实现思路
- Canvas绘图思路:
初始化画布:在onReady回调中获取绘图上下文
分层绘制:先绘制背景,再绘制前景,最后绘制动态元素
坐标系理解:Canvas使用左上角为原点的坐标系
状态管理:通过状态变量控制绘图内容的变化
- 动画实现策略:
缓动函数:通过数学公式实现平滑的动画效果
状态更新:动画过程中更新状态变量,触发重绘
性能优化:避免不必要的重绘,清理动画资源
- 组件化设计:
属性配置:通过@Prop传递组件配置参数
方法暴露:提供公共方法供外部调用
生命周期管理:在aboutToDisappear中清理资源
事件处理:通过回调函数处理用户交互
- 绘图技巧:
路径绘制:使用beginPath()开始新路径
样式设置:分别设置填充样式和描边样式
文字绘制:注意文字对齐和基线设置
颜色计算:根据数值动态计算颜色
使用场景
Canvas适用于需要自定义绘制的各种场景,比如对于数据可视化中的图表、仪表盘、进度条,再比如对于动画效果中粒子效果、波形动画等等。
实现效果
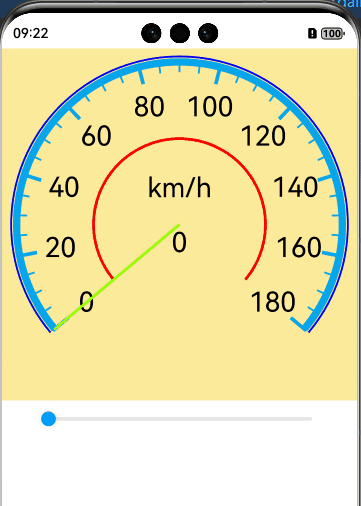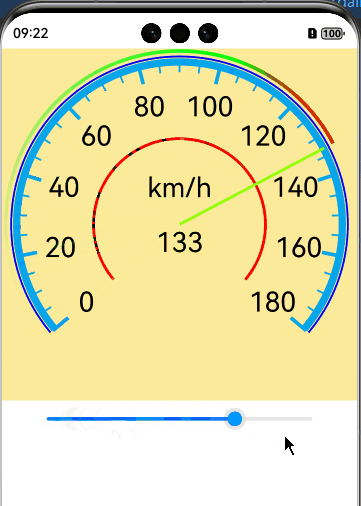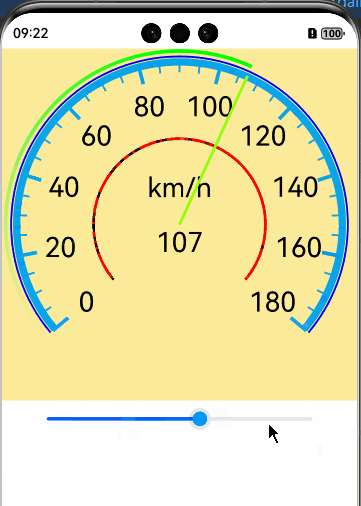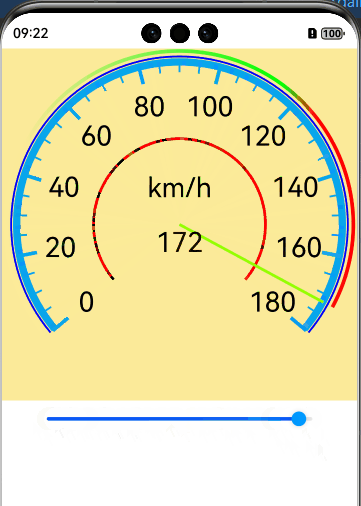
完整代码
@Entry
@ComponentV2
struct CanvasTest {
private settings: RenderingContextSettings = new RenderingContextSettings(true);
private context: CanvasRenderingContext2D = new CanvasRenderingContext2D(this.settings);
private context2: CanvasRenderingContext2D = new CanvasRenderingContext2D(this.settings);
private context3: CanvasRenderingContext2D = new CanvasRenderingContext2D(this.settings);
@Local centerX: number = 0
@Local centerY: number = 0
@Local currentSpeed: number = 0
@Local angle: number = 0
@Local startAngle:number= Math.PI * 140 / 180 //弧线的起始弧度
@Local endAngle:number= Math.PI * 40 / 180 //弧线的起始弧度
//绘制渐变外环
draw(){
this.context3.clearRect(0,0,2*this.centerX,2*this.centerX)
this.context3.beginPath()
let grad = this.context3.createLinearGradient(this.getStartX(), this.getStartY(), this.getEndX(), this.getEndY())
grad.addColorStop(0, '#0000ff00')
grad.addColorStop(0.9, '#00ff00')
if (this.currentSpeed>120) {
grad.addColorStop(1, '#ff0000')
}else {
grad.addColorStop(1, '#00ff00')
}
this.context3.strokeStyle = grad;
this.context3.lineWidth = 4;
this.context3.arc(this.centerX, this.centerY, this.centerX - 4, this.startAngle, Math.PI * (140+(this.currentSpeed * 260 / 180) ) / 180)
this.context3.stroke()
}
build() {
Column() {
Stack() {
Canvas(this.context)
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
.backgroundColor("#fceb99")
.onReady(() => {
//绘制外环
this.context.beginPath()
this.context.strokeStyle = '#0000ff';
this.context.lineWidth = 2;
this.context.arc(this.centerX, this.centerY, this.centerX - 10, this.startAngle, this.endAngle)
this.context.stroke()
//绘制内环
this.context.beginPath()
this.context.strokeStyle = '#07A6EC';
this.context.lineWidth = 8;
this.context.arc(this.centerX, this.centerY, this.centerX - 16, this.startAngle, this.endAngle)
this.context.stroke()
//绘制刻度
this.context.save()
this.context.translate(this.centerX, this.centerY);
this.context.rotate(Math.PI * 50 / 180)
for (let i = 0; i <= 36; i++) {
if (i % 4 == 0) {
this.context.beginPath()
this.context.lineWidth = 4;
this.context.strokeStyle = '#07A6EC';
this.context.moveTo(0, this.centerY - 34);
this.context.lineTo(0, this.centerY - 12);
this.context.stroke();
