Golang高效ORM框架GDAO:提升开发效率与性能的轻量级解决方案
Golang高效ORM框架GDAO:提升开发效率与性能的轻量级解决方案
GDAO —— Go 持久化框架
一个简化的 Go 持久化框架,具有更高的生产力和性能
为 Go 应用结合 Hibernate 的抽象性与 MyBatis 的灵活性
简介
Gdao 是一个创新的持久层解决方案,旨在减少编码工作量、提高生产力、增强性能、支持多数据源集成以及促进数据读写分离。通过利用 Gdao,开发者可以将持久层所需的代码量减少 30% 到 50%,建立统一的编码标准,减少错误,并确保更易于维护和扩展。
Gdao 对于 Go 而言,相当于 Hibernate + MyBatis 对于 Java。Gdao 框架结合了 Hibernate 的抽象性和 MyBatis 的灵活性,并解决了它们各自在 ORM 框架上长期使用存在的痛点。关于 Hibernate 和 MyBatis 之间的痛点,请参考 jdao 使用文档。
- GDAO 的设计结构既简洁又严谨,所有接口和函数的命名都具有描述性,其用途一目了然。
- 即使您是 GDAO 的新手,也能快速理解其代码和相关的数据行为。
- GDAO 的简洁性确保您能在几分钟内掌握其用法。
Github
官方网站
文档
演示
主要特性
- 代码生成:使用 Gdao 代码生成工具为数据库表创建标准化的实体类,类似于 Thrift/Protobuf。
- 高效序列化:表的标准化实体类实现了高效的序列化和反序列化,性能更高,数据量更小。
- 支持数据读写分离:Gdao 支持绑定多个数据源和数据读写分离,允许将数据源绑定到表、类、映射接口和其他属性。
- 支持数据缓存:Gdao 支持数据缓存,并详细控制缓存数据的生命周期和回收功能。
- 广泛的兼容性:Gdao 理论上支持所有实现了 Go 数据库驱动接口的数据库。
- 高级功能:支持事务、存储过程、批处理和其他数据库操作。
- 支持 SQL 与程序分离:类似于 mybatis,gdao 支持通过 xml 文件编写 sql 映射调用。这是少数支持 SQL 与程序分离的 ORM 特性之一,但功能非常强大。
GDAO 的创新性 ORM 解决方案
Gdao 是 Jdao 的兄弟框架,共享其设计模式。
- 用于单表 CRUD 操作的标准化映射实体类:超过 90% 的单表操作可以通过实体类执行。这些 CRUD 操作通常不涉及复杂的 SQL 优化,可以通过实体类生成,以减少错误率并简化维护。 通过利用缓存和读写分离等机制,持久层变得更加高效和便捷。标准化实体类的数据操作格式不仅仅是对象函数的拼接,更类似于 SQL 操作,更容易理解。
- 复杂 SQL 的执行:复杂的 SQL,特别是多表连接,通常需要根据表结构和索引属性进行优化。使用对象来拼接复杂的 SQL 会增加理解的难度,并可能导致开发者不知道最终执行的 SQL,从而增加风险和维护难度。 因此,Gdao 建议使用 Gdao 的 CRUD 接口来处理复杂的 SQL 问题。Gdao 提供了灵活的数据转换和高效的对象映射实现,避免了过度使用反射等耗时操作。
- SQL 映射文件:对于复杂的 SQL 操作,Gdao 提供了相应的 CRUD 接口。它还支持通过 XML 配置映射 SQL 以进行接口调用,类似于 Java 的 MyBatis ORM 框架。然而,与 MyBatis 需要映射所有 SQL 操作不同,Gdao 提供了完整的 SQL 映射接口,但建议仅映射复杂的 SQL 或标准化实体类无法完成的操作。 Gdao 的 SQL 配置文件参考了 MyBatis 的配置文件格式,实现了一个新的解析器,允许更高的灵活性和对配置参数类型的容忍度(请参阅文档)。
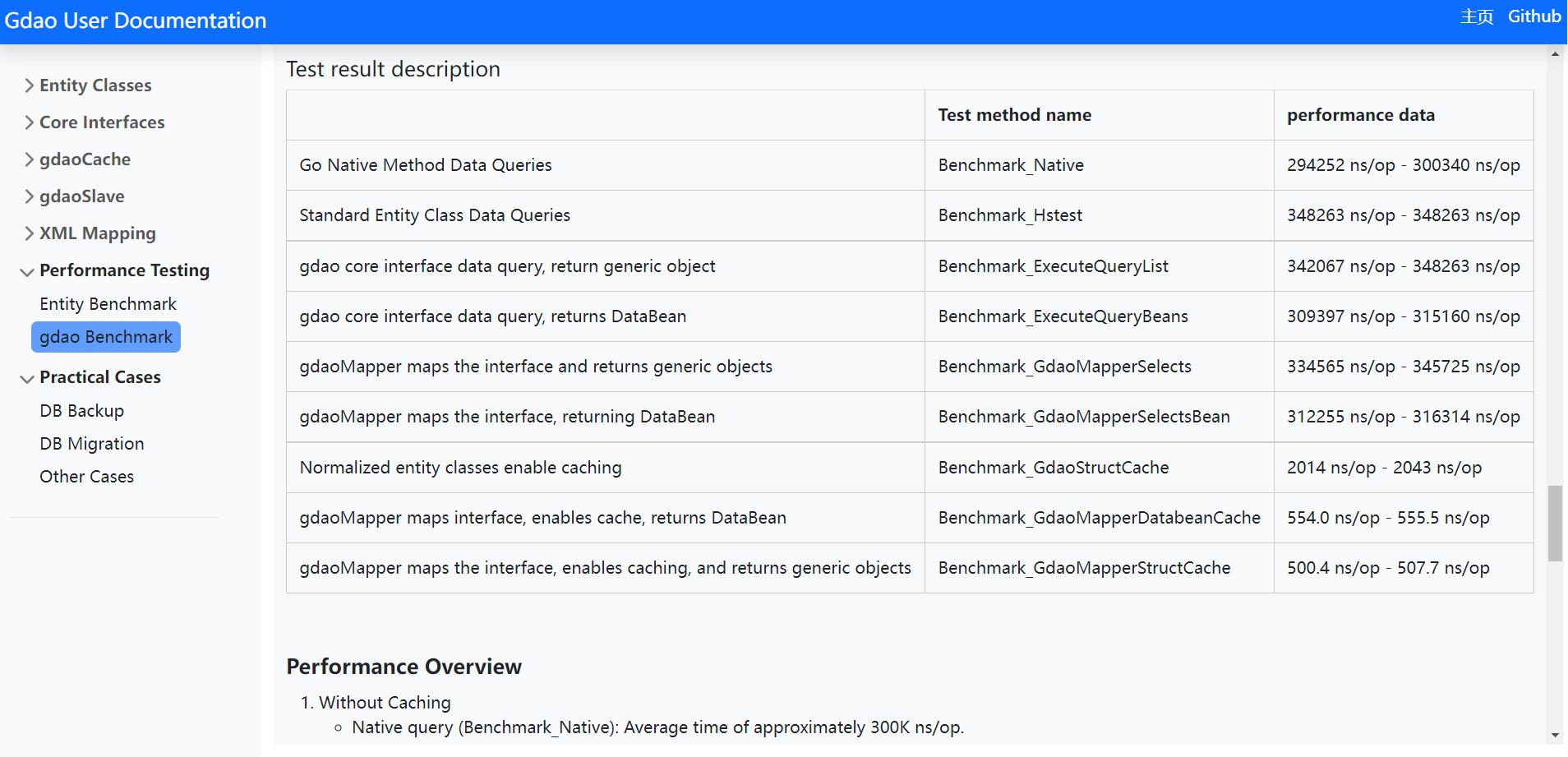
