Golang红黑树实现 - 插入操作案例5详解
Golang红黑树实现 - 插入操作案例5详解 大家好,
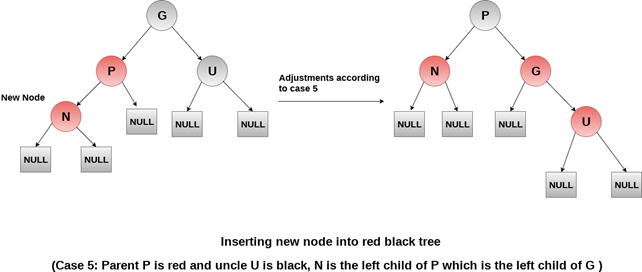
在向红黑树添加节点时,第五种也是最后一种情况是:新节点为红色,父节点为红色,祖父节点为黑色,叔父节点为黑色。
这棵树(红色父节点、黑色祖父节点和黑色非空叔父节点)不符合红黑树性质。如果新节点和父节点位于左侧,那么在添加新节点之前,右侧路径上已经包含更多黑色节点。
这个观察是否正确?我们是否仍然需要处理这种情况,仅仅是因为在插入时进行旋转/重新着色的其他操作中会出现这种情况?
更多关于Golang红黑树实现 - 插入操作案例5详解的实战教程也可以访问 https://www.itying.com/category-94-b0.html
根据红黑树的定义(来自维基百科):
- 每个节点要么是红色,要么是黑色
- 根节点是黑色。这条规则有时会被省略。由于根节点总是可以从红色改为黑色,但反过来不一定成立,因此这条规则对分析影响不大
- 所有叶子节点(NIL)都是黑色
- 如果一个节点是红色,那么它的两个子节点都是黑色
- 从任意节点到其所有后代叶子节点的每条路径都包含相同数量的黑色节点
更多关于Golang红黑树实现 - 插入操作案例5详解的实战系列教程也可以访问 https://www.itying.com/category-94-b0.html
在红黑树的插入操作中,第五种情况确实需要专门处理,你的观察是正确的。这种情况出现在新节点(红色)、父节点(红色)和祖父节点(黑色)构成一条直线路径,且叔父节点为黑色时。此时违反了红黑树的性质4(红色节点的子节点必须为黑色),需要通过旋转和重新着色来修复。
这种情况通常是在处理第三种或第四种情况后出现的。具体来说,当新节点和父节点都位于左侧(或都位于右侧)时,需要进行一次旋转操作来平衡树结构。
以下是针对左侧情况的Go语言实现示例:
type Color bool
const (
RED Color = true
BLACK Color = false
)
type Node struct {
key int
color Color
left *Node
right *Node
parent *Node
}
func (n *Node) uncle() *Node {
if n.parent == nil || n.parent.parent == nil {
return nil
}
if n.parent == n.parent.parent.left {
return n.parent.parent.right
}
return n.parent.parent.left
}
func (n *Node) grandparent() *Node {
if n.parent != nil {
return n.parent.parent
}
return nil
}
func rotateLeft(root *Node, x *Node) *Node {
y := x.right
x.right = y.left
if y.left != nil {
y.left.parent = x
}
y.parent = x.parent
if x.parent == nil {
root = y
} else if x == x.parent.left {
x.parent.left = y
} else {
x.parent.right = y
}
y.left = x
x.parent = y
return root
}
func rotateRight(root *Node, y *Node) *Node {
x := y.left
y.left = x.right
if x.right != nil {
x.right.parent = y
}
x.parent = y.parent
if y.parent == nil {
root = x
} else if y == y.parent.left {
y.parent.left = x
} else {
y.parent.right = x
}
x.right = y
y.parent = x
return root
}
func fixInsertCase5(root *Node, n *Node) *Node {
g := n.grandparent()
if n == n.parent.left && n.parent == g.left {
// Left-left case
root = rotateRight(root, g)
n.parent.color, g.color = g.color, n.parent.color
} else if n == n.parent.right && n.parent == g.right {
// Right-right case
root = rotateLeft(root, g)
n.parent.color, g.color = g.color, n.parent.color
}
return root
}
在这个实现中:
- 当新节点和父节点都在祖父节点的左侧时,执行右旋转
- 当新节点和父节点都在祖父节点的右侧时,执行左旋转
- 旋转后交换父节点和祖父节点的颜色
这种情况确实需要处理,因为它是红黑树插入修复过程中的一个必要步骤。如果不处理这种情况,树将无法保持红黑树的平衡性质,导致搜索性能下降。这种情况通常是在处理完第三种或第四种情况(父节点和叔父节点都是红色)后出现的,通过旋转操作可以最终恢复红黑树的性质。






