HarmonyOS鸿蒙Next中云函数怎么使用postman调试?
HarmonyOS鸿蒙Next中云函数怎么使用postman调试? 在开发鸿蒙app中写了云函数,用DevEco Studio 中的插件可以正常调试;但是接口比较多,有上下依赖;
想尝试使用可以关联、编程的类似postman api接口工具调试,但是尝试过很多次依然无法调用;
1 比如我构建的云函数为 用户业务相关的,统一的handler;
export class userService {
async handler(event: any, context?: any): Promise<any> {
try {
let request = {
method: event.httpMethod || event.method || 'GET',
path: event.path || event.requestContext?.path || '',
body: parseBody(event.body),
query: event.queryStringParameters || event.query || {},
headers: event.headers || {}
};
const method = request.method;
const path = request.path;
const body = request.body;
const query = request.query;
// 路由分发
if (path.includes('/login') && method === 'POST') {
return await login(body);
} else if (path.includes('/register') && method === 'POST') {
return await register(body);
} else if (path.includes('/huawei-login') && method === 'POST') {
return await huaweiLogin(body);
} else if (path.includes('/profile') && method === 'GET') {
return await getUserInfo(request);
} else if (path.includes('/profile') && method === 'PUT') {
return await updateUserInfo(request, body);
} else if (path.includes('/location') && method === 'PUT') {
return await updateLocation(request, body);
} else {
return errorResponse(404, `接口不存在: ${method} ${path}`);
}
} catch (error: any) {
console.error('[user-service] Error:', error);
return errorResponse(500, error.message || '服务器错误');
}
}
}
2 启动服务,查看日志和 ide自带的插件调试,可以正常response;
“E:\Program Files\Huawei\DevEco Studio\tools\node\node.exe” --inspect-brk --inspect-port=9229 wrapper.js 18090 envs.json
Debugger listening on ws://127.0.0.1:9229/9570552e-cc59-44e0-8e8c-2d8f2f142863
For help, see: https://nodejs.org/en/docs/inspector
Debugger attached.
[2025-11-10T14:03:26.778] [INFO] function-runtime - HTTP server created successfully, with the listening port: 18090.
[2025-11-10T14:03:27.622] [INFO] function-runtime - Function URI: http://localhost:18090/user-service/invoke.
使用 DevEco Studio 请求数据可以正常返回response;
3 使用postman请求均失败,尝试多种方式、组合。
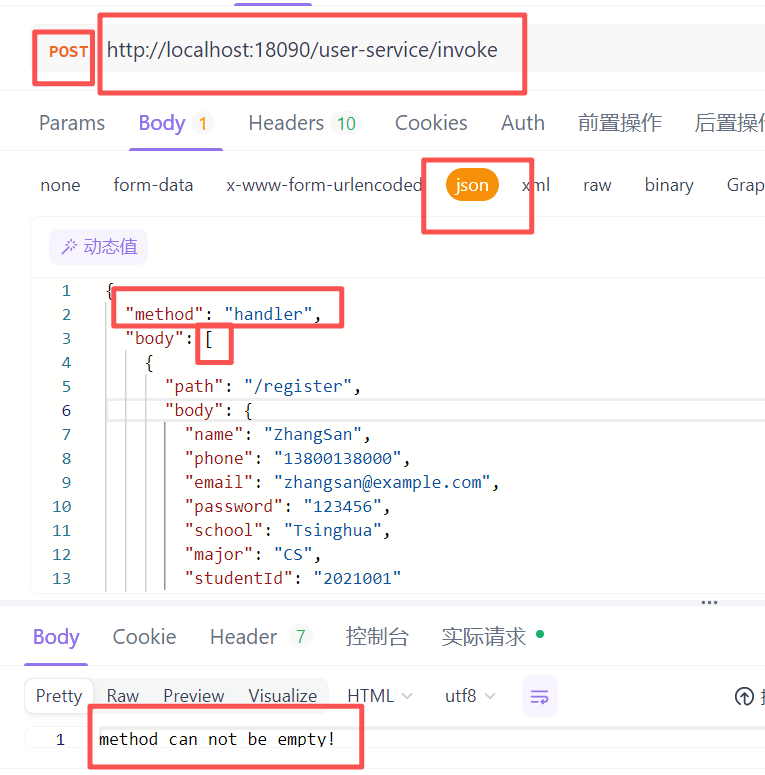
请问如何用postman构建请求url path和params呢?
