HarmonyOS 鸿蒙Next中如何创建和使用自定义组件?
HarmonyOS 鸿蒙Next中如何创建和使用自定义组件? 在开发中,我们发现很多UI在不同页面中重复使用,比如一个带图标的按钮卡片。每次都写一遍相同的代码很麻烦,而且维护起来也很困难。我应该如何将这些可复用的UI封装成自定义组件?自定义组件如何接收参数?如何向外发送事件?
实现思路
1. 组件设计思路:
单一职责:每个组件应该只负责一个特定的功能或UI展示
高内聚低耦合:组件内部逻辑紧密相关,对外依赖最小化
可复用性:设计时要考虑在不同场景下的复用需求
2. 参数传递策略:
基础数据:通过构造函数参数传递,如cardData
事件回调:通过函数类型参数传递,如onClick1
复杂UI:使用@BuilderParam定义插槽,允许父组件传入自定义UI
3. 状态管理原则:
组件内部状态使用@State装饰器管理
外部传入的数据不要在组件内部直接修改
通过事件回调的方式通知父组件状态变化
4. 样式和交互设计:
使用stateStyles实现按压效果
合理使用阴影、圆角等视觉元素
添加适当的动画和过渡效果
使用场景
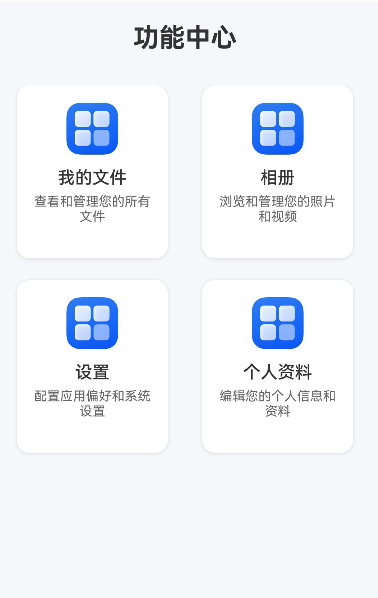
设想一个应用中有多个功能模块入口,每个入口都是一个包含图标、标题和描述的卡片:
首页:显示"我的文件"、“相册”、"设置"等功能卡片
个人中心:显示"个人资料"、“安全设置”、"帮助反馈"等功能卡片
这些卡片样式相同,只是内容不同,非常适合封装成自定义组件。
实现效果
完整代码
FunctionCard.ets : 核心封装的自定义组件
// 定义卡片数据接口
export interface CardData {
icon: Resource;
title: string;
description: string;
}
// 定义点击事件回调类型
type CardClickCallback = (cardData: CardData) => void;
@Component
export struct FunctionCard {
// 1. 接收外部传入的卡片数据
@Prop cardData: CardData = {
title:"",
description:"",
icon:$r("app.media.startIcon")
};
// 2. 接收点击事件回调函数
private onClick1?: CardClickCallback;
// 3. 定义状态变量
[@State](/user/State) isPressed: boolean = false;
// 构造函数
constructor(cardData: CardData, onClick?: CardClickCallback) {
super();
this.cardData = cardData;
this.onClick1 = onClick;
}
build() {
Column() {
// 图标区域
Image(this.cardData.icon)
.width(48)
.height(48)
.objectFit(ImageFit.Contain)
.margin({ bottom: 12 })
// 标题
Text(this.cardData.title)
.fontSize(16)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Medium)
.fontColor('#333333')
.margin({ bottom: 6 })
// 描述
Text(this.cardData.description)
.fontSize(12)
.fontColor('#666666')
.textAlign(TextAlign.Center)
.maxLines(2)
.textOverflow({ overflow: TextOverflow.Ellipsis })
}
.width(140)
.height(160)
.padding(16)
.backgroundColor('#FFFFFF')
.borderRadius(12)
.shadow({
radius: 8,
color: '#1F000000',
offsetX: 0,
offsetY: 2
})
// 4. 添加点击效果
.stateStyles({
normal: {
.scale({ x: 1.0, y: 1.0 })
.backgroundColor('#FFFFFF')
},
pressed: {
.scale({ x: 0.95, y: 0.95 })
.backgroundColor('#F5F5F5')
}
})
.onClick(() => {
// 5. 触发点击事件回调
if (this.onClick1) {
this.onClick1(this.cardData);
}
})
.onTouch((event: TouchEvent) => {
// 处理按压状态
if (event.type === TouchType.Down) {
this.isPressed = true;
} else if (event.type === TouchType.Up || event.type === TouchType.Cancel) {
this.isPressed = false;
}
})
}
}
Index.ets
import { FunctionCard, CardData } from './FunctionCard';
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
// 定义功能卡片数据
private functionCards: CardData[] = [
{
icon: $r('app.media.startIcon'),
title: '我的文件',
description: '查看和管理您的所有文件'
},
{
icon: $r('app.media.startIcon'),
title: '相册',
description: '浏览和管理您的照片和视频'
},
{
icon: $r('app.media.startIcon'),
title: '设置',
description: '配置应用偏好和系统设置'
},
{
icon: $r('app.media.startIcon'),
title: '个人资料',
description: '编辑您的个人信息和资料'
}
];
