HarmonyOS鸿蒙Next中后端返回的富文本如何根据alias-label匹配渲染对应组件
HarmonyOS鸿蒙Next中后端返回的富文本如何根据alias-label匹配渲染对应组件
后端返回的一个富文本,然后在页面渲染的时候回根据alias-label 去匹配是什么组件 假如说这个值等于video的时候 那么在对应的位置渲染一个video组件这样的一个功能该如何实现
更多关于HarmonyOS鸿蒙Next中后端返回的富文本如何根据alias-label匹配渲染对应组件的实战教程也可以访问 https://www.itying.com/category-93-b0.html
后端返回了富文本内容这个内容都是有规则的< img style="" draggable=“false” src="/storage/A4AE61E66CD26E888F4592833D56497F" duration= “291000” width=“233” audio-src="/storage/D12C09216463D988592B30CBAC5C986F" source-url="/storage/D12C09216463D988592B30CBAC 5C986F" alias-label=“audio” name=“大青蛙夫为妻纲.mp3” height=“auto”> 好比这个标签,虽然返回的是img但是实际上根据alias-label=“audio” 这个来判断他是一个audio那么就将返回的富文本用下面的办法进行处理一下
export interface TextItem {
type: 'text';
value: string;
}
export interface ImageItem {
type: 'image';
src: string;
}
export interface VideoItem {
type: 'video';
src: string;
poster?: string;
duration?: number;
}
export interface PdfItem {
type: 'pdf';
src: string;
}
export interface AudioItem {
type: 'audio';
src: string;
duration?: number;
}
export type ContentItem = TextItem | ImageItem | VideoItem | PdfItem | AudioItem;
export function parseRichTextAsync(html: string): Promise<ContentItem[]> {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
const result: ContentItem[] = [];
// 匹配 iframe、img、p 标签
const regex = /(<iframe[^>]*pdfiframe="true"[^>]*>[\s\S]*?<\/iframe>|<img[^>]*>|<p[^>]*>[\s\S]*?<\/p>)/gi;
let lastIndex = 0;
let match: RegExpExecArray | null;
while ((match = regex.exec(html)) !== null) {
const tag = match[0];
const index = match.index;
// 标签前的纯文本
if (index > lastIndex) {
const text = html.substring(lastIndex, index).trim();
if (text) result.push({ type: 'text', value: text });
}
// 处理 iframe → pdf
if (tag.startsWith('<iframe')) {
const srcMatch = tag.match(/_src="([^"]+)"/i);
if (srcMatch) result.push({ type: 'pdf', src: srcMatch[1] });
// iframe 内部文字或者后面紧跟文字
// 去掉 iframe 标签,再生成 text
const textAfterIframe = tag.replace(/<iframe[^>]*>[\s\S]*?<\/iframe>/i, '').trim();
if (textAfterIframe) result.push({ type: 'text', value: textAfterIframe });
}
// 处理 img
else if (tag.startsWith('<img')) {
const aliasMatch = tag.match(/alias-label="([^"]+)"/i);
const alias = aliasMatch ? aliasMatch[1] : '';
const srcMatch = tag.match(/src="([^"]+)"/i);
const src = srcMatch ? srcMatch[1] : '';
const durationMatch = tag.match(/duration="([^"]+)"/i);
const duration = durationMatch ? Number(durationMatch[1]) : undefined;
const posterMatch = tag.match(/video-pic="([^"]+)"/i);
const poster = posterMatch ? posterMatch[1] : undefined;
if (alias === 'video') result.push({ type: 'video', src, poster, duration });
else if (alias === 'audio') result.push({ type: 'audio', src, duration });
else result.push({ type: 'image', src });
}
// 处理 p 标签 → text(保留 span 样式)
else if (tag.startsWith('<p')) {
let inner = tag.replace(/^<p[^>]*>/i, '').replace(/<\/p>$/i, '').trim();
// 如果 p 内有 img / iframe,再用同样正则递归解析
const innerMatches = inner.match(/<iframe[^>]*pdfiframe="true"[^>]*>[\s\S]*?<\/iframe>|<img[^>]*>/gi);
if (innerMatches) {
