HarmonyOS鸿蒙Next中代码工坊的AI matting示例代码抠图,想要保存带白边的效果如何实现
HarmonyOS鸿蒙Next中代码工坊的AI matting示例代码抠图,想要保存带白边的效果如何实现 【问题描述】:参照代码工坊的AI matting示例代码抠图,图片选中之后,周围有一圈白边效果,但是复制之后粘贴就没有白边的效果,我想把抠出来的图片做成贴纸,这个白边效果正好是我想要的,请问如何能保存这个白边的效果,或者是如何给一个图片添加这个白边的效果,有方案实现吗,效果图如下
【问题现象】:
抠图效果

粘贴后的效果

【版本信息】:API20
【复现代码】:不涉及
【尝试解决方案】:不涉及
更多关于HarmonyOS鸿蒙Next中代码工坊的AI matting示例代码抠图,想要保存带白边的效果如何实现的实战教程也可以访问 https://www.itying.com/category-93-b0.html
我用了另外一种方案来实现楼主可以参考,更改为图片加白边
【解决方案】
读取像素:获取扣好图的 PixelMap 数据。
生成白底:遍历所有不透明的像素,在它的周围(由边框宽度决定)填充白色。这就像把主体“放大”了一圈白色。
合成:将原始的主体图片覆盖在这个“白色放大版”上面。
输出:生成一张新的带白边的图片。
【实现效果】
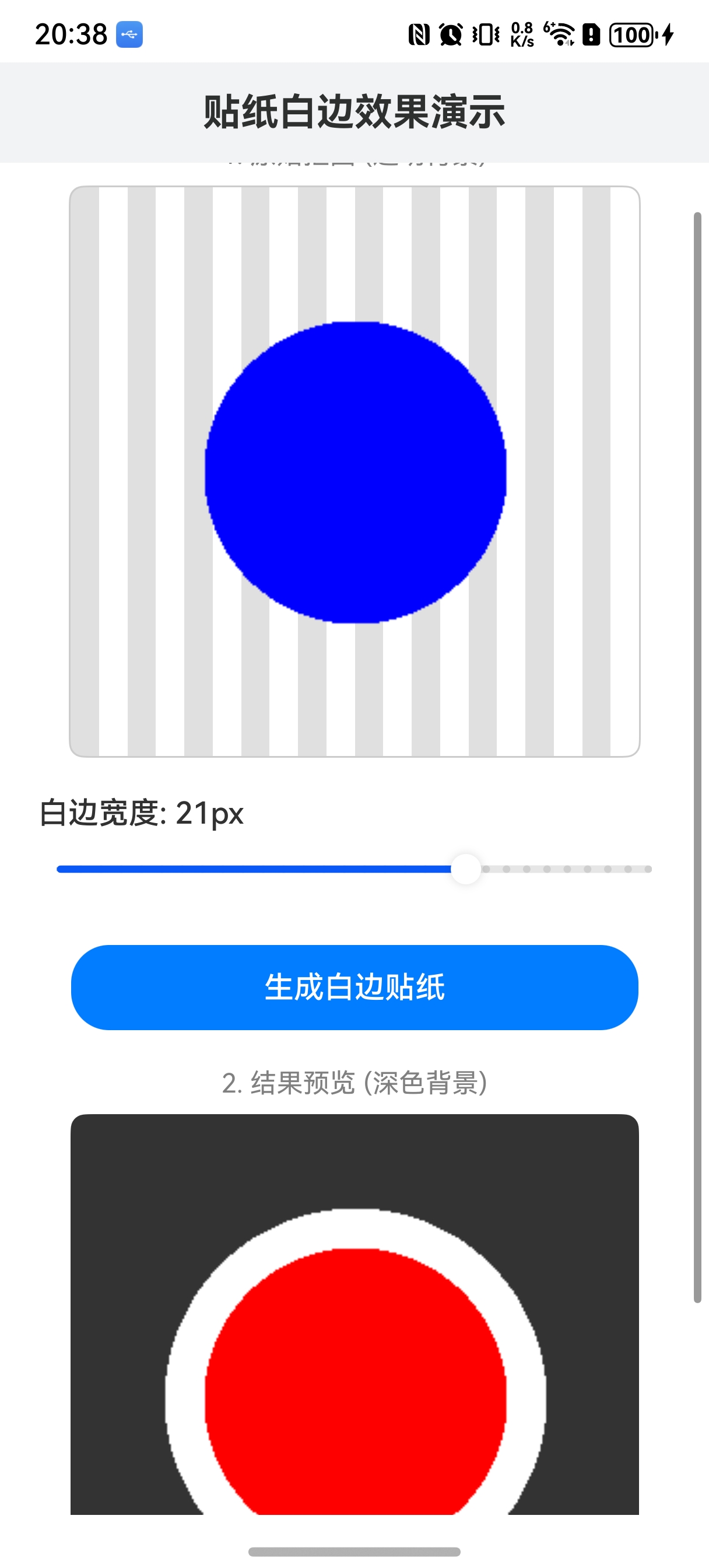
【demo代码】
import image from '@ohos.multimedia.image';
import promptAction from '@ohos.promptAction';
@Entry
@Component
struct StickerPage {
@State originalImage: image.PixelMap | null = null;
@State stickerImage: image.PixelMap | null = null;
@State isProcessing: boolean = false;
@State strokeWidth: number = 10; // 默认描边宽度
// 页面加载时生成一个测试用的透明底图片
async aboutToAppear() {
this.originalImage = await this.createMockPixelMap();
}
// 创建一个测试图片(透明背景上的红色爱心),模拟抠图结果
async createMockPixelMap(): Promise<image.PixelMap> {
const width = 300;
const height = 300;
const buffer = new ArrayBuffer(width * height * 4);
const pixels = new Uint8Array(buffer); // RGBA
// 简单的算法画一个爱心或者圆形,这里画一个红色的圆作为主体
const cx = width / 2;
const cy = height / 2;
const radius = 80;
for (let y = 0; y < height; y++) {
for (let x = 0; x < width; x++) {
const index = (y * width + x) * 4;
// 简单的圆形方程
const dist = Math.sqrt((x - cx) * (x - cx) + (y - cy) * (y - cy));
if (dist < radius) {
// 红色主体 (R=255, G=0, B=0, A=255)
pixels[index] = 255;
pixels[index + 1] = 0;
pixels[index + 2] = 0;
pixels[index + 3] = 255;
} else {
// 透明背景
pixels[index] = 0;
pixels[index + 1] = 0;
pixels[index + 2] = 0;
pixels[index + 3] = 0;
}
}
}
const opts: image.InitializationOptions = {
editable: true,
pixelFormat: image.PixelMapFormat.RGBA_8888,
size: { height, width }
};
return await image.createPixelMap(buffer, opts);
}
// 生成贴纸的核心方法
async generateSticker() {
if (!this.originalImage) {
return;
}
// 防止重复点击
if (this.isProcessing) {
return;
}
this.isProcessing = true;
const startTime = Date.now();
try {
// 调用工具类
// 这里的 strokeWidth 是界面上滑块控制的
const result = await StickerUtils.addStickerStroke(this.originalImage, this.strokeWidth);