更多关于HarmonyOS鸿蒙Next中云函数怎么使用postman调试?的实战教程也可以访问 https://www.itying.com/category-93-b0.html
输入示例如下:
{
"body": {
"method": "handler",
"params": [
{
"name":"xxxx",
"phone":"xxxx",
}
]
}
}
更多关于HarmonyOS鸿蒙Next中云函数怎么使用postman调试?的实战系列教程也可以访问 https://www.itying.com/category-93-b0.html
如何查看Linux系统版本信息
一、查看Linux内核版本
1. 使用 uname 命令
uname 命令用于显示系统信息,常用选项如下:
-a:显示所有信息-r:显示内核发行版本-v:显示内核版本-m:显示机器硬件名称-o:显示操作系统
示例:
# 显示所有系统信息
uname -a
# 显示内核版本
uname -r
2. 查看 /proc/version 文件
/proc/version 文件包含了 Linux 内核的版本信息。
cat /proc/version
3. 使用 hostnamectl 命令(Systemd系统)
hostnamectl 命令除了设置主机名,还可以查看系统信息,包括内核版本。
hostnamectl
二、查看Linux发行版信息
1. 查看 /etc/os-release 文件
这是查看发行版信息最标准的方法,适用于大多数现代 Linux 发行版。
cat /etc/os-release
2. 查看 /etc/issue 文件
该文件包含了发行版标识信息,通常在登录前显示。
cat /etc/issue
3. 使用 lsb_release 命令
lsb_release 命令用于显示 LSB(Linux Standard Base)信息。如果系统未安装,可能需要先安装 lsb-release 包。
# 显示所有LSB信息
lsb_release -a
# 显示描述信息
lsb_release -d
# 显示发行版ID
lsb_release -i
4. 查看发行版特定的文件
不同发行版可能有自己特定的版本文件:
-
Red Hat / CentOS / Fedora:
cat /etc/redhat-release cat /etc/system-release -
Debian / Ubuntu:
cat /etc/debian_version cat /etc/lsb-release -
Arch Linux:
cat /etc/arch-release -
openSUSE:
cat /etc/SuSE-release
三、查看系统架构
1. 使用 uname 命令
uname -m
2. 使用 arch 命令
arch
3. 使用 lscpu 命令
lscpu 命令显示 CPU 架构信息,包括系统架构。
lscpu
四、综合示例
以下是一个综合示例,展示如何快速获取系统信息:
echo "=== 内核版本 ==="
uname -r
echo "=== 发行版信息 ==="
if [ -f /etc/os-release ]; then
. /etc/os-release
echo "ID: $ID"
echo "VERSION_ID: $VERSION_ID"
echo "PRETTY_NAME: $PRETTY_NAME"
elif [ -f /etc/redhat-release ]; then
cat /etc/redhat-release
elif [ -f /etc/debian_version ]; then
cat /etc/debian_version
fi
echo "=== 系统架构 ==="
uname -m
五、总结
| 信息类型 | 命令/文件 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 内核版本 | uname -r |
最常用 |
cat /proc/version |
包含编译信息 | |
| 发行版信息 | cat /etc/os-release |
标准方法 |
lsb_release -a |
需要安装 lsb-release | |
| 系统架构 | uname -m 或 arch |
查看硬件架构 |
通过以上方法,您可以快速准确地获取 Linux 系统的版本和架构信息。
在HarmonyOS Next中调试云函数,可通过以下步骤使用Postman:
- 在DevEco Studio中获取云函数的URL和认证信息(如AppGallery Connect生成的客户端ID、密钥)。
- 在Postman中新建请求,选择POST方法,输入云函数URL。
- 在Headers中添加Content-Type: application/json。
- 在Body中选择raw,输入JSON格式的请求参数。
- 如有认证要求,在Authorization中选择相应类型(如Bearer Token)并填入Token。
- 发送请求查看响应结果。
在HarmonyOS Next中,使用Postman调试本地运行的云函数,关键在于正确构建请求体以匹配云函数运行时的预期事件格式。
根据你的代码,云函数期望一个包含 httpMethod、path、body、queryStringParameters 等字段的事件对象。当通过本地HTTP服务器(如你日志中的 http://localhost:18090/user-service/invoke)调用时,你需要向这个端点发送一个特定的JSON结构,而不是直接模拟最终API路径。
正确的Postman请求构建方法如下:
- 请求方法:
POST - 请求URL:
http://localhost:18090/user-service/invoke(即日志中输出的Function URI) - 请求头:
Content-Type: application/json - 请求体(Body):选择 raw 和 JSON 格式,并填入一个模拟事件对象。其结构需与你代码中
event参数的解析逻辑对应。
针对你的 /login 接口,一个有效的请求体示例为:
{
"httpMethod": "POST",
"path": "/login",
"body": "{\"username\":\"test\",\"password\":\"123456\"}",
"queryStringParameters": {},
"headers": {}
}
关键点解析:
httpMethod:对应你代码路由判断中的method。path:对应你代码路由判断中的path。你的路由逻辑使用path.includes('/login'),因此这里设置为"/login"。body:需要是一个 JSON字符串。你的parseBody函数(代码中未展示)很可能设计为解析字符串化的JSON。因此,你需要将真正的JSON对象(如{"username":"test","password":"123456"})转换为字符串传入。queryStringParameters:用于传递URL查询参数,格式为键值对对象。headers:可以在此处模拟传入的HTTP头。
对于其他接口,如GET请求的 /profile,请求体应类似:
{
"httpMethod": "GET",
"path": "/profile",
"body": null,
"queryStringParameters": {
"userId": "123"
},
"headers": {
"Authorization": "Bearer your_token_here"
}
}
这样,你的云函数 handler 会接收到这个结构化的 event 对象,并根据其中的 path 和 httpMethod 正确路由到 getUserInfo(request) 方法,同时可以从 request.query 中获取到 userId 参数。
总结:你不能直接用Postman请求 http://localhost:18090/login。必须将目标路径(如 /login)、方法、参数等信息,封装成云函数运行时约定的JSON事件格式,发送到云函数统一的调用端点(/invoke)。






