Flutter有限状态机管理插件immutable_fsm的使用
Flutter有限状态机管理插件immutable_fsm的使用
ImmutableFSM 是一个 Dart 包,实现了支持瞬态状态的不可变有限状态机(FSM),可以与各种状态和数据管理框架(如 Riverpod)无缝集成,并且非常适合用于用户界面应用程序。
关键特性
- 不可变性:每个操作都会创建一个新的 FSM 实例,带有更新后的不可变状态和数据,确保行为可预测并减少副作用。
- 瞬态状态:FSM 支持瞬态状态——这些状态可以根据内部条件自动链到其他状态,使过渡过程无缝且高效。
- 响应式转换:状态可以提供
onEnter和onExit处理程序,当进入或离开某个状态时执行特定操作,从而实现响应式和事件驱动的行为。 - UI 兼容性:由于不可变性,
ImmutableFSM非常适合用于 UI 应用程序,并且可以与数据和状态管理框架(如 Riverpod)无缝集成。
开始使用
要开始使用 ImmutableFSM,在你的 pubspec.yaml 文件中添加它作为依赖项:
dependencies:
immutable_fsm: ^1.0.0
然后运行 flutter pub get 来安装包。
导入包
在 Dart 文件中导入包:
import 'package:immutable_fsm/immutable_fsm.dart';
使用示例
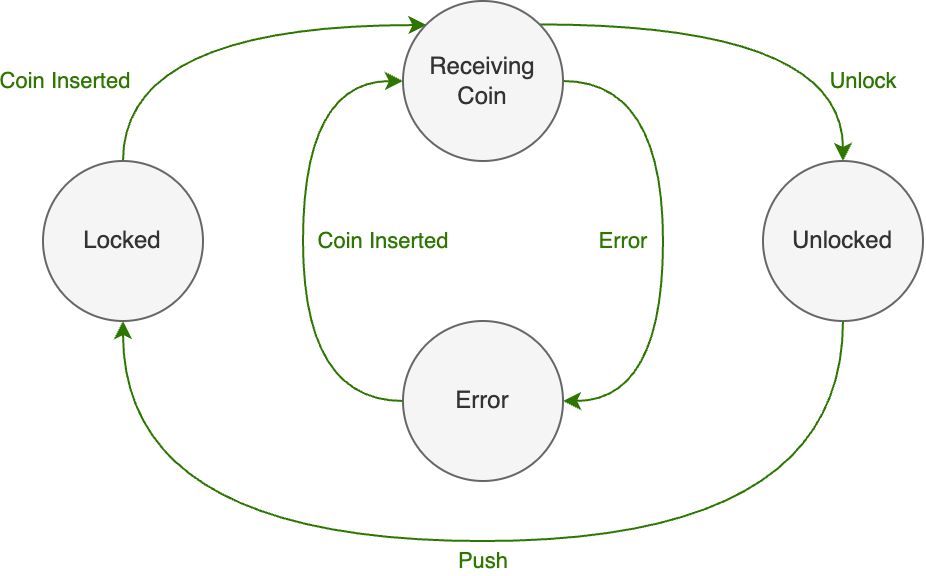
我们考虑一个需要使用状态机建模的简单系统——一个投币式旋转门。用户需要向旋转门投入一枚特定面值的硬币才能通过。
定义状态和事件
对于我们的示例,我们将使用两个关键状态——Locked(锁定)和Unlocked(解锁)。为了使系统更健壮和全面,我们还将添加两个额外的状态——ReceivingCoin(接收硬币)是一个瞬态状态,在这个状态下会验证硬币;CoinError(硬币错误)是当旋转门被锁定,但错误灯亮起并且如果有一枚硬币则会被退还给用户。
现在我们已经定义了状态,我们需要定义触发状态之间转换的事件。我们将使用以下事件:
coinInserted(硬币插入):用户将硬币投入旋转门的投币口。push(推):用户试图通过旋转门推过去。unlock(解锁):解锁旋转门,允许用户通过。error(错误):发生错误。
下面是上述模型的可视化表示:
创建FSM
首先定义FSM的状态和事件。状态代表系统的不同条件或模式(例如Locked或Unlocked),而事件是导致这些状态之间转换的触发器(例如coinInserted或push)。状态是通过扩展FSMState<Event, Data>类来创建的,其中Event通常是一个枚举列表,列出了可能的触发器,Data代表在转换过程中使用的元数据。
enum TurnstileEvent {
coinInserted,
unlock,
push,
error,
}
[@immutable](/user/immutable)
class TurnstileMetadata {
const TurnstileMetadata({this.coinValue = 0, this.error});
final int coinValue;
final Object? error;
}
class Locked extends FSMState<TurnstileEvent, TurnstileMetadata> {
const Locked();
}
class ReceivingCoin extends FSMState<TurnstileEvent, TurnstileMetadata> {
const ReceivingCoin();
[@override](/user/override)
Future<void> onEnter(TurnstileMetadata? data, {
required FSMStateOnEnterResponse<TurnstileEvent, TurnstileMetadata> response,
}) async {
// 处理硬币(详见示例完整代码)。
}
}
class Unlocked extends FSMState<TurnstileEvent, TurnstileMetadata> {
const Unlocked();
}
class CoinError extends FSMState<TurnstileEvent, TurnstileMetadata> {
const CoinError();
}
初始化FSM
通过指定初始状态来初始化FSM:
final fsm = ImmutableFSM<TurnstileEvent, TurnstileMetadata>(initialState: const Locked());
添加转换
使用 addTransition 方法定义状态转换,指定 from 状态、to 状态和触发转换的 event。每次新的转换都会创建一个具有更新转换配置的新FSM副本。
final fsm = ImmutableFSM<TurnstileEvent, TurnstileMetadata>(initialState: const Locked())
.addTransition(
from: const Locked(),
to: const ReceivingCoin(),
event: TurnstileEvent.coinInserted,
)
.addTransition(
from: const ReceivingCoin(),
to: const Unlocked(),
event: TurnstileEvent.unlock,
)
.addTransition(