this.stickerImage = result;
const duration = Date.now() - startTime;
promptAction.showToast({ message: `生成完毕,耗时: ${duration}ms` });
} catch (error) {
console.error('生成失败:', error);
promptAction.showToast({ message: '生成失败,请查看日志' });
} finally {
this.isProcessing = false;
}
}
build() {
Column() {
// 标题栏
Text('贴纸白边效果演示')
.fontSize(20)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.width('100%')
.padding(15)
.backgroundColor('#F1F3F5')
.textAlign(TextAlign.Center)
Scroll() {
Column({ space: 20 }) {
// 1. 展示原图区域
Column() {
Text('1. 原始抠图 (透明背景)')
.fontSize(14)
.fontColor(Color.Gray)
.margin({ bottom: 8 })
Stack() {
// 棋盘格背景,用于展示透明效果
GridRow({ columns: 20 }) {
ForEach(new Array(400).fill(0), (_: number, index: number) => {
GridCol()
.height(15)
.backgroundColor(index % 2 === 0 ? '#E0E0E0' : '#FFFFFF')
})
}
.width(300)
.height(300)
.clip(true)
if (this.originalImage) {
Image(this.originalImage)
.width(300)
.height(300)
.objectFit(ImageFit.Contain)
}
}
.borderRadius(8)
.clip(true)
.border({ width: 1, color: '#CCCCCC' })
}
// 2. 控制区域
Column() {
Row() {
Text(`白边宽度: ${this.strokeWidth.toFixed(0)}px`)
.fontSize(16)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Medium)
}
.width('100%')
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Start)
Slider({
value: this.strokeWidth,
min: 1,
max: 30,
step: 1,
style: SliderStyle.OutSet
})
.showSteps(true)
.onChange((value: number) => {
this.strokeWidth = value;
})
}
.padding({ left: 20, right: 20 })
.width('100%')
Button(this.isProcessing ? '处理中...' : '生成白边贴纸')
.width('80%')
.height(45)
.backgroundColor(this.isProcessing ? '#CCCCCC' : '#007DFF')
.onClick(() => {
this.generateSticker();
})
// 3. 展示结果区域
if (this.stickerImage) {
Column() {
Text('2. 结果预览 (深色背景)')
.fontSize(14)
.fontColor(Color.Gray)
.margin({ bottom: 8 })
Stack() {
// 深色背景,方便看清白边
Rect()
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
.fill('#333333')
Image(this.stickerImage)
.width(300)
.height(300)
.objectFit(ImageFit.Contain)
}
.width(300)
.height(300)
.borderRadius(8)
.clip(true)
}
.animation({ duration: 300 })
}
}
.padding({ top: 20, bottom: 50 })
.width('100%')
}
.layoutWeight(1)
}
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
.backgroundColor('#FFFFFF')
}
}
export class StickerUtils {
/**
* 给图片添加白色描边效果(制作贴纸)