核心组件
1. gdao
主要核心入口点,提供以下功能:
- 设置数据源
- SQL CRUD 函数
2. gdaoCache
缓存入口点,支持以下功能:
- 绑定或解绑包、类和其他属性以启用或禁用查询缓存
3. gdaoSlave
读写分离操作入口点,支持以下功能:
- 绑定或解绑包、类和其他属性以启用或禁用读写分离
4. gdaoMapper
通过调用 Gdao 的 CRUD 接口直接执行 SQL,或使用 XML 文件映射并通过 Mapper Id 通过 gdaoMapper 调用
快速入门
1. 安装
# 导入 gdao
go get github.com/donnie4w/gdao
2. 配置数据源
gdao.Init(mysqlDB, gdao.MYSQL)
// gdao.MYSQL 是数据库类型
3. 生成表实体类
使用 Gdao 代码生成工具为数据库表生成标准化的实体类。
4. 实体类操作
// 设置数据源
gdao.Init(mysqlDB, gdao.MYSQL)
// 读取
hs := dao.NewHstest()
hs.Where(hs.Id.EQ(10))
h, _ := hs.Select(hs.Id, hs.Value, hs.Rowname)
logger.Debug(h)
//[DEBUG][SELECT ONE][ select id, value, rowname from hstest where id=?][10]
// 更新
hs := dao.NewHstest()
hs.SetRowname("hello10")
hs.Where(hs.Id.EQ(10))
hs.Update()
//[DEBUG][UPDATE][update hstest set rowname=? where id=?][hello10 10]
// 删除
hs := dao.NewHstest()
hs.Where(hs.Id.EQ(10))
hs.Delete()
//[DEBUG][DELETE][delete from hstest where id=?][10]
// 插入
hs := dao.NewHstest()
hs.SetValue("hello123")
hs.SetLevel(12345)
hs.SetBody([]byte("hello"))
hs.SetRowname("hello1234")
hs.SetUpdatetime(time.Now())
hs.SetFloa(123456)
hs.SetAge(123)
hs.Insert()
//[DEBUG][INSERT][insert into hstest(floa, age, value, level, body, rowname, updatetime) values(?,?,?,?,?,?,?)][123456 123 hello123 12345 [104 101 108 108 111] hello1234 2024-07-17 19:36:44]
5. gdao api
CRUD 操作
// 查询,返回单条记录
bean, _ := gdao.ExecuteQueryBean("select id, value, rowname from hstest where id=?", 10)
logger.Debug(bean)
// 插入
i := gdao.ExecuteUpdate("insert into hstest2(rowname, value) values(?,?)", "helloWorld", "123456789")
// 更新
i := gdao.ExecuteUpdate("update hstest set value=? where id=1", "hello")
