Python中使用TensorFlow和Google物体识别API识别电影中的物体(以《生活大爆炸》为例)
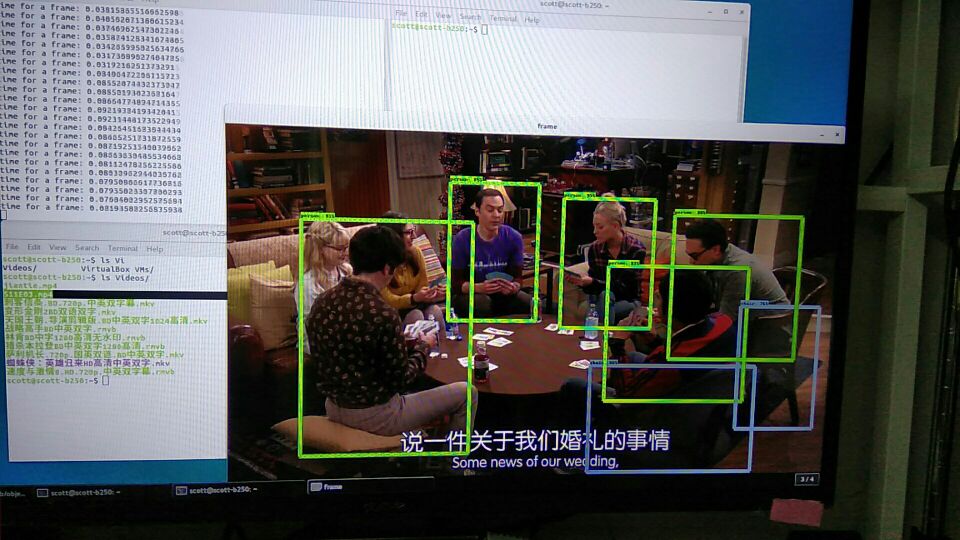
使用 google 物体识别的 api 来识别电影里面的物体。目前可以做到每秒 30 帧。
https://github.com/scotthuang1989/object_detection_with_tensorflow
分享自 TensorFlow QQ 群的彼岸:314148034
Target
detect people in a video or from camera. can choose what detection method we are using. Project Structure
From google
object label and detecion api data object_detection My module
myutil: help function object_detection_tf.py: main module for detecting object Usage
run following command python object_detection_tf.py -v /home/scott/Videos/S11E03.mp4
you need replace the video file with your choice Current Status
on my nvidia 1060 (6GB RAM ), the speed is ~25 frame per second, but gpu utilization is below 30%, I will use multiprocessing to speed up.
更多机器学习资源: http://www.tensorflownews.com/
Python中使用TensorFlow和Google物体识别API识别电影中的物体(以《生活大爆炸》为例)
我理解你想用TensorFlow结合Google的物体识别API来分析《生活大爆炸》剧集中的物体。不过这里有个概念需要澄清:Google物体识别API是云端服务,而TensorFlow是本地深度学习框架。通常我们会选择其中一种方案。
方案一:使用TensorFlow Object Detection API(本地部署) 这是更常见的做法,可以在本地视频帧上运行检测模型:
import cv2
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from object_detection.utils import label_map_util
from object_detection.utils import visualization_utils as vis_util
# 1. 加载预训练模型和标签
MODEL_NAME = 'ssd_mobilenet_v2_coco_2018_03_29'
PATH_TO_CKPT = f'{MODEL_NAME}/frozen_inference_graph.pb'
PATH_TO_LABELS = 'mscoco_label_map.pbtxt'
detection_graph = tf.Graph()
with detection_graph.as_default():
od_graph_def = tf.compat.v1.GraphDef()
with tf.io.gfile.GFile(PATH_TO_CKPT, 'rb') as fid:
od_graph_def.ParseFromString(fid.read())
tf.import_graph_def(od_graph_def, name='')
# 加载标签映射
category_index = label_map_util.create_category_index_from_labelmap(
PATH_TO_LABELS, use_display_name=True)
# 2. 处理视频帧
def detect_objects_in_video(video_path, output_path):
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(video_path)
frame_width = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH))
frame_height = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT))
fps = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS))
fourcc = cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*'mp4v')
out = cv2.VideoWriter(output_path, fourcc, fps,
(frame_width, frame_height))
with detection_graph.as_default():
with tf.compat.v1.Session(graph=detection_graph) as sess:
while cap.isOpened():
ret, frame = cap.read()
if not ret:
break
# 转换为RGB并扩展维度
image_np_expanded = np.expand_dims(
cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB), axis=0)
# 获取张量
image_tensor = detection_graph.get_tensor_by_name(
'image_tensor:0')
boxes = detection_graph.get_tensor_by_name(
'detection_boxes:0')
scores = detection_graph.get_tensor_by_name(
'detection_scores:0')
classes = detection_graph.get_tensor_by_name(
'detection_classes:0')
num_detections = detection_graph.get_tensor_by_name(
'num_detections:0')
# 运行检测
(boxes, scores, classes, num_detections) = sess.run(
[boxes, scores, classes, num_detections],
feed_dict={image_tensor: image_np_expanded})
# 可视化结果
vis_util.visualize_boxes_and_labels_on_image_array(
frame,
np.squeeze(boxes),
np.squeeze(classes).astype(np.int32),
np.squeeze(scores),
category_index,
use_normalized_coordinates=True,
line_thickness=2)
out.write(frame)
cap.release()
out.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
# 使用示例
detect_objects_in_video('big_bang_theory_episode.mp4', 'output_detected.mp4')
方案二:使用Google Cloud Vision API(云端服务) 如果坚持要用Google API,需要先安装客户端库并设置认证:
from google.cloud import videointelligence_v1 as vi
import io
def detect_objects_google_cloud(video_path):
client = vi.VideoIntelligenceServiceClient()
with io.open(video_path, 'rb') as f:
video_content = f.read()
features = [vi.Feature.OBJECT_TRACKING]
operation = client.annotate_video(
request={
"features": features,
"input_content": video_content
}
)
result = operation.result(timeout=180)
# 解析结果
for annotation in result.annotation_results[0].object_annotations:
print(f"物体: {annotation.entity.description}")
print(f"置信度: {annotation.confidence:.2%}")
for track in annotation.tracks:
print(f"出现时间: {track.segment.start_time_offset} - "
f"{track.segment.end_time_offset}")
实际建议:
- 对于连续视频分析,TensorFlow本地方案更合适
- 需要先下载预训练模型(如COCO数据集训练的模型)
- 处理电视剧集时考虑采样关键帧以提高效率
用TensorFlow Object Detection API更实际。