* @param sourcePixelMap 原始图片 (必须是背景透明的)
* @param strokeWidth 描边宽度 (像素单位,建议 5-20)
* @returns 处理后的 PixelMap
*/
public static async addStickerStroke(sourcePixelMap: image.PixelMap,
strokeWidth: number = 10): Promise<image.PixelMap> {
const imageInfo = await sourcePixelMap.getImageInfo();
const width = imageInfo.size.width;
const height = imageInfo.size.height;
// 1. 读取原始像素数据
const bufferData = new ArrayBuffer(sourcePixelMap.getPixelBytesNumber());
await sourcePixelMap.readPixelsToBuffer(bufferData);
// 使用 Uint8Array 操作字节,或者是 Int32Array 操作像素点 (RGBA)
// 这里使用 Uint32Array 方便处理整个像素颜色,但在 ArkTS 中需注意大小端问题
// 为兼容性,我们操作 Uint8Array: [R, G, B, A, R, G, B, A...]
const srcPixels = new Uint8Array(bufferData);
// 2. 创建一个新的 Buffer 用于存放结果
// 结果图大小不变(如果主体太大贴边,描边可能会被切掉,建议输入图主体周围留有余白)
const dstPixels = new Uint8Array(bufferData.byteLength);
// 预设白色 (R=255, G=255, B=255, A=255)
// 注意:PixelMap 默认格式通常是 RGBA_8888
// 3. 算法核心:膨胀 (Dilation) 生成白底
// 这是一个高强度的计算,为了性能,我们通过判断“当前点是否不透明”来向四周扩散
// 优化:我们不需要遍历每一个点去画圆,而是遍历原图,如果原图某点有像素,
// 就在目标图对应位置及周围画白。
// 为了防止计算量过大卡顿,这里使用简单的“方框+圆形”逻辑
const w = width;
const h = height;
const dist = Math.ceil(strokeWidth);
const distSq = dist * dist;
// 填充 0 (全透明)
dstPixels.fill(0);
for (let y = 0; y < h; y++) {
for (let x = 0; x < w; x++) {
const idx = (y * w + x) * 4;
const alpha = srcPixels[idx + 3]; // 获取 Alpha 通道
// 如果当前像素不是透明的 (阈值设为 10 过滤杂边)
if (alpha > 10) {
// 在目标图上,以 (x,y) 为中心,dist 为半径画白色
// 优化循环范围,只遍历由于描边宽度影响到的区域
const startY = Math.max(0, y - dist);
const endY = Math.min(h - 1, y + dist);
const startX = Math.max(0, x - dist);
const endX = Math.min(w - 1, x + dist);
for (let dy = startY; dy <= endY; dy++) {
for (let dx = startX; dx <= endX; dx++) {
// 检查距离是否在圆内 (制作圆角描边)
const deltaX = dx - x;
const deltaY = dy - y;
if (deltaX * deltaX + deltaY * deltaY <= distSq) {
const dstIdx = (dy * w + dx) * 4;
// 设置为白色不透明
dstPixels[dstIdx] = 255; // R
dstPixels[dstIdx + 1] = 255; // G
dstPixels[dstIdx + 2] = 255; // B
dstPixels[dstIdx + 3] = 255; // A
}
}
}
}
}
}
// 4. 将原始图片覆盖在白底之上
for (let i = 0; i < srcPixels.length; i += 4) {
const srcA = srcPixels[i + 3];
if (srcA > 0) {
// 简单的 Alpha 混合:如果原图有像素,直接覆盖
// (更严谨的做法是做 alpha blending,但对于贴纸,直接覆盖通常效果最好)
dstPixels[i] = srcPixels[i]; // R
dstPixels[i + 1] = srcPixels[i + 1]; // G
dstPixels[i + 2] = srcPixels[i + 2]; // B
