Golang中使用CGO进行结构体传递的方法
Golang中使用CGO进行结构体传递的方法 存在一个C结构体如下:
struct dcmi_chip_info {
unsigned char chip_type[MAX_CHIP_NAME_LEN];
unsigned char chip_name[MAX_CHIP_NAME_LEN];
unsigned char chip_ver[MAX_CHIP_NAME_LEN];
unsigned int aicore_cnt;
};
以及一个C函数如下:
DCMIDLLEXPORT int dcmi_get_device_chip_info(int card_id, int device_id, struct dcmi_chip_info *chip_info);
然后我想使用CGO来获取结果:
ret = C.dcmi_get_device_id_in_card(card_id_list[card_id_index],
(*C.int)(unsafe.Pointer(&device_id_max)),
(*C.int)(unsafe.Pointer(&mcu_id)),
(*C.int)(unsafe.Pointer(&cpu_id)))
/*chip_info := C.struct_dcmi_chip_info{
chip_type: [C.MAX_CHIP_NAME_LEN]C.uchar{},
chip_name: [C.MAX_CHIP_NAME_LEN]C.uchar{},
chip_ver: [C.MAX_CHIP_NAME_LEN]C.uchar{},
}*/
chip_info := C.struct_dcmi_chip_info{}
ret = C.dcmi_get_device_chip_info(card_id_list[card_id_index], (C.int)(device_id_max), &chip_info)
fmt.Printf("%T\n", chip_info.chip_name)
fmt.Println("chip_type", chip_info.chip_name)
但我得到的结果是:
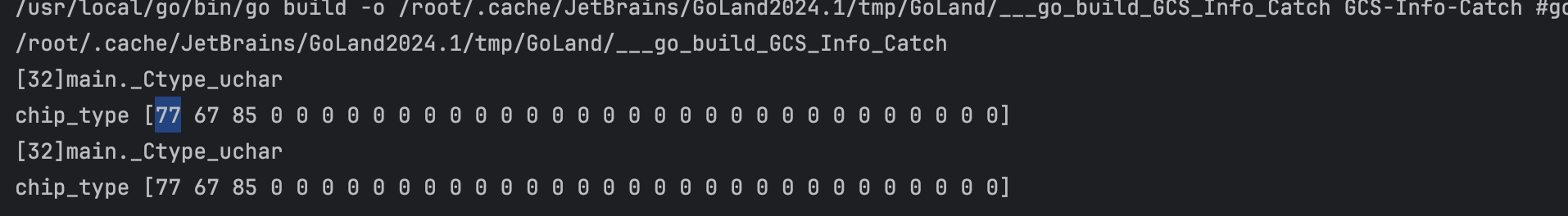
如何才能正确地进行传递?非常感谢。
更多关于Golang中使用CGO进行结构体传递的方法的实战教程也可以访问 https://www.itying.com/category-94-b0.html
谢谢,但错误是:
cannot use &chip_info.chip_name[0] (value of type *_Ctype_uchar) as *_Ctype_char value in argument to (_Cfunc_GoString)
这看起来像是一个以空字符结尾的字符串,内容是“MCU”。因此,你可能需要将
fmt.Println(“chip_type”, chip_info.chip_name)
替换为
fmt.Println(“chip_type”, C.GoString(&chip_info.chip_name[0]))
抱歉。*C.uchar 需要转换为 *C.char,因为 C.GoString 需要的是后者。Go 编译器不允许像 (*C.char)(&chip_info.chip_name[0]) 这样直接进行转换。
然而,任何指针类型都可以转换为 unsafe.Pointer,而 unsafe.Pointer 又可以转换为任何指针类型。
fmt.Println(C.GoString((*C.char)(unsafe.Pointer(&chip_info.chip_name[0]))))
括号太多了。分解开来,可以这样写。
chipNameUCharPointer := &chip_info.chip_name[0]
chipNameUnsafePointer := unsafe.Pointer(chipNameUCharPointer)
chipNameCharPointer := (*C.char)(chipNameUnsafePointer)
chipNameGoString := C.GoString(chipNameCharPointer)
fmt.Println(chipNameGoString)
在Go中通过CGO传递C结构体时,需要正确处理内存对齐和类型转换。以下是正确的实现方法:
package main
/*
#include <string.h>
#define MAX_CHIP_NAME_LEN 32
struct dcmi_chip_info {
unsigned char chip_type[MAX_CHIP_NAME_LEN];
unsigned char chip_name[MAX_CHIP_NAME_LEN];
unsigned char chip_ver[MAX_CHIP_NAME_LEN];
unsigned int aicore_cnt;
};
DCMIDLLEXPORT int dcmi_get_device_chip_info(int card_id, int device_id, struct dcmi_chip_info *chip_info);
*/
import "C"
import (
