核心计时逻辑:
// 记录起始时间戳
let startTime = new Date().getTime();
// 获取当前耗时
function getElapsedTime() {
let currentTime = new Date().getTime();
return currentTime - startTime; // 毫秒数
}
- 格式化显示(将毫秒转为分:秒.毫秒格式):
function formatTime(ms) {
let minutes = Math.floor(ms / 60000);
let seconds = Math.floor((ms % 60000) / 1000);
let milliseconds = ms % 1000;
return `${minutes.toString().padStart(2, '0')}:${seconds.toString().padStart(2, '0')}.${milliseconds.toString().padStart(3, '0')}`;
}
- 实现跑步计时功能:
- 使用
setInterval或requestAnimationFrame进行界面刷新 - 暂停功能:记录暂停时的累计时间,恢复时重新设置起始时间基准
- 圈数记录:将每次
getElapsedTime()的结果存入数组
- 注意事项:
Date的精度足够跑步计时使用(误差约±10ms)- 避免在每次渲染时创建新的
Date对象,应复用时间戳 - 考虑使用
performance.now()获取更高精度的时间戳(如果可用)
此方案能满足跑步计时的基础需求,实际开发中可结合ArkUI组件实现界面交互。