// 删除
i := gdao.ExecuteUpdate("delete from hstest where id = ?", 1)
6. gdaoCache
配置缓存
// 绑定 Hstest 以启用缓存,缓存过期时间设置为 300 秒
gdaoCache.BindClass[dao.Hstest]()
// 首次查询 Hstest 并根据条件设置数据缓存
hs := dao.NewHstest()
hs.Where((hs.Id.Between(0, 2)).Or(hs.Id.Between(10, 15)))
hs.Limit(3)
hs.Selects()
// 对于相同的条件,数据直接从缓存中获取
hs = dao.NewHstest()
hs.Where((hs.Id.Between(0, 2)).Or(hs.Id.Between(10, 15)))
hs.Limit(3)
hs.Selects()
执行结果
[DEBUG][SELECT LIST][ select id, age, rowname, value, updatetime, body, floa, level from hstest where id between ? and ? or (id between ? and ?) LIMIT ? ][0 2 10 15 3]
[DEBUG][SET CACHE][ select id, age, rowname, value, updatetime, body, floa, level from hstest where id between ? and ? or (id between ? and ?) LIMIT ? ][0 2 10 15 3]
[DEBUG][SELECT LIST][ select id, age, rowname, value, updatetime, body, floa, level from hstest where id between ? and ? or (id between ? and ?) LIMIT ? ][0 2 10 15 3]
[DEBUG][GET CACHE][ select id, age, rowname, value, updatetime, body, floa, level from hstest where id between ? and ? or (id between ? and ?) LIMIT ? ][0 2 10 15 3]
7. gdaoSlave
读写分离
// 设置从数据源:mysql
mysqlDB, _ := getDataSource("mysql.json")
gdaoSlave.BindClass[dao.Hstest](mysqlDB, gdao.MYSQL)
// 这里主数据库是 sqlite,从数据库是 mysql。Hstest 从 mysql 读取数据
hs := dao.NewHstest()
hs.Where(hs.Id.Between(0, 5))
hs.OrderBy(hs.Id.Desc())
hs.Limit(3)
hs.Selects()
8. gdaoMapper
使用 XML 映射 SQL
<!-- MyBatis 风格的 XML 配置文件 -->
<mapper namespace="user">
<select id="selectHstest1" parameterType="int64" resultType="hstest1">
SELECT * FROM hstest1 ORDER BY id DESC LIMIT #{limit}
</select>
</mapper>
// 设置数据源