"fmt"
"unsafe"
)
func main() {
var card_id C.int = 0
var device_id C.int = 0
// 创建C结构体实例
var chip_info C.struct_dcmi_chip_info
// 调用C函数
ret := C.dcmi_get_device_chip_info(card_id, device_id, &chip_info)
if ret != 0 {
fmt.Printf("Error: %d\n", ret)
return
}
// 正确转换C字符串到Go字符串
chipType := C.GoString((*C.char)(unsafe.Pointer(&chip_info.chip_type[0])))
chipName := C.GoString((*C.char)(unsafe.Pointer(&chip_info.chip_name[0])))
chipVer := C.GoString((*C.char)(unsafe.Pointer(&chip_info.chip_ver[0])))
fmt.Printf("Chip Type: %s\n", chipType)
fmt.Printf("Chip Name: %s\n", chipName)
fmt.Printf("Chip Version: %s\n", chipVer)
fmt.Printf("AI Core Count: %d\n", chip_info.aicore_cnt)
}
如果C函数返回的字符串可能包含空字符,使用以下方法:
// 使用C.GoStringN处理可能包含空字符的字符串
chipType := C.GoStringN((*C.char)(unsafe.Pointer(&chip_info.chip_type[0])), C.MAX_CHIP_NAME_LEN)
chipName := C.GoStringN((*C.char)(unsafe.Pointer(&chip_info.chip_name[0])), C.MAX_CHIP_NAME_LEN)
chipVer := C.GoStringN((*C.char)(unsafe.Pointer(&chip_info.chip_ver[0])), C.MAX_CHIP_NAME_LEN)
// 去除尾部空字符
chipType = strings.TrimRight(chipType, "\x00")
chipName = strings.TrimRight(chipName, "\x00")
chipVer = strings.TrimRight(chipVer, "\x00")
对于需要预先分配内存的情况:
// 方法1:直接声明结构体变量
var chipInfo C.struct_dcmi_chip_info
// 方法2:使用new创建指针
chipInfoPtr := new(C.struct_dcmi_chip_info)
ret := C.dcmi_get_device_chip_info(card_id, device_id, chipInfoPtr)
// 方法3:使用malloc分配内存(需要手动释放)
chipInfoPtr := (*C.struct_dcmi_chip_info)(C.malloc(C.sizeof_struct_dcmi_chip_info))
defer C.free(unsafe.Pointer(chipInfoPtr))
// 清零内存
C.memset(unsafe.Pointer(chipInfoPtr), 0, C.sizeof_struct_dcmi_chip_info)
如果需要在Go中定义对应的结构体类型:
type ChipInfo struct {
ChipType [C.MAX_CHIP_NAME_LEN]byte
ChipName [C.MAX_CHIP_NAME_LEN]byte
ChipVer [C.MAX_CHIP_NAME_LEN]byte
AICoreCnt uint32
}
// 将C结构体转换为Go结构体
func convertToGoStruct(cInfo *C.struct_dcmi_chip_info) ChipInfo {
var goInfo ChipInfo
// 复制字节数组
copy(goInfo.ChipType[:], C.GoBytes(unsafe.Pointer(&cInfo.chip_type[0]), C.MAX_CHIP_NAME_LEN))
copy(goInfo.ChipName[:], C.GoBytes(unsafe.Pointer(&cInfo.chip_name[0]), C.MAX_CHIP_NAME_LEN))
copy(goInfo.ChipVer[:], C.GoBytes(unsafe.Pointer(&cInfo.chip_ver[0]), C.MAX_CHIP_NAME_LEN))
goInfo.AICoreCnt = uint32(cInfo.aicore_cnt)
return goInfo
}
确保在调用C函数前正确初始化参数,并使用正确的类型转换。问题中图片显示的输出异常通常是由于没有正确处理C字符串到Go字符串的转换导致的。