} else {
this.context.beginPath()
this.context.lineWidth = 2;
this.context.strokeStyle = '#07A6EC';
this.context.moveTo(0, this.centerY - 26);
this.context.lineTo(0, this.centerY - 12);
this.context.stroke();
}
this.context.rotate(Math.PI * (260 / 36) / 180)
}
this.context.restore()
//绘制数字
this.context.save()
this.context.translate(this.centerX, this.centerY);
for (let i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
// 转换为弧度
const radians = (140 + i * (260 / 9)) * Math.PI / 180;
// 计算坐标
const x = (this.centerY - 60) * Math.cos(radians);
const y = (this.centerY - 60) * Math.sin(radians);
this.context.textAlign = 'center'
this.context.textBaseline = 'middle'
this.context.font = '30vp sans-serif'
this.context.fillText(i * 20 + '', x, y)
}
//绘制中间单位
this.context.textAlign = 'center'
this.context.textBaseline = 'middle'
this.context.font = '30vp sans-serif'
this.context.fillText('km/h', 0, -40)
this.context.restore()
//绘制红色圆环
this.context.translate(0, 0);
this.context.beginPath()
this.context.strokeStyle = Color.Red;
this.context.lineWidth = 3;
this.context.arc(this.centerX, this.centerY, this.centerX - 100, this.startAngle, this.endAngle)
this.context.stroke()
})
Canvas(this.context3)
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
Canvas(this.context2)
.width('100%')
.height('100%')
.onReady(() => {
this.context2.beginPath()
this.context2.lineWidth = 3;
this.context2.strokeStyle = "#95ff00";
this.context2.moveTo(this.centerX, this.centerY)
this.context2.lineTo(this.centerX, 14)
this.context2.stroke()
})
.rotate({ centerX: this.centerX, centerY: this.centerY, angle: this.cacleAngle() })
Text(this.currentSpeed + '').fontColor(Color.Black).fontSize(30).offset({ y: 20 })
}.height('50%').width('100%')
.onSizeChange((oldValue: SizeOptions, newValue: SizeOptions) => {
this.centerX = (newValue.width as number) / 2
this.centerY = (newValue.height as number) / 2
})
Slider({
value: this.currentSpeed,
min: 0,
max: 180,
step: 1,
})
.width('80%')
.blockColor("#0099ff")//设置滑块的颜色
.onChange((value: number, mode: SliderChangeMode) => {
this.currentSpeed = value
})
}
}
cacleAngle(): number {
this.draw();
// (当前速度/最大速度180)*圆环角度260- 默认其实位置从中心位置向左旋转130
return (this.currentSpeed * 260 / 180) - 130
}
getStartX() {
const angleRadians = 140 * Math.PI / 180;
return this.centerX + this.centerX * Math.cos(angleRadians);
}
getStartY(): number {
const angleRadians = 140 * Math.PI / 180;
return this.centerX + this.centerX * Math.sin(angleRadians);
}
getEndX() {
const angleRadians = (140+(this.currentSpeed * 260 / 180) )* Math.PI / 180;
return this.centerX + this.centerX * Math.cos(angleRadians);
}
getEndY(): number {
const angleRadians = (140+(this.currentSpeed * 260 / 180))* Math.PI / 180;
return this.centerX + this.centerX * Math.sin(angleRadians);
}
}








