Golang分布式任务管理系统分享:Asgard的使用与实践
Golang分布式任务管理系统分享:Asgard的使用与实践
源代码
dalonghahaha/Asgard
Asgarde 框架。通过在 GitHub 上创建帐户,为 dalonghahaha/Asgard 的开发做出贡献。
介绍
Asgard 是一个分布式作业管理系统,旨在全面解决常驻进程应用、计划任务和调度任务。
架构设计
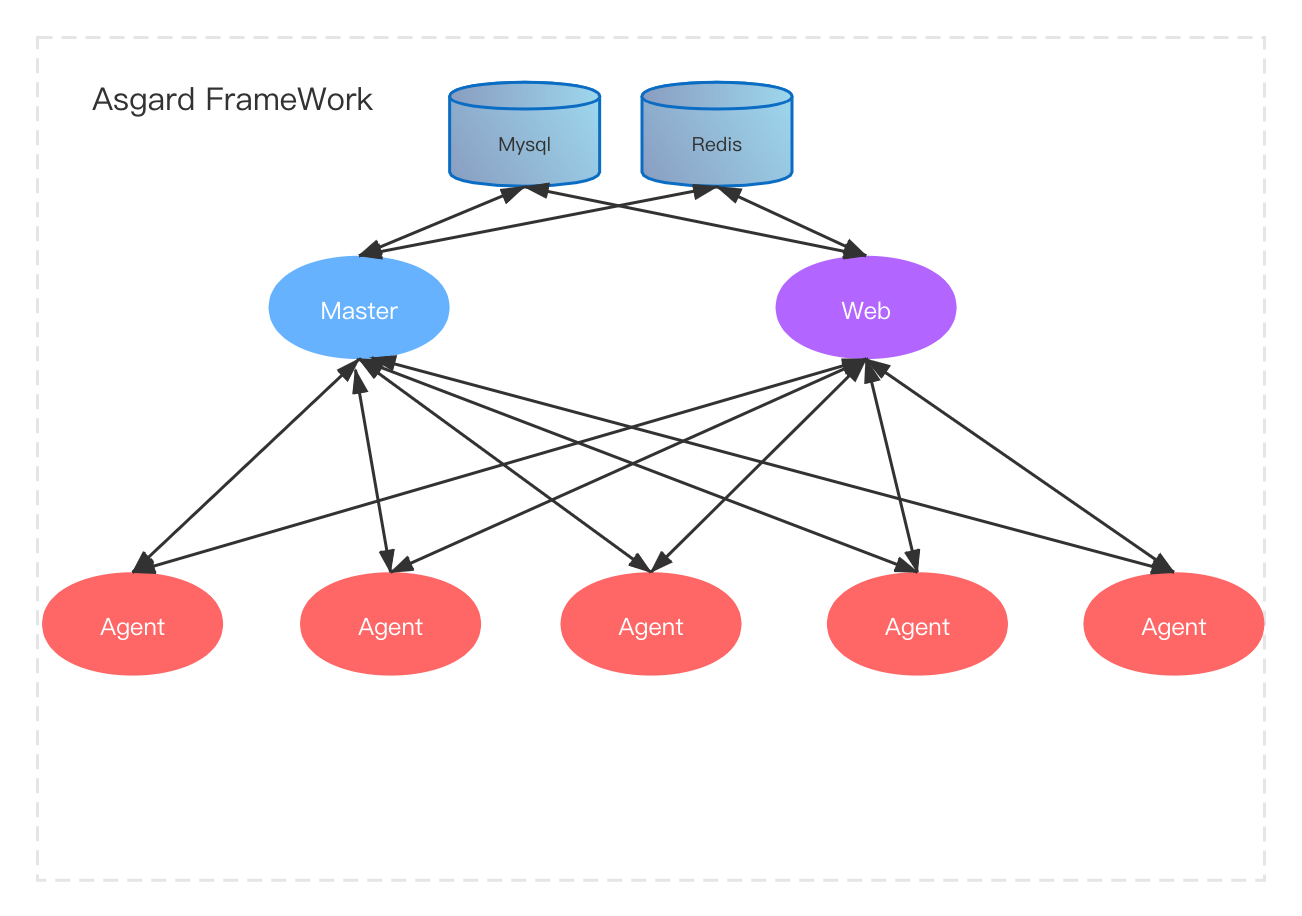
- Asgard 系统由 Web 节点、Master 节点和 Agent 节点组成。
- Web 节点的主要功能包括实例管理、组管理、作业配置、作业运行状态控制、作业运行状态查看、日志查询。
- Master 节点负责 Agent 节点的状态监控,同时接收并转储 Agent 节点上报的运行时数据。
- Agent 节点接收来自 Web 节点的指令,并在相应的服务器中执行相关操作。
- Master 节点和 Agent 节点通过 gRPC 协议交换数据。
更多关于Golang分布式任务管理系统分享:Asgard的使用与实践的实战教程也可以访问 https://www.itying.com/category-94-b0.html
1 回复
更多关于Golang分布式任务管理系统分享:Asgard的使用与实践的实战系列教程也可以访问 https://www.itying.com/category-94-b0.html
Asgard确实是一个设计良好的分布式任务管理系统,其架构清晰且功能全面。从架构图来看,它采用了典型的主从模式,通过gRPC进行高效通信。
让我通过示例代码展示如何快速集成Asgard的Agent节点:
package main
import (
"context"
"log"
"time"
"github.com/dalonghahaha/Asgard/agent"
"github.com/dalonghahaha/Asgard/proto"
)
// 定义一个简单的任务处理器
type MyTaskHandler struct{}
func (h *MyTaskHandler) Execute(ctx context.Context, task *proto.Task) (*proto.Result, error) {
log.Printf("执行任务: %s, 参数: %v", task.Name, task.Params)
// 模拟任务执行
time.Sleep(2 * time.Second)
return &proto.Result{
TaskId: task.Id,
Status: proto.TaskStatus_SUCCESS,
Output: "任务执行成功",
Timestamp: time.Now().Unix(),
}, nil
}
func main() {
// 创建Agent配置
config := &agent.Config{
ServerAddr: "localhost:50051",
WorkerNum: 10,
Group: "default",
}
// 初始化Agent
agt, err := agent.NewAgent(config)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal("创建Agent失败:", err)
