HarmonyOS鸿蒙Next中怎么将多维数组进行降维处理?
HarmonyOS鸿蒙Next中怎么将多维数组进行降维处理? 在后端接口返回多维数组时,需要一个 flatten 函数来降维,进行扁平化处理,方便后续可视化数据。
3 回复
演示图:
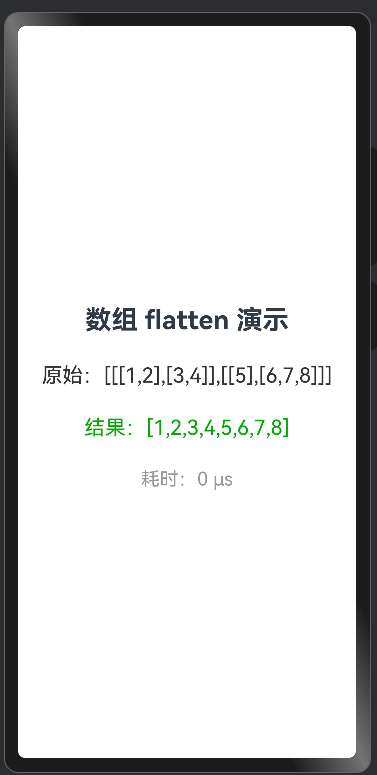
关键函数:
flatten<T>(src: T[]): T[] {
const ans: T[] = [];
for (const item of src) {
if (Array.isArray(item)) {
ans.push(...this.flatten(item as T[]));
} else {
ans.push(item);
}
}
return ans;
}
完整代码:
@Entry
@ComponentV2
struct FlattenPage {
@Local raw: string = '';
@Local flat: string = '';
@Local cost: string = '';
flatten<T>(src: T[]): T[] {
const ans: T[] = [];
for (const item of src) {
if (Array.isArray(item)) {
ans.push(...this.flatten(item as T[]));
} else {
ans.push(item);
}
}
return ans;
}
aboutToAppear(): void {
const nested: number[][][] = [[[1, 2], [3, 4]], [[5], [6, 7, 8]]];
const t0 = new Date().getTime();
const result = this.flatten(nested);
const t1 = new Date().getTime();
this.raw = `原始:${JSON.stringify(nested)}`;
this.flat = `结果:${JSON.stringify(result)}`;
this.cost = `耗时:${(t1 - t0) * 1000} μs`;
}
build() {
Column({ space: 30 }) {
Text('数组 flatten 演示')
.fontSize(28)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
Text(this.raw).fontSize(22).fontColor('#333')
Text(this.flat).fontSize(22).fontColor('#0a0')
Text(this.cost).fontSize(20).fontColor('#999')
}
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
.padding(24)
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
}
}
更多关于HarmonyOS鸿蒙Next中怎么将多维数组进行降维处理?的实战系列教程也可以访问 https://www.itying.com/category-93-b0.html
在HarmonyOS鸿蒙Next中,可以使用ArkTS的数组方法进行降维处理。例如,对于二维数组,可以使用flat()方法将其转换为一维数组:let flattened = arr.flat();。如果需要处理更深层级的嵌套数组,可以指定深度参数:arr.flat(2)。此外,也可以结合reduce和concat方法实现自定义降维逻辑。这些操作适用于ArkTS标准库,不依赖Java或C语言。
在HarmonyOS Next中,可以通过以下两种方式实现多维数组降维(扁平化):
1. 使用递归函数
function flatten(arr: any[]): any[] {
const result: any[] = [];
arr.forEach(item => {
if (Array.isArray(item)) {
result.push(...flatten(item));
} else {
result.push(item);
}
});
return result;
}
// 使用示例
const multiArray = [1, [2, [3, 4], 5], 6];
const flatArray = flatten(multiArray); // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
2. 使用flat()方法(ES2019特性)
// 如果知道具体嵌套深度
const array2 = [1, [2, 3]];
const flat1 = array2.flat(); // [1, 2, 3]
// 完全扁平化(无限深度)
const arrayDeep = [1, [2, [3, [4]]]];
const flatInfinity = arrayDeep.flat(Infinity); // [1, 2, 3, 4]
3. 性能优化版本(避免递归栈溢出)
function flattenIterative(arr: any[]): any[] {
const stack = [...arr];
const result = [];
while (stack.length) {
const next = stack.pop();
if (Array.isArray(next)) {
stack.push(...next);
} else {
result.push(next);
}
}
return result.reverse();
}
注意事项:
- TypeScript类型处理:建议使用泛型或明确类型声明
- 大数据量时,迭代版本比递归版本更稳定
- 如果只需要处理固定深度,使用
flat(depth)方法更简洁
这些方法在HarmonyOS Next的ArkTS/TypeScript环境中都可以直接使用。