from: const ReceivingCoin(),
to: const CoinError(),
event: TurnstileEvent.error,
)
.addTransition(
from: const Unlocked(),
to: const Locked(),
event: TurnstileEvent.push,
)
.addTransition(
from: const CoinError(),
to: const ReceivingCoin(),
event: TurnstileEvent.coinInserted,
);
转换状态
要执行状态转换,使用 tryTransition 方法。由于 ImmutableFSM 是不可变的,调用 tryTransition 不会改变原始FSM,而是返回一个新的FSM实例,该实例处于更新后的状态。这种方法保持了不可变性,使得FSM可预测且防止了意外的副作用。
tryTransition 接受一个事件和可选的数据;如果提供了数据,则会在当前状态退出时将其传递给新状态。如果没有提供数据,FSM将使用与状态关联的现有元数据。
使用不可变FSM可以与状态管理工具集成,因为每个新的FSM实例都可以存储在状态提供者或容器(如Riverpod)中,并在状态变化时触发UI重建。
fsm = await fsm.tryTransition(
event: TurnstileEvent.coinInserted,
data: const TurnstileMetadata(coinValue: 20),
);
处理状态变化
ImmutableFSM 的关键特性之一是其能够对状态变化做出反应。
每个状态可以在进入或退出时执行代码。状态可以通过覆盖 onEnter 和 onExit 方法来定义在进入或退出状态时应发生的操作。
瞬态状态
ImmutableFSM 的一个显著特征是支持瞬态状态,也称为状态链。瞬态状态允许在进入状态后根据内部逻辑自动过渡到另一个状态。
这些转换在内部发生,使得链式过程对执行 tryTransition 的代码透明。
例如,当旋转门处于 Locked 状态时,插入硬币会触发 ReceivingCoin 状态的转换。进入 ReceivingCoin 状态后,硬币被验证,旋转门要么解锁(转换为 Unlocked),要么抛出错误。这里,ReceivingCoin 是一个瞬态状态,基于条件快速进展到下一个状态。
// FSM 状态最初为 Locked
fsm = await fsm.tryTransition(
event: TurnstileEvent.coinInserted,
data: const TurnstileMetadata(coinValue: 20),
);
// FSM 状态现在为 Unlocked,但它经过了 ReceivingCoin
此功能使开发人员能够创建自动化各种操作和场景的状态链,而不会增加主要代码不必要的状态和事件处理负担。
例如,一个旋转门可能有称重和测量硬币的状态,然后再验证和解锁。消费此FSM的UI只需跟踪三个主要状态——锁定、解锁或错误,而无需处理中间状态。
这种方法鼓励SOLID和KISS原则,使状态更小且易于维护。
状态响应
每个状态的 onEnter 和 onExit 方法接收一个响应对象(FSMStateOnEnterResponse 进入时,FSMStateOnExitResponse 退出时),该对象提供了方法如 emitData 和 emitEvent,用于控制状态进展和处理数据更新。
数据
与每个状态关联的元数据充当在转换期间的输入和输出数据的容器。当状态处理转换时,它会产生一个完整的不可变元数据对象。状态可以复制和修改输入数据或创建全新的输出数据,具体取决于转换的具体需求。
元数据全局于FSM,并在每次状态的新元数据对象更新时更新。如果状态未发出新元数据,FSM将保留当前数据,允许多个状态依赖相同的元数据,而无需不断向前传递。
示例
下面是使用 onEnter 控制状态转换和输出数据的瞬态状态示例。
class ReceivingCoin extends FSMState<TurnstileEvent, TurnstileMetadata> {
const ReceivingCoin();
[@override](/user/override)
Future<void> onEnter(TurnstileMetadata? data, {
required FSMStateOnEnterResponse<TurnstileEvent, TurnstileMetadata> response,
}) async {
if (data?.coinValue == 20) {
response
..emitData(const TurnstileMetadata())
..emitEvent(TurnstileEvent.unlock);
return;
}
response.emitEvent(TurnstileEvent.error);
}
}
在这个示例中,ReceivingCoin 状态验证硬币的价值。如果价值匹配,它会发出新的元数据对象并触发 unlock 事件。否则,它会发出错误事件。
完整示例代码
以下是完整示例代码:
/// An example of usage of [ImmutableFSM] based on a modified example
/// of a [coin-operated turnstile](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Finite-state_machine#Example:_coin-operated_turnstile).