if db, err := getDataSource("sqlite.json"); err == nil {
gdao.Init(db, gdao.SQLITE)
gdao.SetLogger(true)
}
// 读取并解析 XML 配置
hs1, _ := gdaoMapper.Select[dao.Hstest1]("user.selectHstest1", 1)
fmt.Println(hs1)
id, _ := gdaoMapper.Select[int64]("user.selectHstest1", 1)
fmt.Println(*id)
执行结果
[DEBUG][Mapper Id] user.selectHstest1
SELECTONE SQL[SELECT * FROM hstest1 ORDER BY id DESC LIMIT ?]ARGS[1]
Id:52, Rowname:rowname>>>123456789, Value:[104 101 108 108 111 32 103 100 97 111], Goto:[49 50 51 52 53]
[DEBUG][Mapper Id] user.selectHstest1
SELECTONE SQL[SELECT * FROM hstest1 ORDER BY id DESC LIMIT ?]ARGS[1]
52
更多关于Golang高效ORM框架GDAO:提升开发效率与性能的轻量级解决方案的实战教程也可以访问 https://www.itying.com/category-94-b0.html
这是一个用于 Gdao 的测试演示程序,包含一个打包好的 SQLite 测试数据库文件 hstest.db,其中已生成数据。该演示程序可以直接运行。除了测试读写分离或多数据源操作外,其他测试默认操作 hstest.db 数据库中的数据,可以直接运行以查看数据操作结果。
更多关于Golang高效ORM框架GDAO:提升开发效率与性能的轻量级解决方案的实战系列教程也可以访问 https://www.itying.com/category-94-b0.html
GDAO框架确实为Go语言开发者提供了一个兼具Hibernate抽象性和MyBatis灵活性的持久层解决方案。以下通过具体示例展示其核心功能:
1. 数据源配置与实体类生成
// 多数据源配置示例
func initDataSources() {
// 主数据源(MySQL)
masterDB, _ := sql.Open("mysql", "user:pass@tcp(127.0.0.1:3306)/db")
gdao.Init(masterDB, gdao.MYSQL)
// 从数据源(PostgreSQL)
slaveDB, _ := sql.Open("postgres", "host=localhost port=5432 user=postgres password=secret dbname=test sslmode=disable")
gdaoSlave.BindClass[dao.User](slaveDB, gdao.POSTGRESQL)
}
// 生成的实体类使用示例
user := dao.NewUser()
user.SetUsername("john_doe")
user.SetEmail("john@example.com")
user.SetCreatedAt(time.Now())
2. 链式查询与条件组合
// 复杂查询条件构建
func queryUsers() {
user := dao.NewUser()
// 多条件组合查询
user.Where(
user.Age.GT(18).
And(user.Status.EQ(1)).