let startIdx = 0;
innerMatches.forEach((m) => {
const idx = inner.indexOf(m, startIdx);
if (idx > startIdx) {
const textPart = inner.substring(startIdx, idx).trim();
if (textPart) result.push({ type: 'text', value: textPart });
}
// 解析 img / iframe
if (m.startsWith('<iframe')) {
const srcMatch = m.match(/_src="([^"]+)"/i);
if (srcMatch) result.push({ type: 'pdf', src: srcMatch[1] });
} else if (m.startsWith('<img')) {
const aliasMatch = m.match(/alias-label="([^"]+)"/i);
const alias = aliasMatch ? aliasMatch[1] : '';
const srcMatch = m.match(/src="([^"]+)"/i);
const src = srcMatch ? srcMatch[1] : '';
const durationMatch = m.match(/duration="([^"]+)"/i);
const duration = durationMatch ? Number(durationMatch[1]) : undefined;
const posterMatch = m.match(/video-pic="([^"]+)"/i);
const poster = posterMatch ? posterMatch[1] : undefined;
if (alias === 'video') result.push({ type: 'video', src, poster, duration });
else if (alias === 'audio') result.push({ type: 'audio', src, duration });
else result.push({ type: 'image', src });
}
startIdx = idx + m.length;
});
// 剩余文字
const remainingText = inner.substring(startIdx).trim();
if (remainingText) result.push({ type: 'text', value: remainingText });
} else if (inner) {
result.push({ type: 'text', value: inner });
}
}
lastIndex = regex.lastIndex;
}
// 标签之后剩余文本
if (lastIndex < html.length) {
const text = html.substring(lastIndex).trim();
if (text) result.push({ type: 'text', value: text });
}
resolve(result);
});
}
处理之后就会返回:
 这样的数据
然后进行判断处理
然后在页面中逐一进行渲染
这样的数据
然后进行判断处理
然后在页面中逐一进行渲染
更多关于HarmonyOS鸿蒙Next中后端返回的富文本如何根据alias-label匹配渲染对应组件的实战系列教程也可以访问 https://www.itying.com/category-93-b0.html
为啥不使用三方库 进行富文本适配, 或者接入 arkWeb 来实现
在HarmonyOS Next中,后端返回的富文本可通过自定义组件结合@Component和@Builder实现alias-label匹配渲染。使用ForEach遍历富文本数据,根据alias值动态创建对应组件。通过@State管理数据,@Builder定义组件映射逻辑,实现条件渲染。
在HarmonyOS Next中实现根据alias-label匹配渲染对应组件的功能,可以通过以下步骤完成:
-
解析富文本:使用
XmlPullParser或第三方HTML解析库解析后端返回的富文本字符串,提取其中的自定义属性(如alias-label)和组件所需参数(如src、duration等)。 -
定义组件映射:创建一个映射关系,将
alias-label的值与对应的ArkUI组件关联。例如:const componentMap = { 'audio': AudioComponent, // 自定义音频组件 'video': VideoComponent, // 自定义视频组件 // 其他alias-label对应的组件 }; -
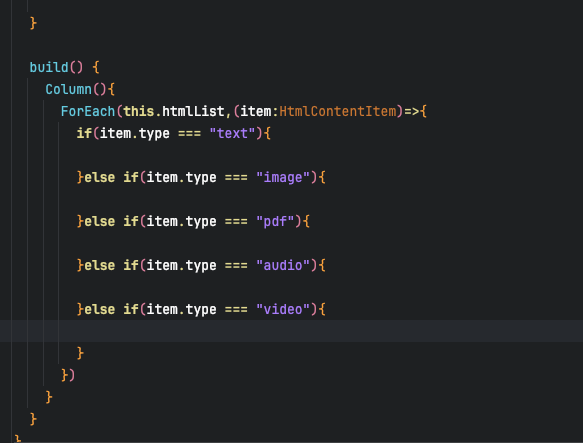
动态渲染组件:在ArkUI的声明式UI中,使用条件渲染或动态组件加载。例如,通过
if语句或ForEach遍历解析后的数据,根据alias-label选择组件:[@Component](/user/Component) struct RichTextView { // 解析后的数据数组,包含alias-label和组件属性 @State elements: Array<RichTextElement> = []; build() { Column() { ForEach(this.elements, (item: RichTextElement) => { // 根据alias-label动态渲染组件 if (item.aliasLabel === 'audio') { AudioComponent({ src: item.src, duration: item.duration }) } else if (item.aliasLabel === 'video') { VideoComponent({ src: item.src }) } else { // 默认文本渲染 Text(item.content) } }) } } } -
封装自定义组件:为
audio、video等类型创建可复用的ArkUI自定义组件,接收解析后的属性参数(如src),并调用HarmonyOS的多媒体API(如<Video>或<Audio>组件)实现功能。 -
处理嵌套结构:如果富文本包含复杂嵌套(如多个标签混合),需递归解析并维护UI层级,确保组件渲染顺序正确。
注意事项:
- 富文本解析需注意安全性,避免XSS攻击,建议对内容进行过滤或转义。
- 多媒体组件需处理资源加载状态(如加载中、错误回调)。
- 性能优化:对于长富文本,考虑分片渲染或懒加载。
此方法通过动态解析和条件渲染,实现了基于alias-label的组件匹配,可灵活扩展其他组件类型。