library;
import 'dart:convert';
import 'dart:io';
import 'package:immutable_fsm/immutable_fsm.dart';
import 'package:meta/meta.dart';
void main() async {
/// The configured turnstile state machine.
ImmutableFSM<TurnstileEvent, TurnstileMetadata?> fsm = _initialFSM;
String? input;
while (input != 'q') {
print('\nTurnstile is: ${fsm.state.runtimeType}');
final Object? error = fsm.data?.error;
if (error != null) {
print('Error: $error');
}
print('Coin: ${fsm.data?.coinValue}');
print('''Enter the following:
- an integer - insert coin of that value
- p - push the turnstile
- hit Enter - prints FSM state and configuration
- q - Quit
''');
stdout.write('> ');
input = stdin.readLineSync(encoding: utf8);
final int? value = int.tryParse(input ?? '');
try {
switch (input) {
case '':
print('\n${fsm.debugDescription}\n');
case 'p':
// Try to push the turnstile
fsm = await fsm.tryTransition(event: TurnstileEvent.push);
case 'q':
break;
default:
if (value != null) {
// Try to put in the coin
fsm = await fsm.tryTransition(
event: TurnstileEvent.coinInserted,
data: TurnstileMetadata(coinValue: value),
);
break;
}
print('Command not recognized');
}
} on Exception catch (exception) {
print('Unable to process input: $exception');
}
}
}
/// Turnstile events that state machine understands.
enum TurnstileEvent {
/// A coin is put into the turnstile.
coinInserted,
/// Unlock the turnstile to allow the passage.
unlock,
/// Push the turnstile to walk through.
push,
/// Turnstile reported an error.
error,
}
/// The data associated with turnstile.
///
/// It covers both input and output of the states, keeping the inserted
/// [coinValue] and [error], if any.
[@immutable](/user/immutable)
class TurnstileMetadata {
const TurnstileMetadata({this.coinValue = 0, this.error});
final int coinValue;
final Object? error;
[@override](/user/override)
String toString() => 'TurnstileMetadata{coinValue: $coinValue, error: $error}';
}
/// Locked turnstile - passage is blocked.
class Locked extends FSMState<TurnstileEvent, TurnstileMetadata> {
const Locked();
}
/// An intermediate state when turnstile processes the coin.
class ReceivingCoin extends FSMState<TurnstileEvent, TurnstileMetadata> {
const ReceivingCoin();
/// When a coin is inserted, it verifies that there is a coin and that it's
/// a coin of the correct value.
///
/// If everything matches, it emits [TurnstileEvent.unlock] and clears the
/// coin from [TurnstileMetadata] to represent that it went through.
[@override](/user/override)
Future<void> onEnter(
TurnstileMetadata? data, {
required FSMStateOnEnterResponse<TurnstileEvent, TurnstileMetadata> response,
}) async {
final int? coinValue = data?.coinValue;
if (coinValue == null) {
response
..emitEvent(TurnstileEvent.error)
..emitData(
const TurnstileMetadata(
error: WrongCoinException(
'You have to put in a real coin.',
),
),
);
return;
}
if (coinValue == 50) {
response
..emitEvent(TurnstileEvent.unlock)
..emitData(const TurnstileMetadata());
return;
}
response
..emitEvent(TurnstileEvent.error)
..emitData(
TurnstileMetadata(
coinValue: coinValue,
error: WrongCoinException(
'A coin of 50 is required, but $coinValue was provided - returned.',
),
),
);
}
}
/// Unlocked turnstile, allowing to walk through.
class Unlocked extends FSMState<TurnstileEvent, TurnstileMetadata> {
const Unlocked();
}
/// An error - representing a state when turnstile refused to accept a coin.
class CoinError extends FSMState<TurnstileEvent, TurnstileMetadata> {
const CoinError();
}
/// An exception, representing an incorrect coin.