dstPixels[i + 3] = srcPixels[i + 3]; // A
}
}
// 5. 创建新的 PixelMap
const opts: image.InitializationOptions = {
editable: true,
pixelFormat: image.PixelMapFormat.RGBA_8888,
size: { height: height, width: width }
};
const newPixelMap = await image.createPixelMap(dstPixels.buffer, opts);
return newPixelMap;
}
}
可以参考:拖拽图像增加水印。
改成拖拽后加个白边就好了。
期待HarmonyOS能在未来带来更多创新的技术和理念。
这种异形的图片怎么增加白边
在HarmonyOS Next中,AI Matting示例代码生成的抠图结果(Alpha遮罩)默认是透明背景。您看到的“白边”效果实际上是UI组件(如Image)在透明区域叠加的视觉边框,并非图像数据的一部分。要实现保存带白边的贴纸效果,需要对抠图结果进行后处理。
核心方案是:获取抠图结果的Alpha通道,创建一个新图像,在透明区域(Alpha值较低的区域)填充白色,然后将处理后的图像保存到文件。
以下是基于@kit.ArkGraphics2D(2D图形库)的关键实现步骤:
- 获取图像数据:从AI Matting的输出结果(通常是一个包含RGBA数据的
PixelMap对象)中获取原始的像素数据。 - 处理Alpha通道:遍历每个像素的Alpha值。您可以设定一个阈值(例如,Alpha < 10)。对于低于此阈值的像素(即原图中完全透明或接近透明的区域),将其RGB通道的值设置为白色(255, 255, 255),同时将Alpha通道设置为不透明(255)。对于Alpha值较高的像素(主体部分),保留其原有的RGB颜色和Alpha值。
- 创建并保存新图像:将处理后的像素数据重新封装为
PixelMap,然后使用image组件的packing方法或相关API将其编码为PNG等格式保存到应用沙箱路径。
示例代码片段:
import { image } from '@kit.ArkGraphics2D';
import { BusinessError } from '@kit.BasicServicesKit';
// 假设 mattingResultPixelMap 是AI Matting后得到的 PixelMap 对象
async function addWhiteBorderAndSave(mattingResultPixelMap: image.PixelMap): Promise<void> {
const imageInfo: image.InitializationOptions = mattingResultPixelMap.getImageInfo();
const buffer: ArrayBuffer = await mattingResultPixelMap.getPixelBytesBuffer();
// 获取像素数据(假设为RGBA_8888格式)
const pixelArray = new Uint8Array(buffer);
const alphaThreshold = 10; // 透明度阈值,可调整
for (let i = 0; i < pixelArray.length; i += 4) {
const alpha = pixelArray[i + 3];
if (alpha < alphaThreshold) {
// 透明区域填充为白色不透明
pixelArray[i] = 255; // R
pixelArray[i + 1] = 255; // G
pixelArray[i + 2] = 255; // B
pixelArray[i + 3] = 255; // A
}
// 非透明区域保留原色
}
// 创建新的PixelMap
const newPixelMap: image.PixelMap = await image.createPixelMap(pixelArray.buffer, imageInfo);
// 保存为PNG文件到应用沙箱
const packOpts: image.PackingOption = {
format: "image/png",
quality: 100
};
const filePath = '您的沙箱路径/贴纸_with_border.png'; // 替换为实际路径
await image.packing(newPixelMap, filePath, packOpts);
// 释放资源
newPixelMap.release();
}
注意事项:
- 确保已申请必要的文件读写权限(
ohos.permission.READ_MEDIA,ohos.permission.WRITE_MEDIA)。 - 处理完成后及时调用
release()释放PixelMap资源,避免内存泄漏。 - 阈值
alphaThreshold可根据实际视觉效果调整,以控制白边的“硬度”。
此方法直接修改图像数据,保存后的文件将永久包含白色边框,适合用于创建贴纸等素材。