Or(user.Email.Like("%@gmail.com"))
)
// 排序和分页
user.OrderBy(user.CreatedAt.Desc())
user.Limit(10).Offset(0)
// 选择特定字段
results, err := user.Selects(user.ID, user.Username, user.Email)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
for _, u := range results {
fmt.Printf("User: %+v\n", u)
}
}
3. 事务处理示例
func transferFunds(fromID, toID int64, amount float64) error {
// 开启事务
tx, err := gdao.Begin()
if err != nil {
return err
}
defer func() {
if err != nil {
tx.Rollback()
}
}()
// 扣款操作
accountFrom := dao.NewAccount()
accountFrom.SetBalance(accountFrom.Balance.Sub(amount))
accountFrom.Where(accountFrom.ID.EQ(fromID))
if _, err := accountFrom.Update(); err != nil {
return err
}
// 存款操作
accountTo := dao.NewAccount()
accountTo.SetBalance(accountTo.Balance.Add(amount))
accountTo.Where(accountTo.ID.EQ(toID))
if _, err := accountTo.Update(); err != nil {
return err
}
// 提交事务
return tx.Commit()
}
4. 批量操作优化
func batchInsertUsers(users []*dao.User) {
// 开启批量模式
gdao.StartBatch()
defer gdao.EndBatch()
for _, user := range users {
user.Insert()
}
// 执行批量提交
if err := gdao.ExecuteBatch(); err != nil {
log.Printf("Batch insert failed: %v", err)
}
}
5. 自定义SQL映射与动态查询
<!-- user_mapper.xml -->
<mapper namespace="user">
<select id="searchUsers" parameterType="map" resultType="user">
SELECT * FROM users
WHERE 1=1
<if test="username != null">
AND username LIKE CONCAT('%', #{username}, '%')
</if>
<if test="minAge != null">
AND age >= #{minAge}
</if>
<if test="maxAge != null">
AND age <= #{maxAge}
</if>
ORDER BY ${orderBy} ${orderDir}
LIMIT #{limit} OFFSET #{offset}
</select>
</mapper>
// Go代码调用
func searchUsers(params map[string]interface{}) {
results, err := gdaoMapper.Select[[]dao.User](
"user.searchUsers",
params,
)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
for _, user := range results {
fmt.Printf("Found user: %s\n", user.GetUsername())
}
}
6. 缓存策略配置
func setupCache() {
// 类级别缓存,过期时间300秒
gdaoCache.BindClass[dao.Product](300)
// 方法级别缓存
gdaoCache.BindMethod("GetHotProducts", 60)
// 自定义缓存键生成
gdaoCache.SetKeyGenerator(func(sql string, args ...interface{}) string {
hash := sha256.Sum256([]byte(fmt.Sprintf("%s%v", sql, args)))
return hex.EncodeToString(hash[:])
})
}
7. 读写分离实战
func handleUserRequest() {
user := dao.NewUser()
// 写操作走主库
user.SetUsername("new_user")
user.Insert() // 自动使用主库
// 读操作走从库
user.Where(user.ID.EQ(1))
user.SelectOne() // 自动使用从库
// 强制使用主库读取
gdaoSlave.UnbindClass[dao.User]()
user.SelectOne() // 使用主库
gdaoSlave.BindClass[dao.User](slaveDB, gdao.MYSQL)
}
8. 存储过程调用
func callStoredProcedure() {
// 调用存储过程并获取结果集
results, err := gdao.ExecuteQuery(
"CALL GetUserStatistics(?, ?)",
"2024-01-01",
"2024-12-31",
)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
// 处理结果
for results.Next() {
var stat struct {
Month string
NewUsers int
Active int
}
results.Scan(&stat.Month, &stat.NewUsers, &stat.Active)
fmt.Printf("%s: %d new users, %d active\n",
stat.Month, stat.NewUsers, stat.Active)
}
}
9. 性能监控集成
func withMetrics() {
// 添加SQL执行监控
gdao.SetInterceptor(func(sql string, args []interface{}, duration time.Duration) {
metrics.RecordQuery(sql, duration)
if duration > 100*time.Millisecond {
log.Printf("Slow query detected: %s (took %v)", sql, duration)
}
})
// 执行查询
product := dao.NewProduct()
product.Where(product.Price.GT(100))
product.Selects()
}
这些示例展示了GDAO框架在实际生产环境中的应用方式。框架通过代码生成减少重复工作,通过缓存和读写分离提升性能,同时保持SQL的透明性和灵活性。实体类的链式API设计使得查询构建直观,而XML映射支持则解决了复杂SQL的管理问题。