class WrongCoinException implements Exception {
const WrongCoinException(this.message);
final String message;
[@override](/user/override)
String toString() => 'WrongCoinException: $message';
}
/// The configuration of the state machine, which is also it's initial state.
final ImmutableFSM<TurnstileEvent, TurnstileMetadata> _initialFSM =
const ImmutableFSM<TurnstileEvent, TurnstileMetadata>(
initialState: Locked(),
data: TurnstileMetadata(),
)
.addTransition(
from: const Locked(),
to: const ReceivingCoin(),
event: TurnstileEvent.coinInserted,
)
.addTransition(
from: const ReceivingCoin(),
to: const Unlocked(),
event: TurnstileEvent.unlock,
)
.addTransition(
from: const ReceivingCoin(),
to: const CoinError(),
event: TurnstileEvent.error,
)
.addTransition(
from: const Unlocked(),
to: const Locked(),
event: TurnstileEvent.push,
)
.addTransition(
from: const CoinError(),
to: const ReceivingCoin(),
event: TurnstileEvent.coinInserted,
);
更多关于Flutter有限状态机管理插件immutable_fsm的使用的实战教程也可以访问 https://www.itying.com/category-92-b0.html
更多关于Flutter有限状态机管理插件immutable_fsm的使用的实战系列教程也可以访问 https://www.itying.com/category-92-b0.html
immutable_fsm 是一个用于 Flutter 的有限状态机(FSM)管理插件,它提供了一种简洁且不可变的方式来管理应用的状态。通过使用 immutable_fsm,你可以更容易地定义、转换和管理应用的状态,从而保持代码的可维护性和可扩展性。
安装
首先,你需要在 pubspec.yaml 文件中添加 immutable_fsm 依赖:
dependencies:
flutter:
sdk: flutter
immutable_fsm: ^0.1.0 # 请检查最新版本
然后运行 flutter pub get 来安装依赖。
基本用法
1. 定义状态和事件
首先,你需要定义应用的状态和事件。状态和事件通常用枚举来表示。
enum MyState {
idle,
loading,
success,
error,
}
enum MyEvent {
startLoading,
finishLoading,
failLoading,
}
2. 创建状态机
使用 immutable_fsm 创建状态机。你可以定义一个 Fsm 实例,并指定初始状态和状态转换逻辑。
import 'package:immutable_fsm/immutable_fsm.dart';
final myFsm = Fsm<MyState, MyEvent>(
initialState: MyState.idle,
transitions: {
MyState.idle: {
MyEvent.startLoading: MyState.loading,
},
MyState.loading: {
MyEvent.finishLoading: MyState.success,
MyEvent.failLoading: MyState.error,
},
MyState.success: {
MyEvent.startLoading: MyState.loading,
},
MyState.error: {
MyEvent.startLoading: MyState.loading,
},
},
);
3. 处理事件和状态转换
你可以通过调用 sendEvent 方法来触发事件,并更新状态。
void main() {
print('Initial State: ${myFsm.state}'); // Output: Initial State: MyState.idle
myFsm.sendEvent(MyEvent.startLoading);
print('State after startLoading: ${myFsm.state}'); // Output: State after startLoading: MyState.loading
myFsm.sendEvent(MyEvent.finishLoading);
print('State after finishLoading: ${myFsm.state}'); // Output: State after finishLoading: MyState.success
}
4. 监听状态变化
你还可以监听状态的变化,以便在状态改变时执行某些操作。
myFsm.onStateChange.listen((newState) {
print('State changed to: $newState');
});
高级用法
1. 带有数据的复杂状态
如果你需要在状态中包含一些数据,可以使用 FsmState 类来封装状态和数据。
class MyDataState extends FsmState<MyState, MyEvent> {
final String? data;
MyDataState(MyState state, {this.data}) : super(state);
}
然后你可以在状态转换时传递数据:
final myFsm = Fsm<MyDataState, MyEvent>(
initialState: MyDataState(MyState.idle),
transitions: {
MyDataState(MyState.idle): {
MyEvent.startLoading: MyDataState(MyState.loading, data: 'Loading...'),
},
MyDataState(MyState.loading): {
MyEvent.finishLoading: MyDataState(MyState.success, data: 'Data Loaded!'),
MyEvent.failLoading: MyDataState(MyState.error, data: 'Error!'),
},
},
);
2. 自定义状态转换逻辑
你可以通过 transitionCallback 参数来自定义状态转换逻辑。
final myFsm = Fsm<MyState, MyEvent>(
initialState: MyState.idle,
transitions: {
MyState.idle: {
MyEvent.startLoading: MyState.loading,
},
MyState.loading: {
MyEvent.finishLoading: MyState.success,
MyEvent.failLoading: MyState.error,
},
},
transitionCallback: (fromState, event, toState) {
print('Transitioning from $fromState to $toState on event $event');
},
);