}
// 注册任务处理器
agt.RegisterHandler("my_task", &MyTaskHandler{})
// 启动Agent
ctx := context.Background()
if err := agt.Start(ctx); err != nil {
log.Fatal("启动Agent失败:", err)
}
// 保持运行
select {}
}
对于Master节点的监控功能,可以这样实现数据收集:
// Master节点监控示例
func monitorAgents(master *agent.Master) {
ticker := time.NewTicker(30 * time.Second)
defer ticker.Stop()
for range ticker.C {
agents := master.GetActiveAgents()
log.Printf("活跃Agent数量: %d", len(agents))
for _, agent := range agents {
stats := agent.GetStats()
log.Printf("Agent %s: CPU使用率 %.2f%%, 内存使用 %.2fMB",
agent.ID, stats.CPUUsage, stats.MemoryUsage/1024/1024)
}
}
}
Web节点的任务调度可以通过REST API实现:
// Web节点API示例
func scheduleTask(web *web.Server) {
task := &proto.Task{
Id: uuid.New().String(),
Name: "data_processing",
Params: map[string]string{"input": "/data/source.csv"},
Cron: "0 */5 * * * *", // 每5分钟执行一次
}
// 通过Web API提交任务
resp, err := http.Post("http://localhost:8080/api/tasks",
"application/json",
bytes.NewBuffer(task.ToJSON()))
if err != nil {
log.Fatal("提交任务失败:", err)
}
defer resp.Body.Close()
log.Println("任务已提交,ID:", task.Id)
}
Asgard的gRPC协议定义确保了节点间的高效通信:
// 任务定义
message Task {
string id = 1;
string name = 2;
map<string, string> params = 3;
string cron = 4;
int64 timeout = 5;
}
// 执行结果
message Result {
string task_id = 1;
TaskStatus status = 2;
string output = 3;
int64 timestamp = 4;
string error = 5;
}
这个系统的优势在于其模块化设计,每个节点职责明确。Agent节点的插件化架构使得扩展新任务类型非常方便,只需实现对应的Handler接口即可。Master节点的状态监控机制能够实时跟踪整个集群的健康状况。