// 处理卡片点击事件
private handleCardClick(cardData: CardData) {
console.info(`点击了卡片: ${cardData.title}`);
// 这里可以添加页面跳转或其他业务逻辑
// 例如:router.pushUrl({ url: `pages/${cardData.title}Page` });
}
build() {
Column() {
// 页面标题
Text('功能中心')
.fontSize(24)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.margin({ top: 20, bottom: 30 })
.fontColor('#333333')
// 功能卡片网格
Grid() {
ForEach(this.functionCards, (cardData: CardData) => {
GridItem() {
// 6. 使用自定义组件
FunctionCard({
cardData: cardData,
onClick1: (data: CardData) => {
this.handleCardClick(data);
}
})
}
}, (cardData: CardData) => cardData.title)
}
.columnsTemplate('1fr 1fr')
.rowsGap(20)
.columnsGap(20)
.width('90%')
.height('auto')
.margin({ bottom: 30 })
// 底部说明
Text('点击任意功能卡片进入对应页面')
.fontSize(14)
.fontColor('#999999')
.margin({ bottom: 20 })
}
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
.backgroundColor('#F5F7FA')
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Start)
.alignItems(HorizontalAlign.Center)
}
}
更多关于HarmonyOS 鸿蒙Next中如何创建和使用自定义组件?的实战系列教程也可以访问 https://www.itying.com/category-93-b0.html
在HarmonyOS Next中,创建自定义组件需使用ArkTS语言。首先,通过@Component装饰器定义组件,在struct中实现build()方法描述UI结构。组件可包含@Prop、@Link等装饰器管理的状态变量。
使用自定义组件时,在父组件的build()方法中直接声明组件标签。可通过属性初始化或状态绑定传递参数。组件支持生命周期回调,如aboutToAppear。
示例代码框架:
@Component
struct CustomComponent {
build() {
// UI描述
}
}
// 使用
CustomComponent()
在HarmonyOS Next中,创建和使用自定义组件是构建可复用UI、提升开发效率的核心。以下是具体方法:
1. 创建自定义组件
创建一个ArkTS文件(如IconButtonCard.ets),使用@Component装饰器定义组件结构。
@Component
export struct IconButtonCard {
// 组件内部状态
@State isPressed: boolean = false;
// 接收外部参数:使用[@Prop](/user/Prop)或[@Link](/user/Link)装饰器
[@Prop](/user/Prop) iconSrc: Resource; // 图标资源
[@Prop](/user/Prop) buttonText: string; // 按钮文字
build() {
Column() {
Image(this.iconSrc)
.width(40)
.height(40)
Text(this.buttonText)
.fontSize(16)
.opacity(this.isPressed ? 0.6 : 1.0)
}
.onClick(() => {
this.isPressed = !this.isPressed;
// 可在此触发事件
})
}
}
2. 接收参数
- @Prop:单向同步,父组件设置后子组件同步更新,子组件内部修改不会影响父组件。
- @Link:双向同步,父子组件数据联动更新。
- @Provide/@Consume:跨层级数据传递。
- 常规参数:直接通过构造函数传递(需在组件内声明并初始化)。
3. 发送事件
使用自定义事件处理器:
@Component
export struct IconButtonCard {
// 定义事件回调
private onButtonClick?: () => void;
build() {
Column()
.onClick(() => {
this.onButtonClick?.(); // 触发事件
})
}
// 设置事件处理函数的方法
setOnClick(handler: () => void) {
this.onButtonClick = handler;
}
}
更规范的方式是结合@Watch监听状态变化并通知父组件。
4. 使用自定义组件
在父组件中导入并使用:
import { IconButtonCard } from './IconButtonCard';
@Entry
@Component
struct ParentComponent {
private iconRes: Resource = $r('app.media.icon');
build() {
Column() {
IconButtonCard({
iconSrc: this.iconRes,
buttonText: '点击我'
})
.setOnClick(() => {
console.log('卡片被点击');
})
}
}
}
关键点
- 组件化思维:将UI、状态和行为封装在独立组件中。
- 装饰器选择:根据数据流需求选用
[@Prop](/user/Prop)、[@Link](/user/Link)或@State。 - 事件通信:通过回调函数或状态监听实现父子组件通信。
- 复用性:合理设计组件接口,确保适应不同场景。
通过以上方式,你可以有效封装重复UI逻辑,提升代码可维护性和开发效率。






